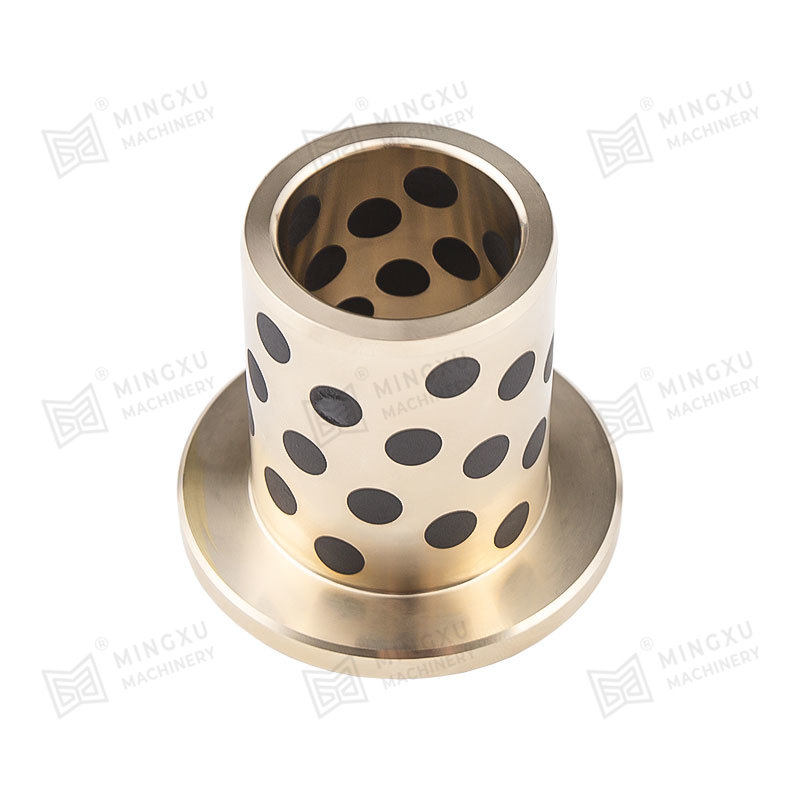
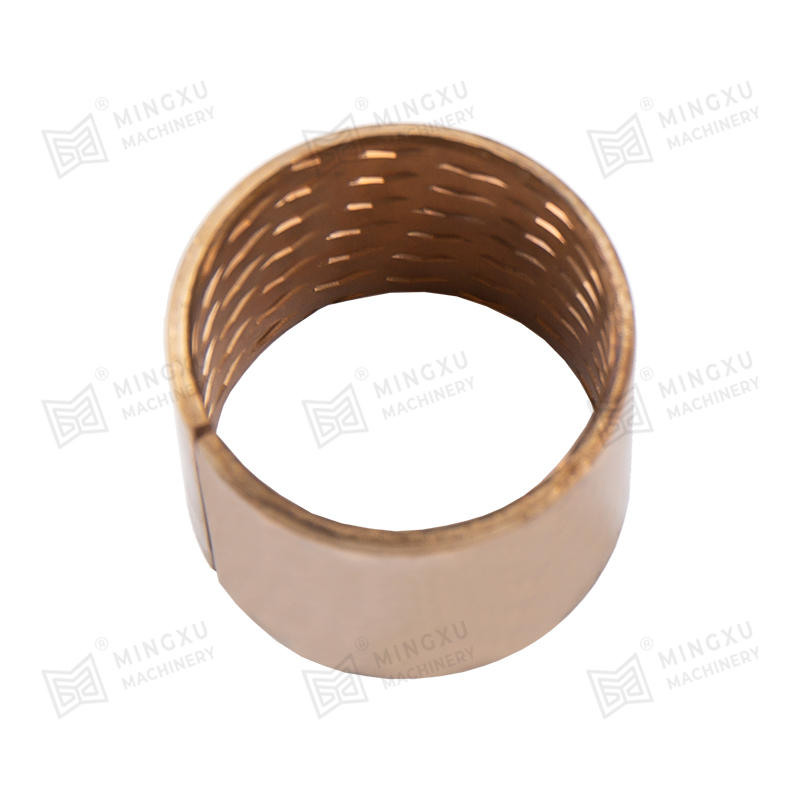
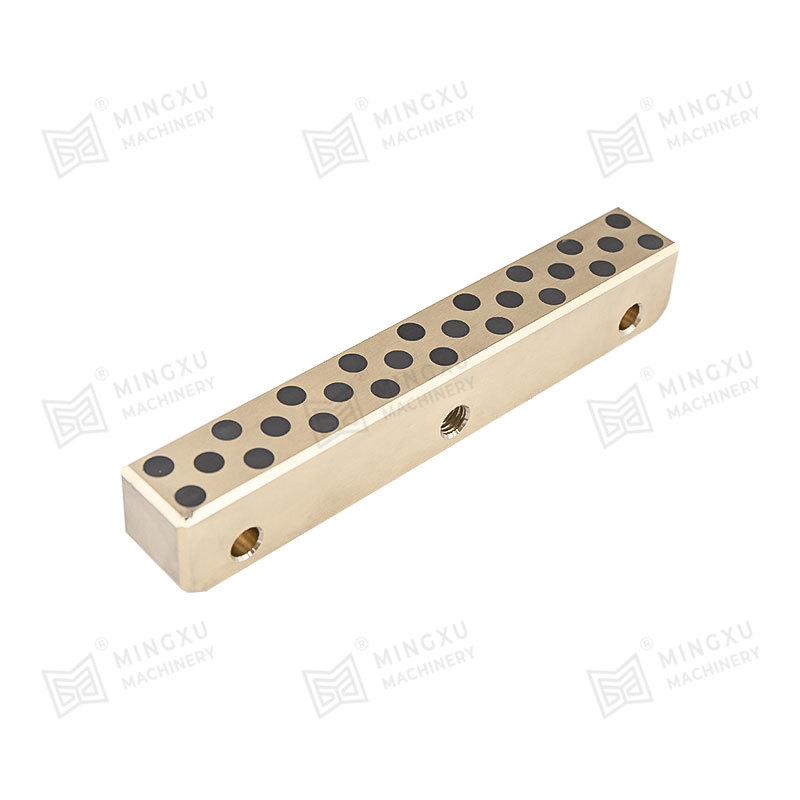
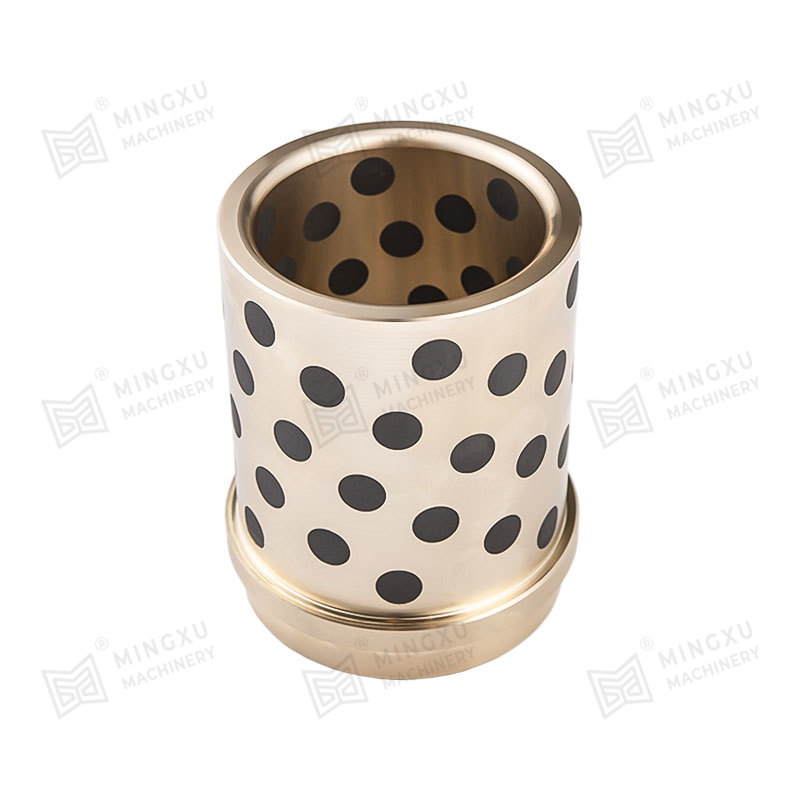
An oilless sliding wear plate is a self-lubricating bearing component designed to operate without external lubrication. It combines a high-strength metal base with embedded solid lubricant plugs or layers. During sliding motion, the solid lubricant gradually transfers to the mating surface, forming a stable lubricating film. This film reduces friction, minimizes wear, and prevents metal-to-metal contact under load.
Unlike conventional lubricated guide plates that require grease channels or periodic oil supply, an oilless sliding wear plate relies on internal lubrication reservoirs. As pressure and movement occur, microscopic lubricant particles are released and evenly distributed across the contact surface. This structure allows continuous operation in environments where oil contamination, dust, or maintenance restrictions make traditional lubrication impractical.
