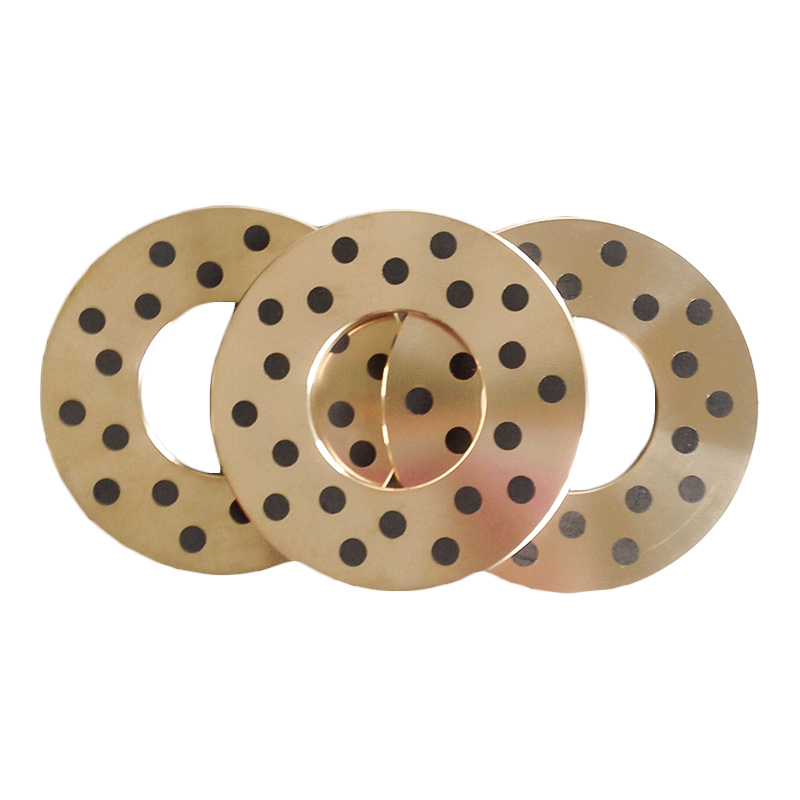
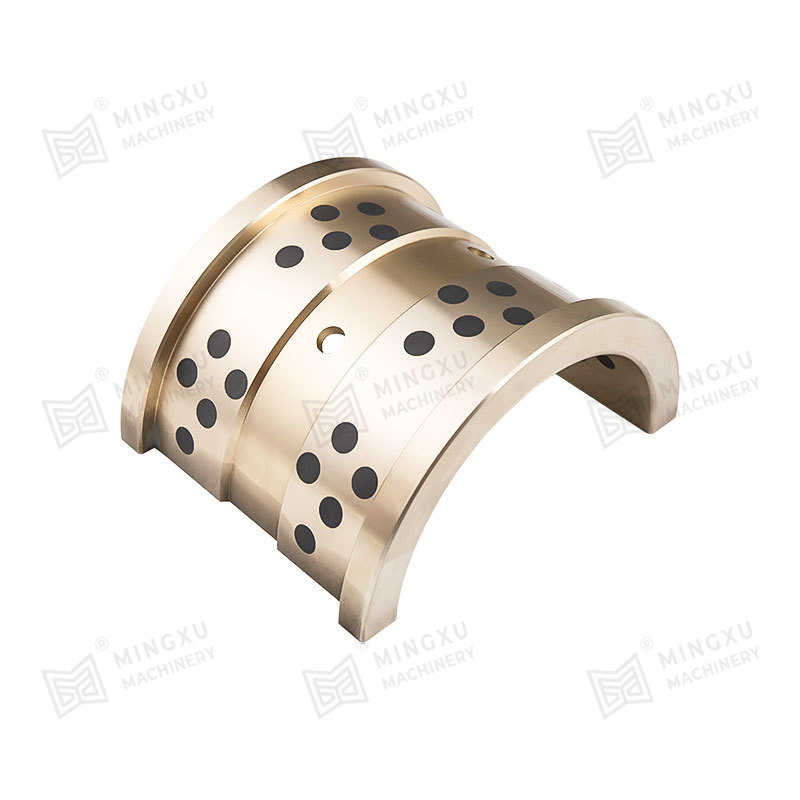
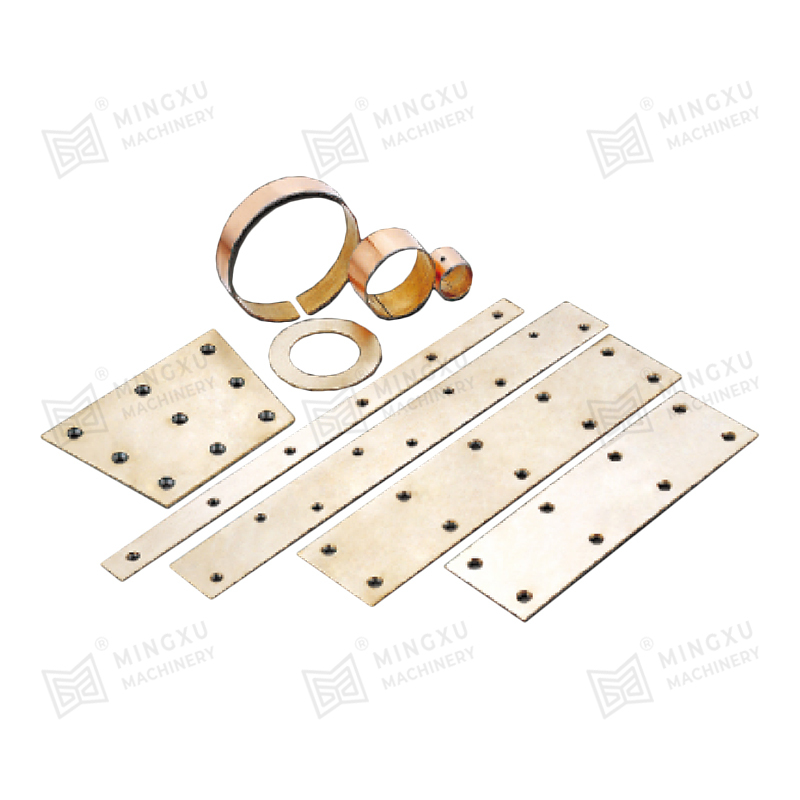
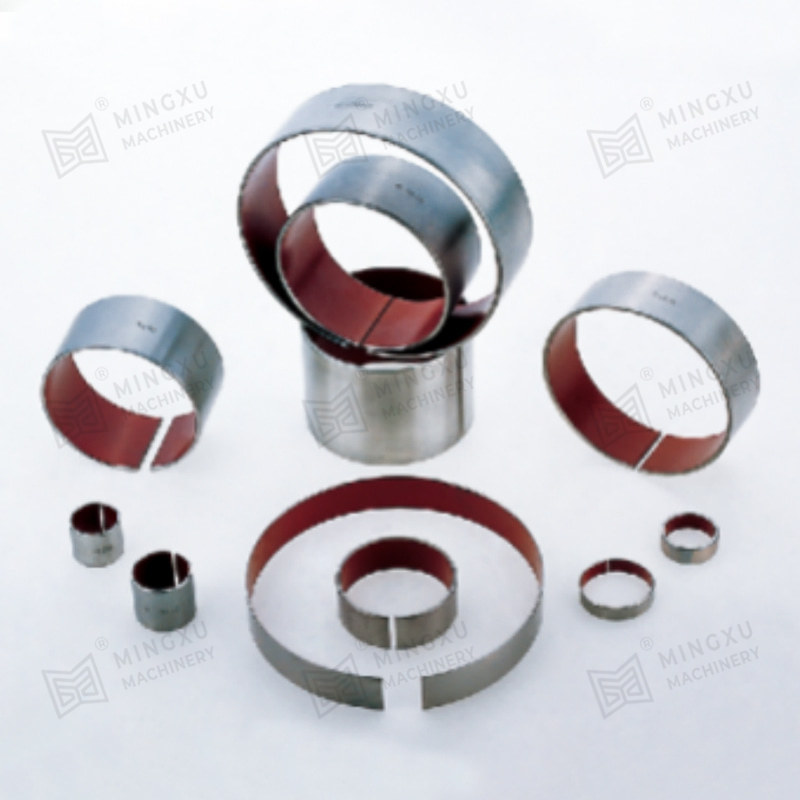
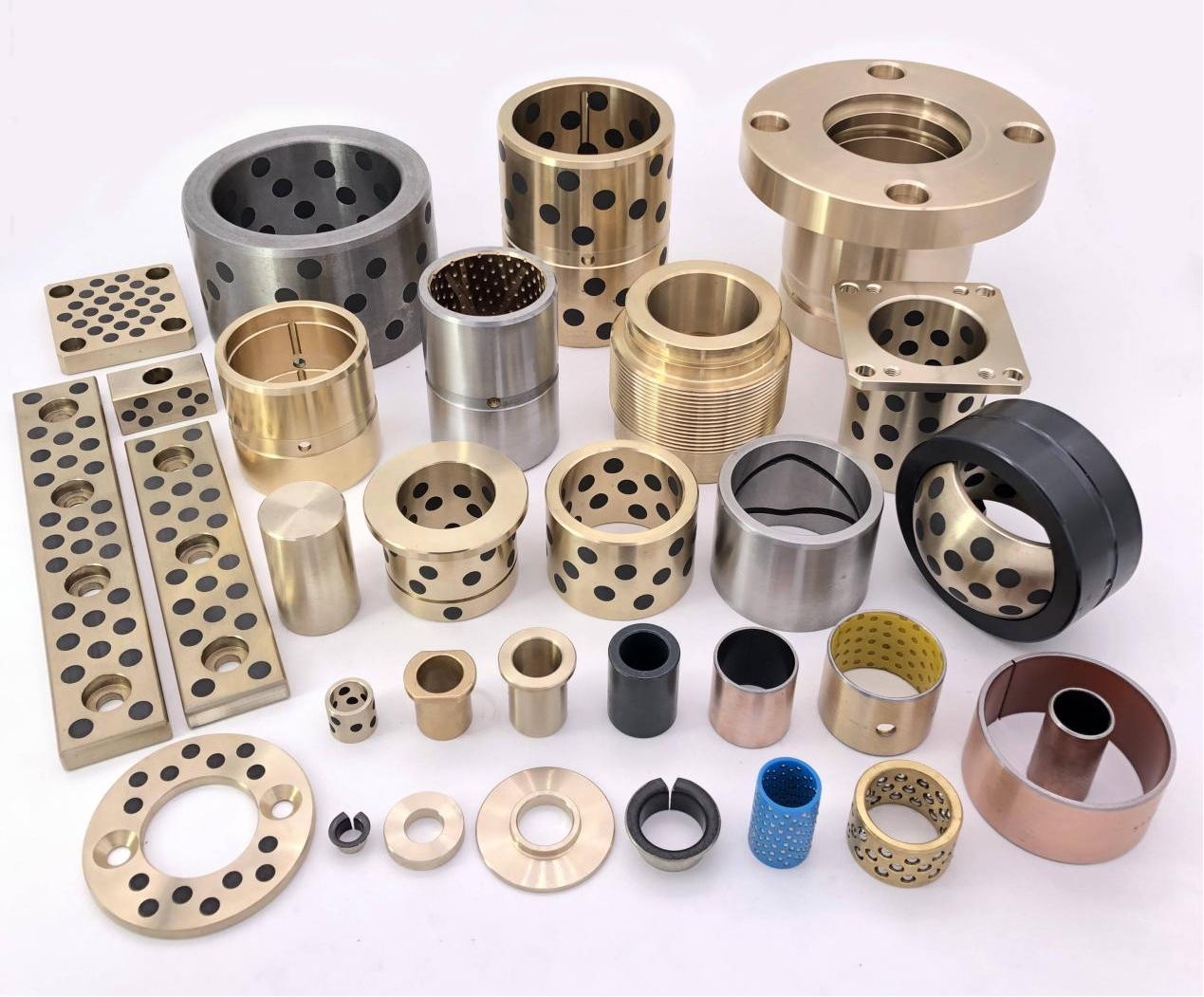
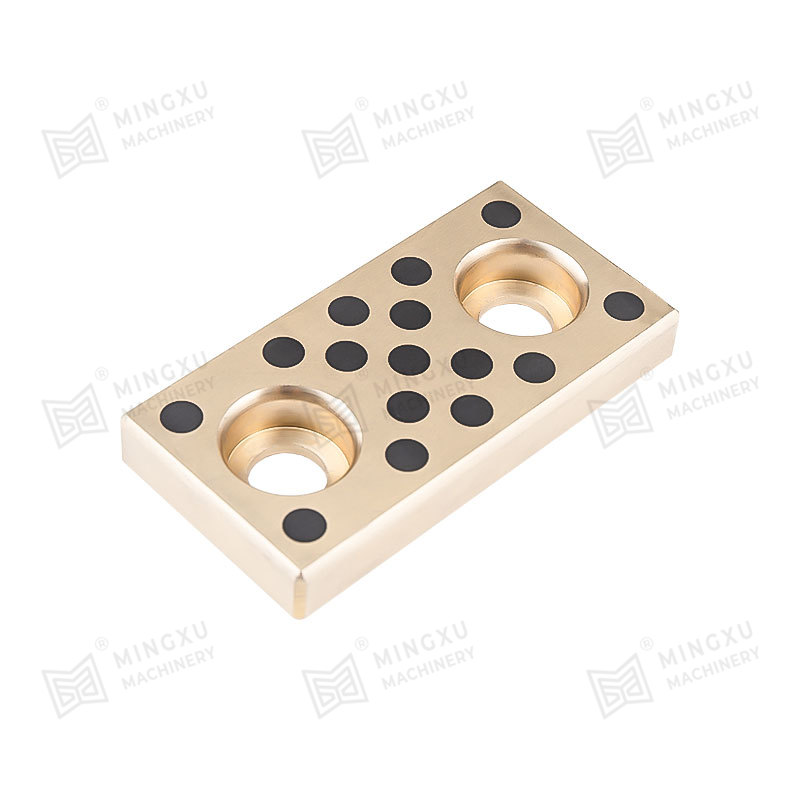
A self-lubricating wear plate is a solid sliding component designed to reduce friction and surface wear without the need for external lubricants. It integrates lubricating phases directly into the base material, allowing continuous lubrication during operation. This structure makes it suitable for equipment exposed to heavy loads, low-speed movement, or conditions where conventional grease or oil lubrication is difficult to maintain.
