How Self-Lubricating Bearings Work in Real Operating Conditions
A self-lubricating bearing is designed to operate without the need for external grease or oil supply. Its core function relies on embedded or transferred lubricating materials that form a low-friction film between the bearing surface and the mating shaft during motion. As the bearing runs, microscopic amounts of the lubricating component are released, maintaining stable friction behavior even under continuous or intermittent load.
This working mechanism is particularly valuable in environments where manual lubrication is impractical, inconsistent, or prohibited. Instead of relying on maintenance schedules, the bearing itself becomes the lubrication source, reducing dependency on human intervention and minimizing performance variation caused by lubrication failure.
Material Structures Used in Self-Lubricating Bearings
Material selection directly defines the performance range of a self-lubricating bearing. Most designs combine a load-bearing matrix with a lubricating phase. The matrix provides mechanical strength, while the lubricating phase reduces friction and wear. Common material systems are engineered to balance compressive strength, wear resistance, and lubrication consistency.
Common Self-Lubricating Bearing Material Types
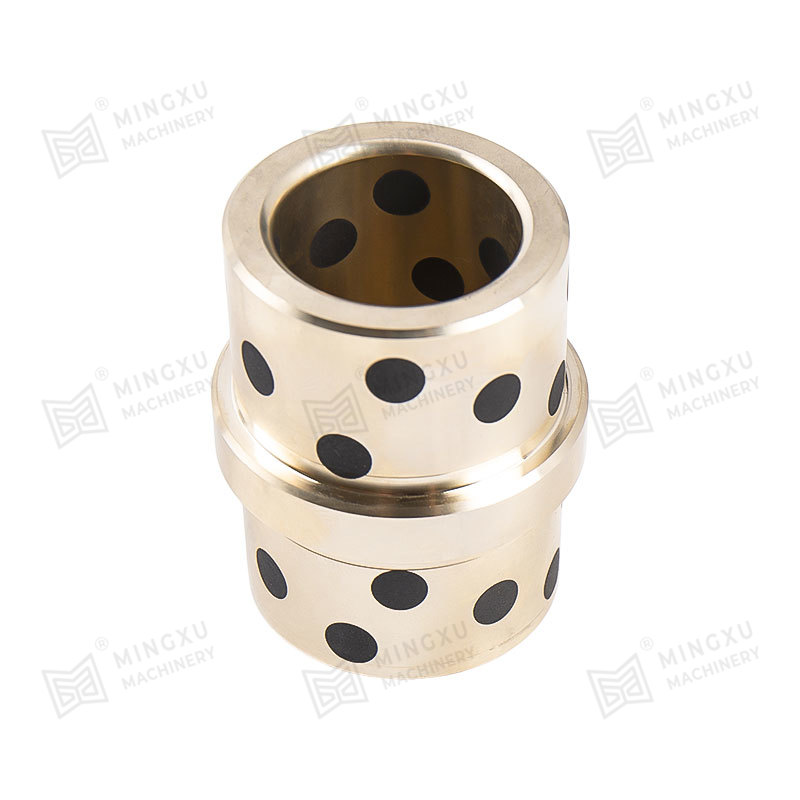
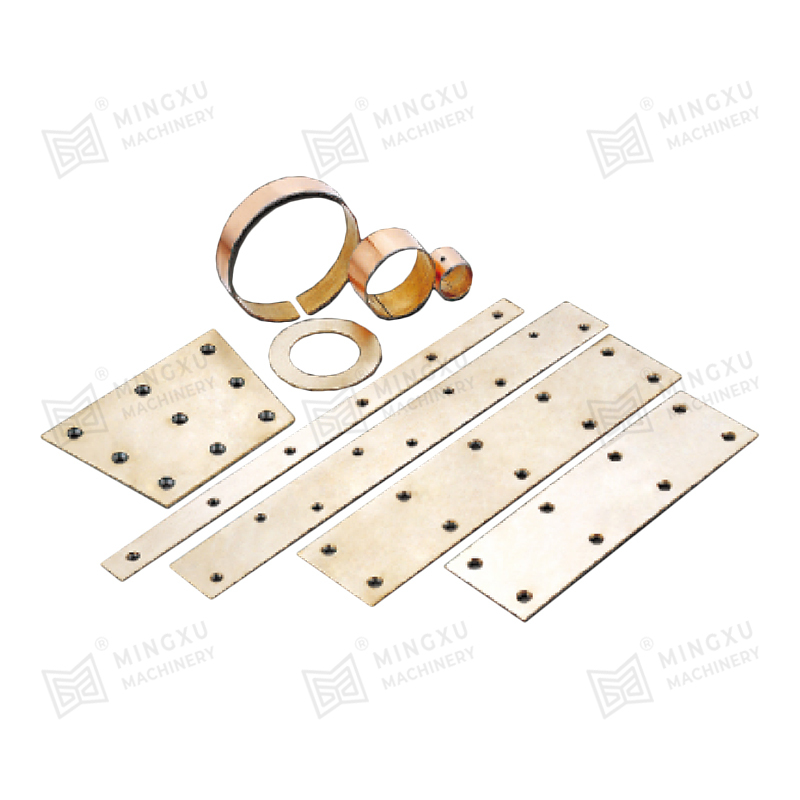
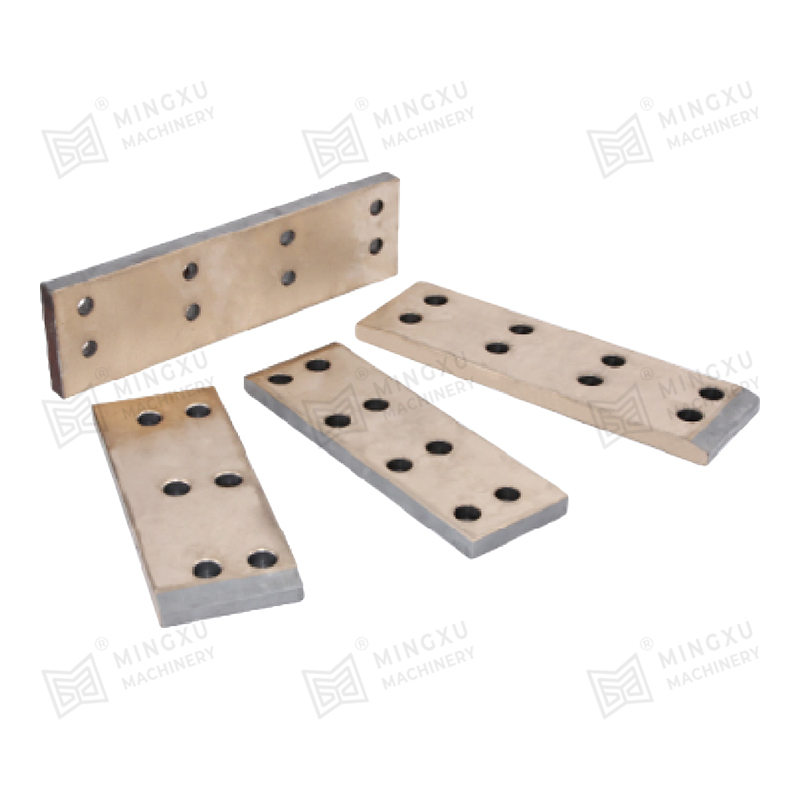
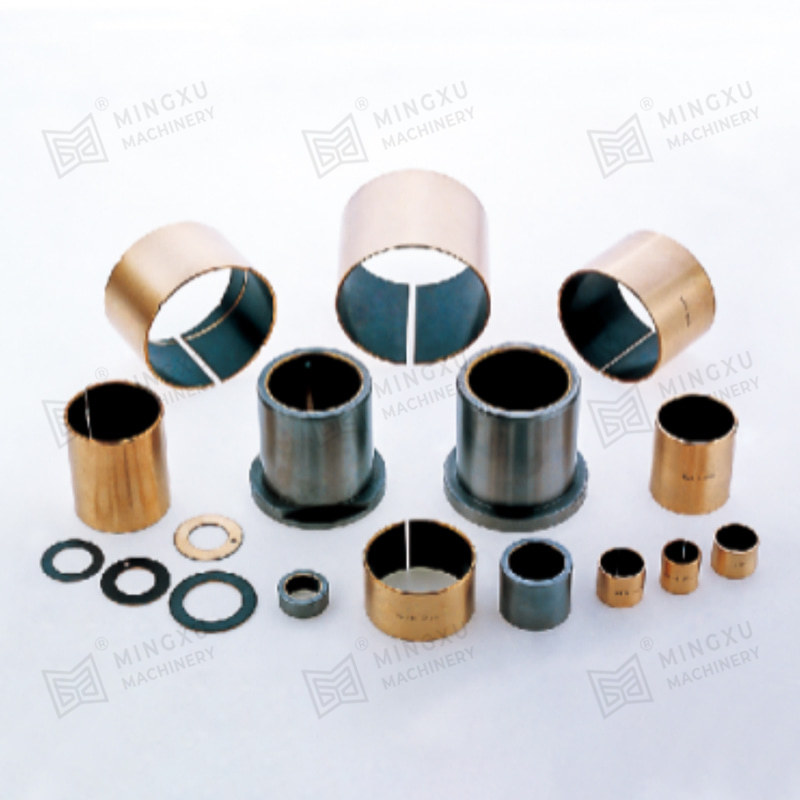
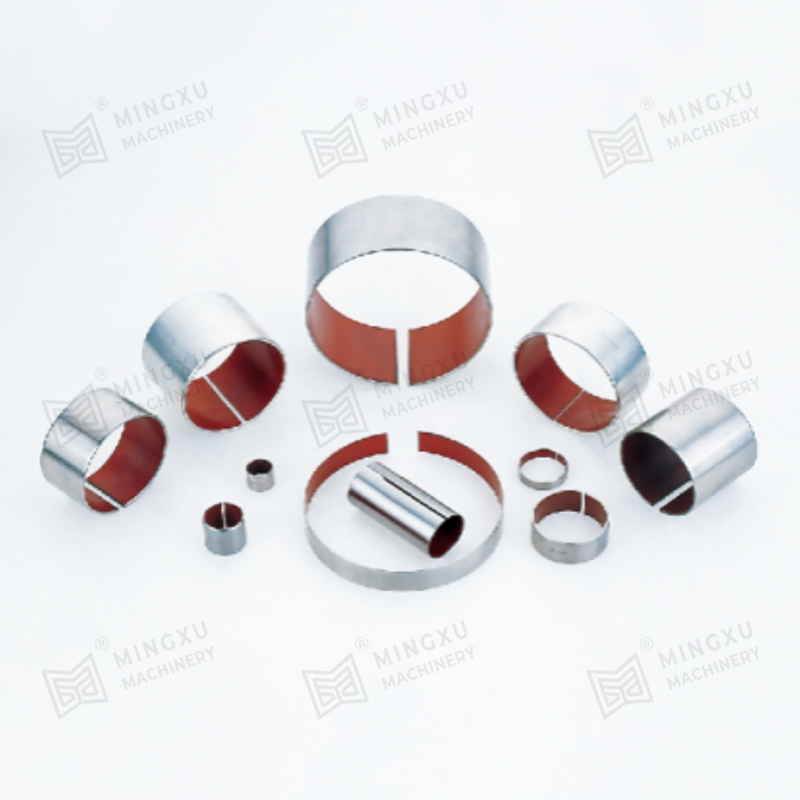
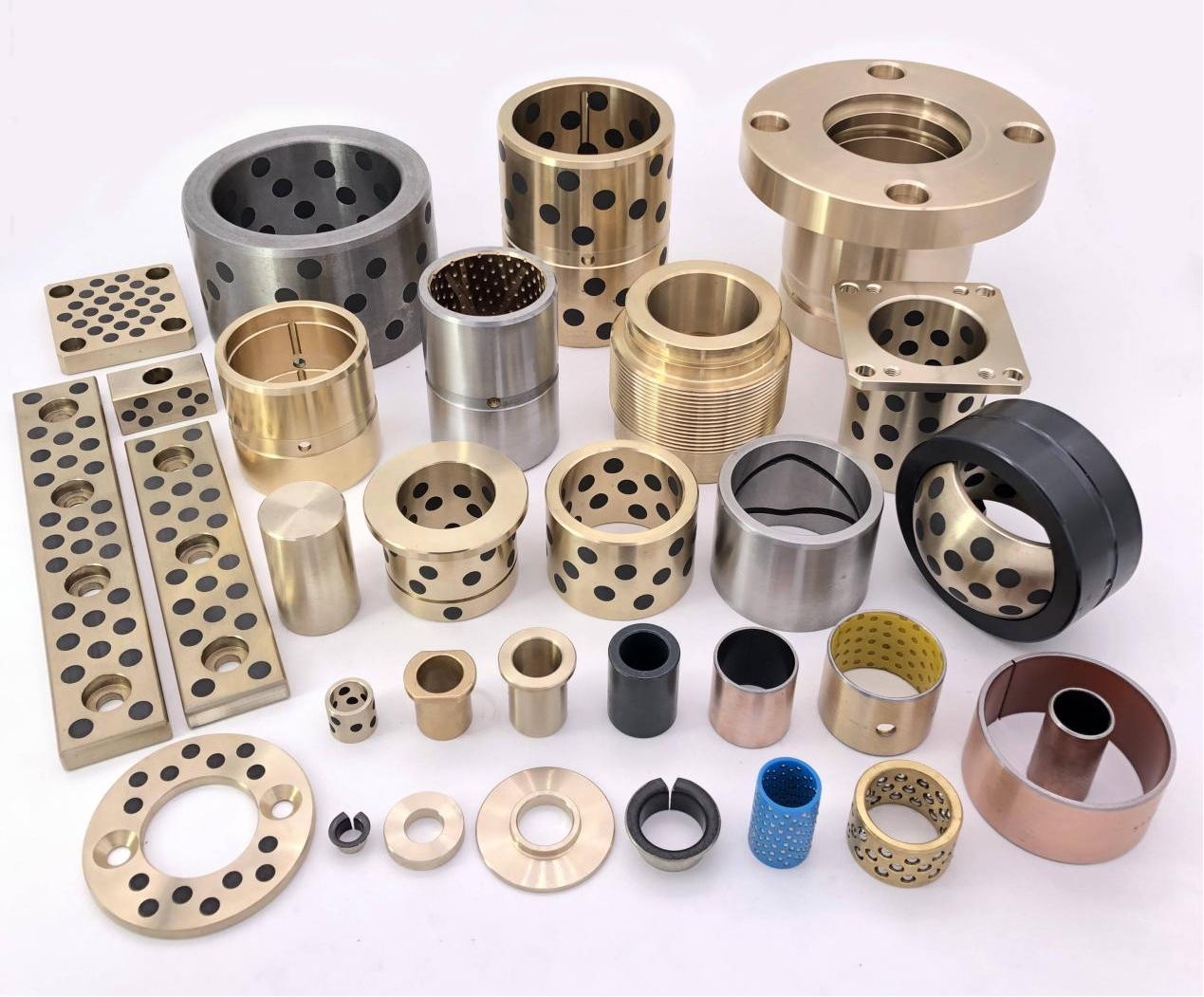
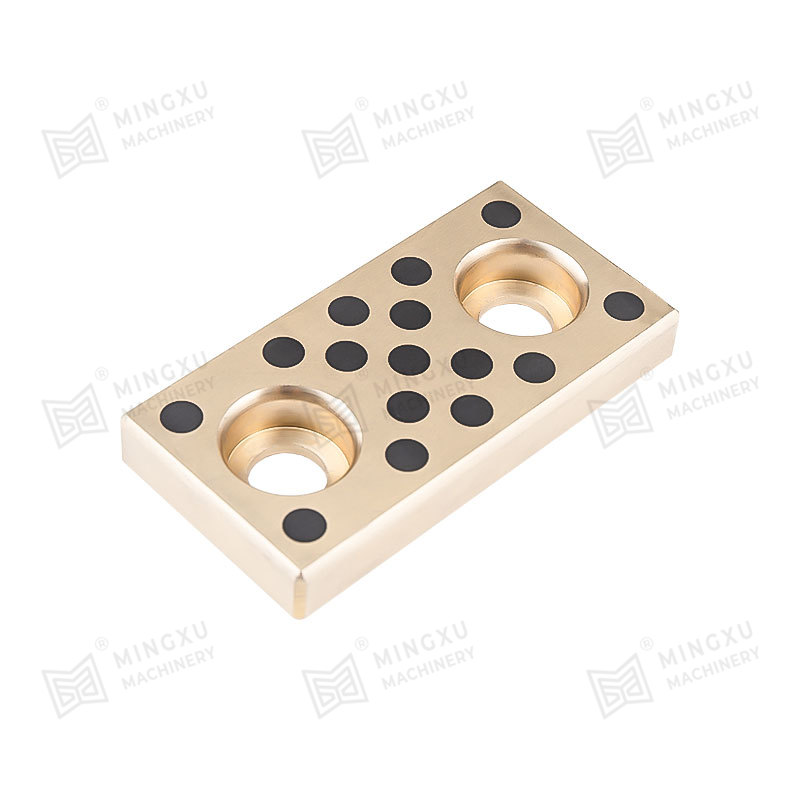
- Metal-based bearings with solid lubricant inserts or coatings
- Polymer composite bearings reinforced with fibers or fillers