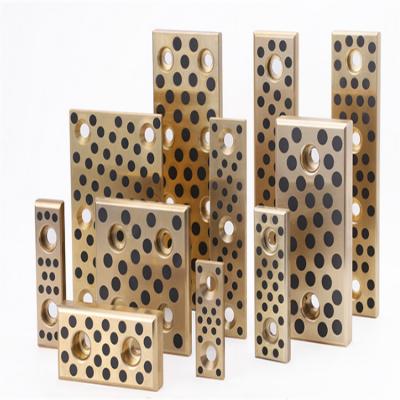

Material Structure and Composition
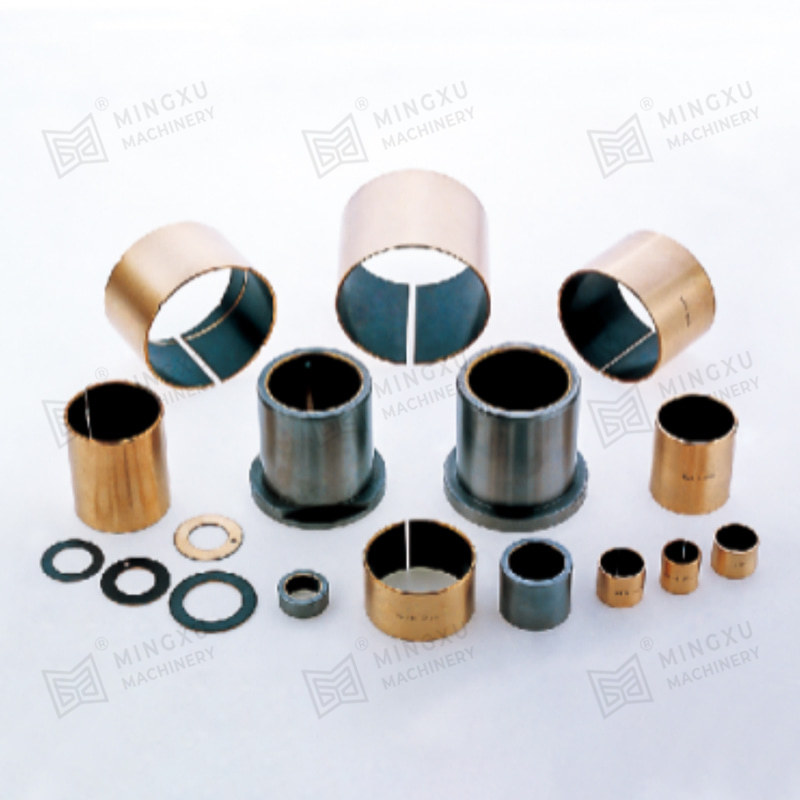
The performance of an oilless sliding wear plate depends largely on its composite structure. Most products consist of a bronze, steel, or cast iron base combined with graphite or PTFE-based solid lubricants. The base material provides mechanical strength and load-bearing capacity, while the lubricant phase controls friction characteristics.
Common Base Materials
- High-strength bronze alloys for mold components and precision guides
- Carbon steel backing for heavy-load industrial machinery
- Cast iron substrates for structural equipment applications
Solid Lubricant Options
- Graphite plugs for high-temperature and dry environments
- PTFE composites for low-friction precision motion
- Molybdenum disulfide blends for heavy-load sliding
Load Capacity and Friction Characteristics
An oilless sliding wear plate is engineered to withstand significant static and dynamic loads. Load capacity depends on contact area, material hardness, and lubricant distribution density. Under proper installation, the plate maintains dimensional stability and consistent sliding resistance.
Friction coefficients typically remain stable across a wide operating range. Because lubrication is internally regulated, friction does not fluctuate due to grease breakdown or oil evaporation. This stability improves positioning accuracy in molds and automated equipment.
| Performance Factor |
Oilless Sliding Wear Plate |
Conventional Lubricated Plate |
| Lubrication Method |
Solid embedded lubricant |
Grease or oil supply |
| Maintenance Frequency |
Low |
Regular re-lubrication |
| Environmental Suitability |
Dusty or dry conditions |
Clean and controlled environments |
Installation Guidelines and Surface Matching
Proper installation directly affects service life. The mounting surface must be flat and rigid to prevent uneven load distribution. Fastening bolts should be tightened in sequence to avoid deformation. Tolerance control between the wear plate and guide surface is critical to maintaining uniform sliding behavior.
Surface finish of the mating component should match the plate specification. Excessively rough surfaces accelerate wear, while extremely polished surfaces may reduce lubricant film retention. Hardness compatibility between the wear plate and counter surface must also be considered to prevent adhesive wear.
Installation Recommendations
- Verify flatness of mounting surface before fixing
- Maintain consistent tightening torque
- Control alignment to prevent edge loading
- Confirm operating load matches design capacity
Industrial Applications and Design Considerations
Oilless sliding wear plates are widely used in injection molds, stamping dies, heavy equipment, automation systems, and construction machinery. In molds, they guide moving cores and sliders with consistent accuracy. In heavy machinery, they support structural components exposed to dust and vibration where lubrication systems are difficult to maintain.
When integrating an oilless sliding wear plate into equipment design, engineers evaluate load distribution, sliding speed, temperature range, and environmental contamination. Plate thickness and lubricant density are selected based on cycle frequency and expected lifespan. For vertical installations, secure fixing and anti-slip positioning are necessary to prevent displacement under repetitive motion.
Selecting a suitable oilless sliding wear plate improves operational stability, reduces downtime caused by lubrication failure, and supports clean production requirements. With proper design and installation, it delivers consistent sliding performance in demanding industrial environments.


 English
English Español
Español















Contact Us