In practical use, self-lubricating wear plates are commonly installed between moving metal surfaces such as guide rails, sliding blocks, support shoes, and bearing interfaces. As friction occurs, the embedded lubricating material is gradually released to form a transfer film, reducing direct metal-to-metal contact and stabilizing the coefficient of friction over time.
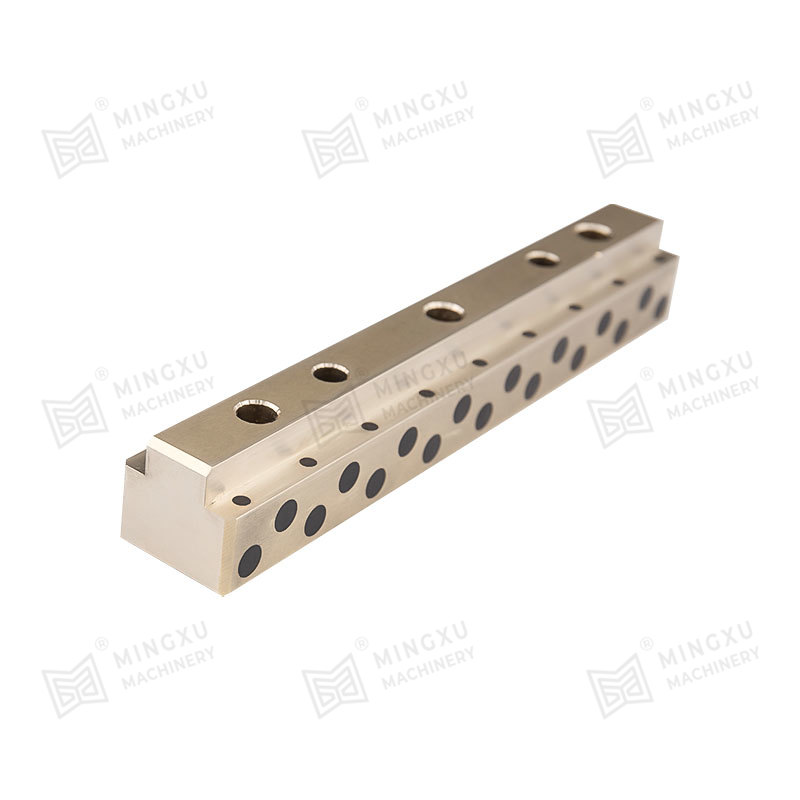

Material Structure and Lubrication Mechanism
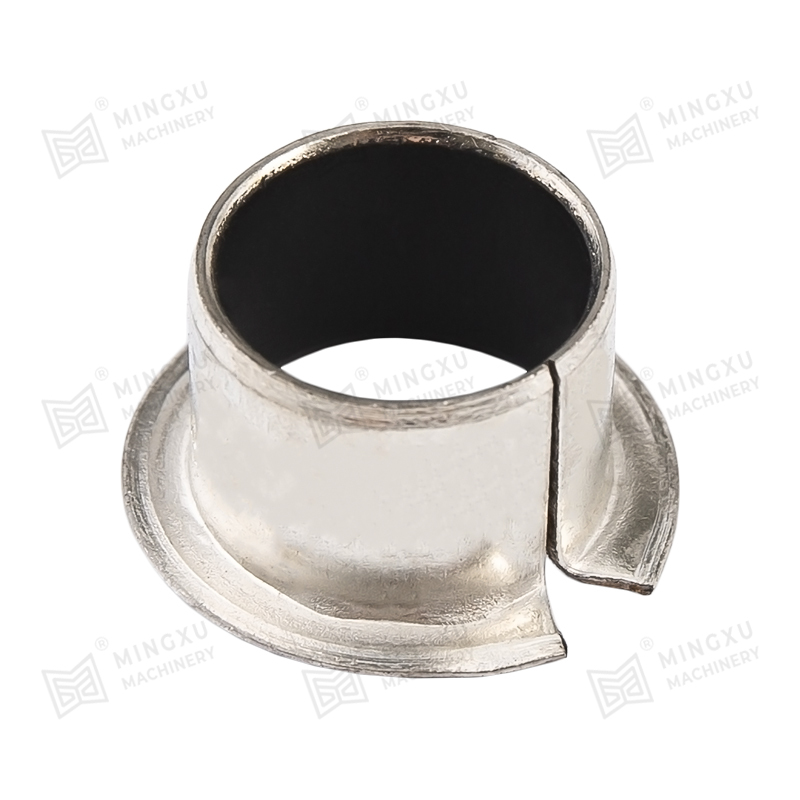
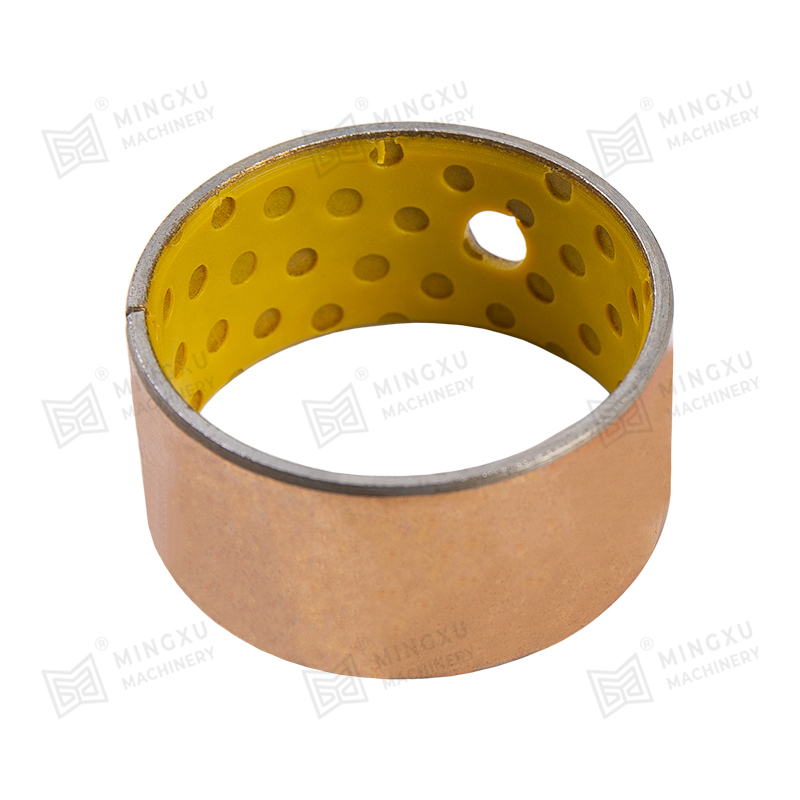
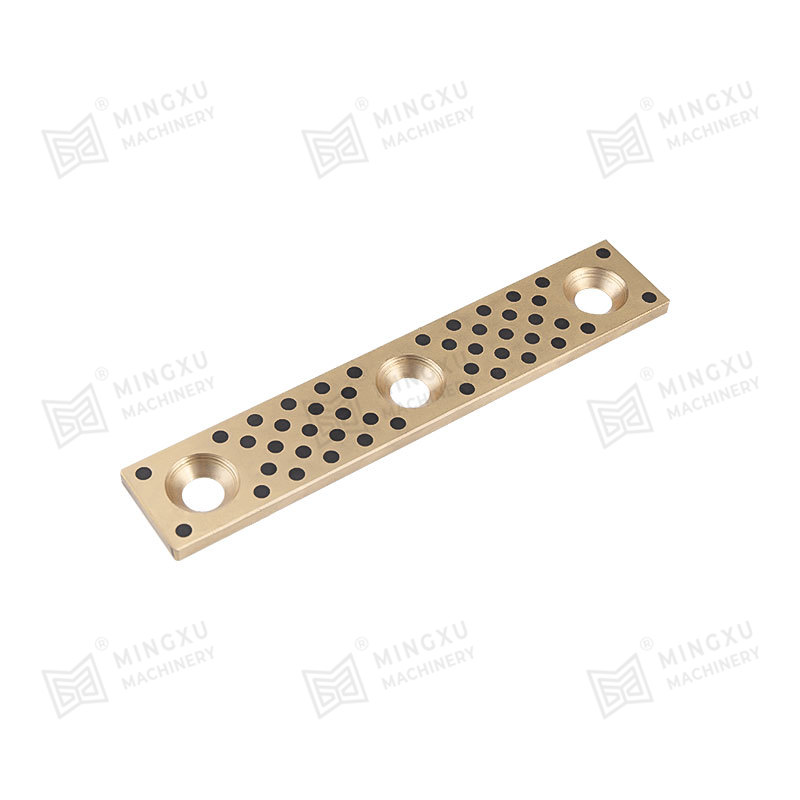
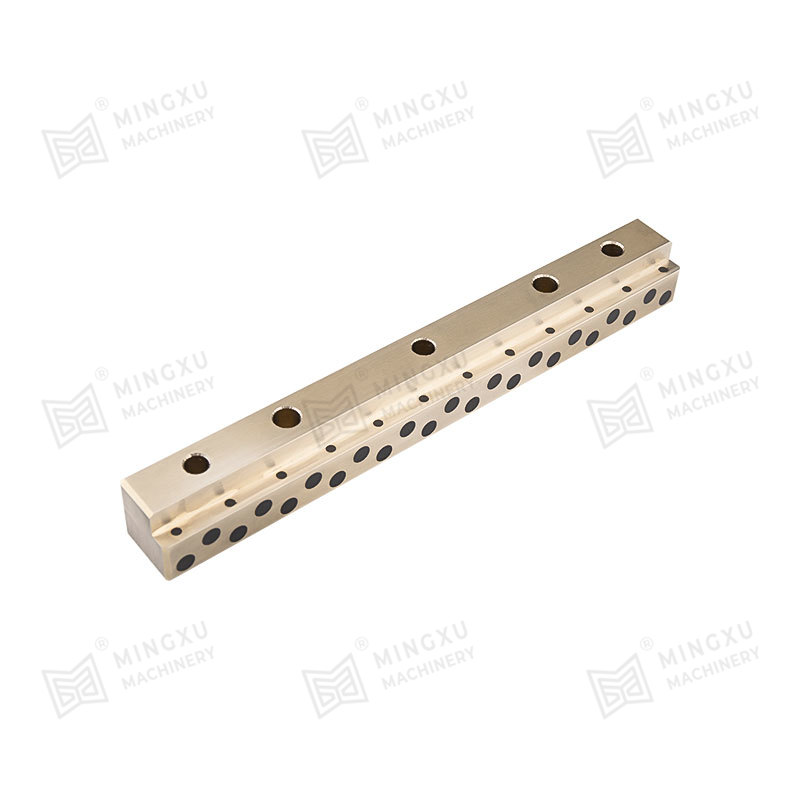
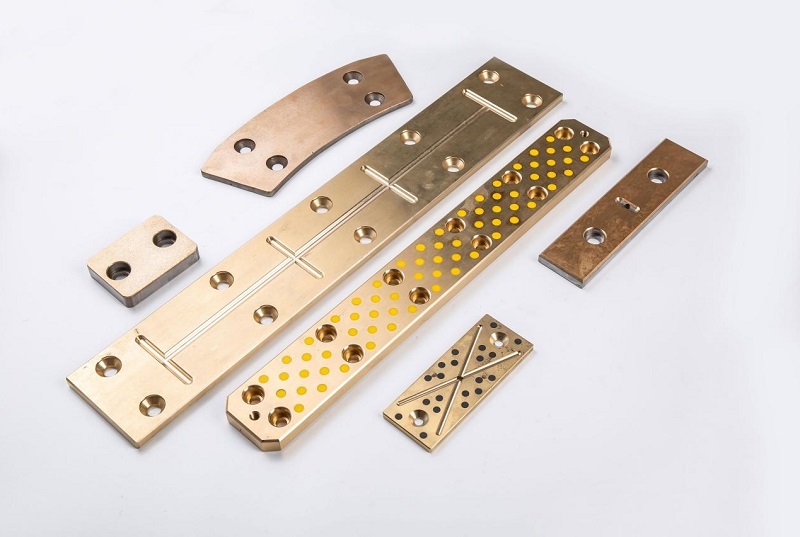