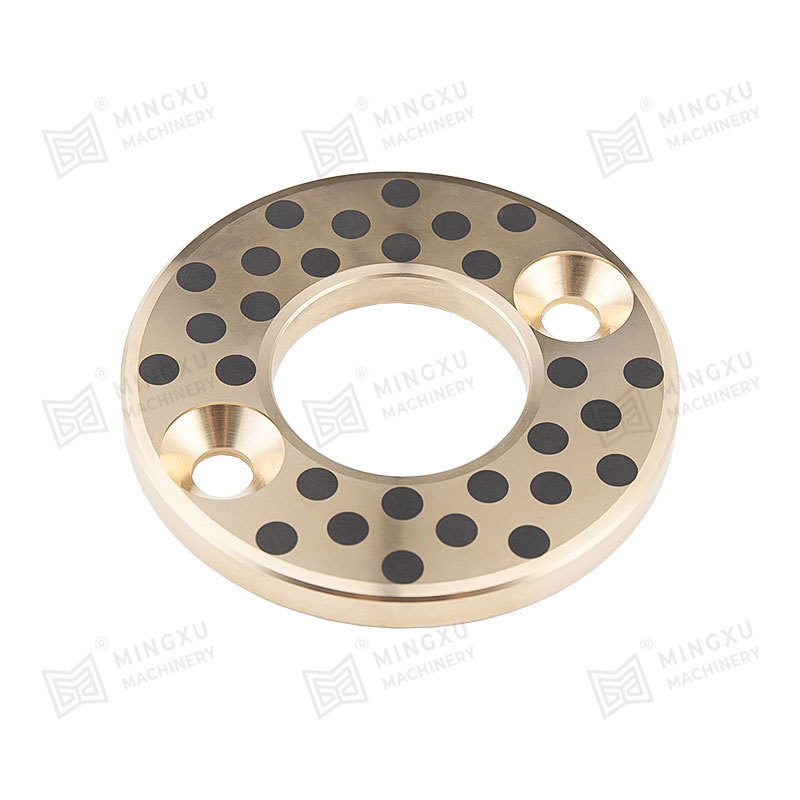
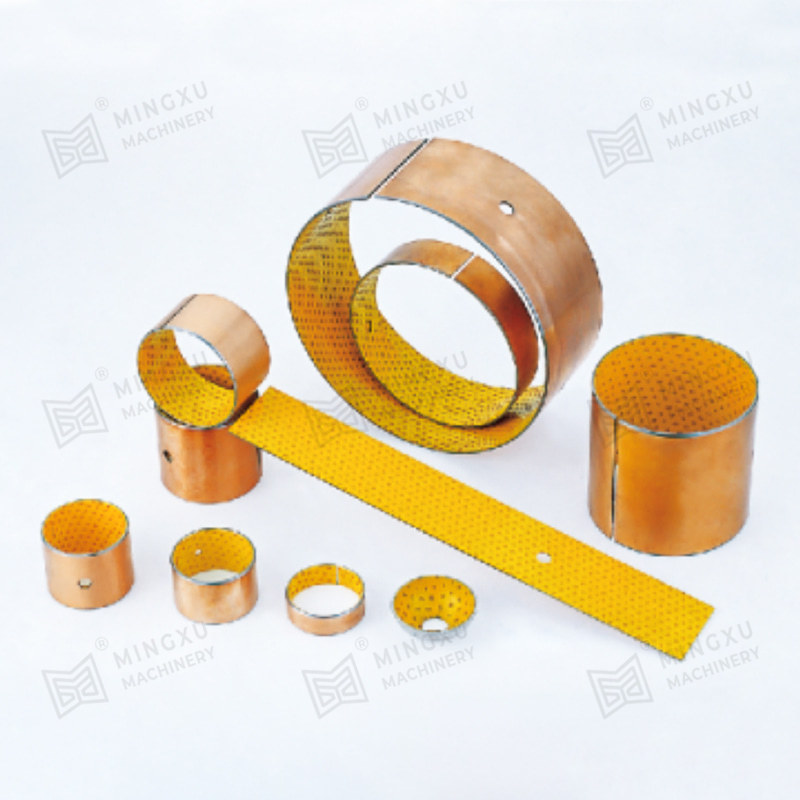
- Sintered bronze bearings impregnated with lubricant
- Layered bearings combining steel backing with sliding layers
Each structure serves different operating demands, such as higher load capacity, resistance to corrosion, or suitability for dry-running conditions. Selecting the appropriate material system is essential for stable long-term operation.