The performance of a self-lubricating wear plate depends heavily on its internal material structure. Most designs consist of a load-bearing metal matrix combined with evenly distributed solid lubricant inserts. This configuration allows the plate to maintain mechanical strength while providing consistent lubrication during sliding motion.
Metal Matrix as Load Support
The metal base typically serves as the structural backbone of the wear plate. It is responsible for handling compressive forces, impact loads, and long-term mechanical stress. The matrix material is selected based on required strength, thermal stability, and compatibility with the mating surface.
Solid Lubricant Distribution
Solid lubricants are embedded in the metal matrix in the form of plugs, strips, or dispersed phases. During sliding, microscopic amounts of lubricant migrate to the contact surface. This process creates a stable lubricating layer that reduces friction and slows wear without contaminating surrounding components.
Key Performance Characteristics in Real Applications
Self-lubricating wear plates are selected for applications where reliability and maintenance reduction are priorities. Their performance advantages become more apparent under challenging operating conditions that accelerate wear in conventional sliding components.
- Stable friction behavior under varying loads and speeds, reducing stick-slip movement in precision mechanisms
- Reduced dependence on external lubrication systems, lowering maintenance workload and operational downtime
- Improved wear resistance in dusty, wet, or high-temperature environments where oil or grease may degrade
Common Industrial Use Scenarios
Self-lubricating wear plates are widely used across heavy-duty and precision industries. Their ability to operate reliably with minimal lubrication support makes them suitable for both continuous-duty and intermittent-motion systems.
| Construction Machinery |
Boom guides, sliding pads, support plates |
| Metallurgical Equipment |
Furnace door slides, transfer tables, guide systems |
| Hydraulic Systems |
Wear pads for cylinders, support bearings |
| Industrial Automation |
Linear guides, positioning slides |
Installation and Surface Matching Considerations
Correct installation plays a critical role in achieving the expected service life of a self-lubricating wear plate. Surface flatness, alignment accuracy, and proper fastening all influence how evenly the load is distributed across the sliding interface.
The mating surface should have appropriate hardness and surface finish to allow formation of a stable transfer film. Excessively rough or uneven surfaces can accelerate wear, while overly polished surfaces may reduce lubricant retention during initial operation.
Maintenance Behavior and Service Life Expectations
One of the practical advantages of self-lubricating wear plates is their predictable wear pattern. As the lubricating material is gradually consumed, friction remains relatively stable rather than increasing abruptly. This allows maintenance teams to plan inspections and replacements based on measurable wear thickness rather than sudden failure.
In many applications, periodic visual inspection and dimensional checks are sufficient. External lubrication may still be applied in certain systems, but the wear plate itself continues to function effectively even if lubrication intervals are extended or temporarily missed.


 English
English Español
Español
















Contact Us