Where Self-Lubricating Bearings Deliver the Most Value
Self-lubricating bearings are widely applied in equipment where maintenance access is limited or environmental factors interfere with traditional lubrication. Typical examples include automated production lines, material handling systems, and outdoor mechanical assemblies exposed to dust or moisture.
They are also commonly used in applications requiring clean operation. In food processing machinery, medical devices, and electronics manufacturing, eliminating grease reduces contamination risk while maintaining smooth motion control.
Performance Advantages Compared to Conventional Bearings
The most direct advantage of a self-lubricating bearing is reduced maintenance demand. Without periodic relubrication, downtime caused by servicing is significantly reduced. This contributes to higher equipment availability and more predictable operating costs.
Another advantage is consistent friction behavior. Traditional bearings can suffer from over-lubrication or lubricant starvation, both of which affect motion stability. Self-lubricating bearings maintain a controlled friction profile, improving positioning accuracy and reducing vibration in precision systems.
Limitations and Design Considerations
Despite their advantages, self-lubricating bearings are not universal solutions. Load capacity, speed limits, and operating temperature must be carefully evaluated. Excessive load or surface speed may accelerate wear of the lubricating layer, shortening service life.
Proper shaft material and surface finish are also critical. Incompatible mating surfaces can prevent effective lubricant transfer, reducing performance. Designers should account for alignment, clearance, and environmental exposure during the selection process.
Comparison of Typical Bearing Solutions
| Bearing Type |
Lubrication Method |
Maintenance Demand |
| Self-lubricating bearing |
Built-in solid or embedded lubricant |
Minimal |
| Grease-lubricated bearing |
Periodic manual lubrication |
Moderate to high |
| Oil-lubricated bearing |
Continuous oil supply |
High |
Key Factors When Selecting a Self-Lubricating Bearing
Selecting the right self-lubricating bearing requires a clear understanding of operating conditions. Load type, motion pattern, speed, and environmental exposure should be evaluated together rather than independently. Matching these factors to the bearing’s material system and structural design helps achieve stable performance throughout its service life.
When properly selected and applied, self-lubricating bearings provide a reliable solution for reducing maintenance effort while maintaining consistent mechanical performance across a wide range of industrial applications.


 English
English Español
Español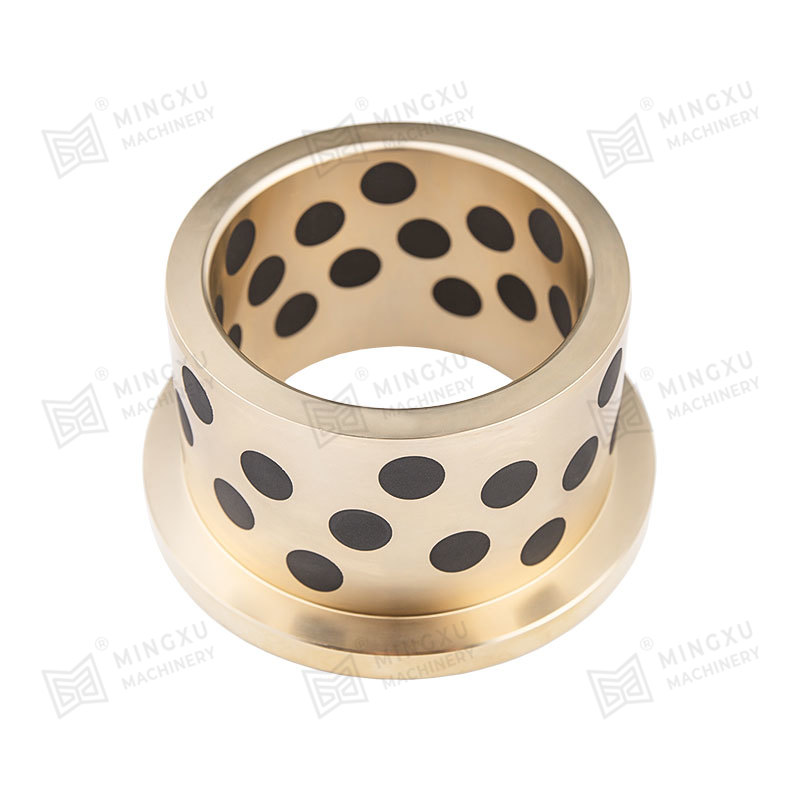















Contact Us