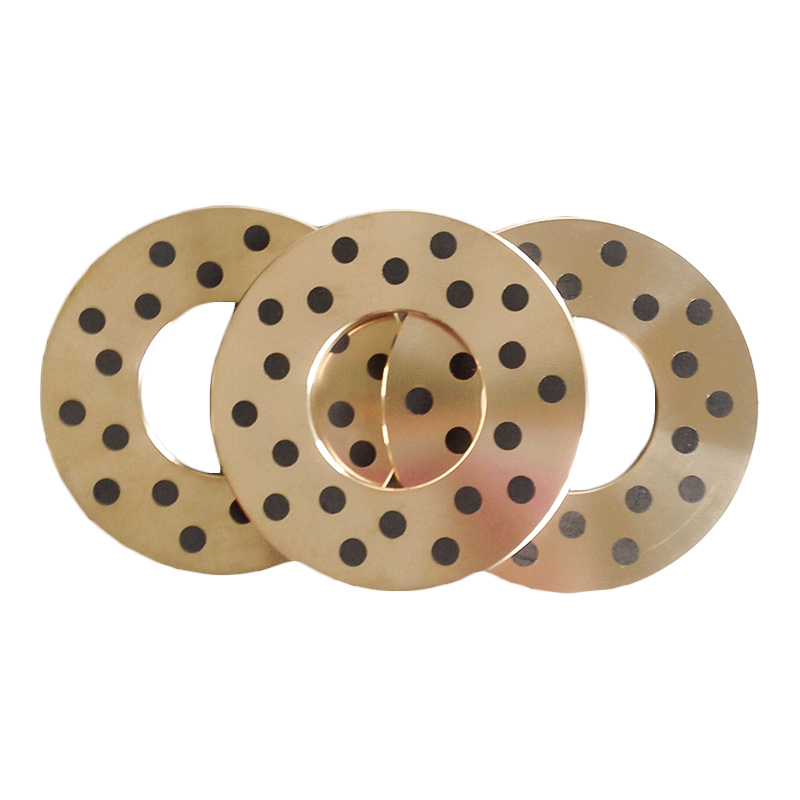
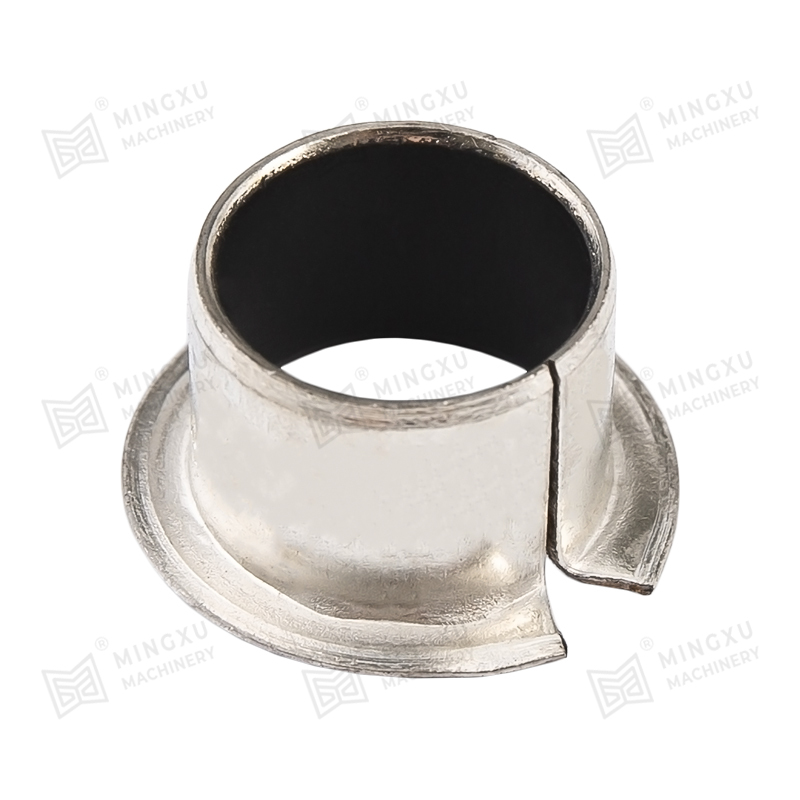
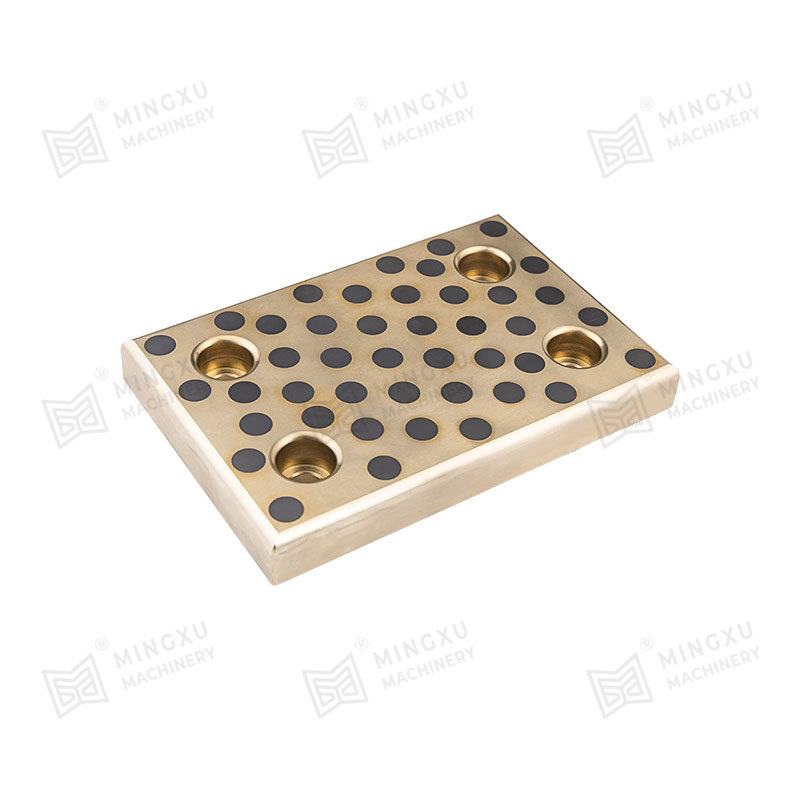
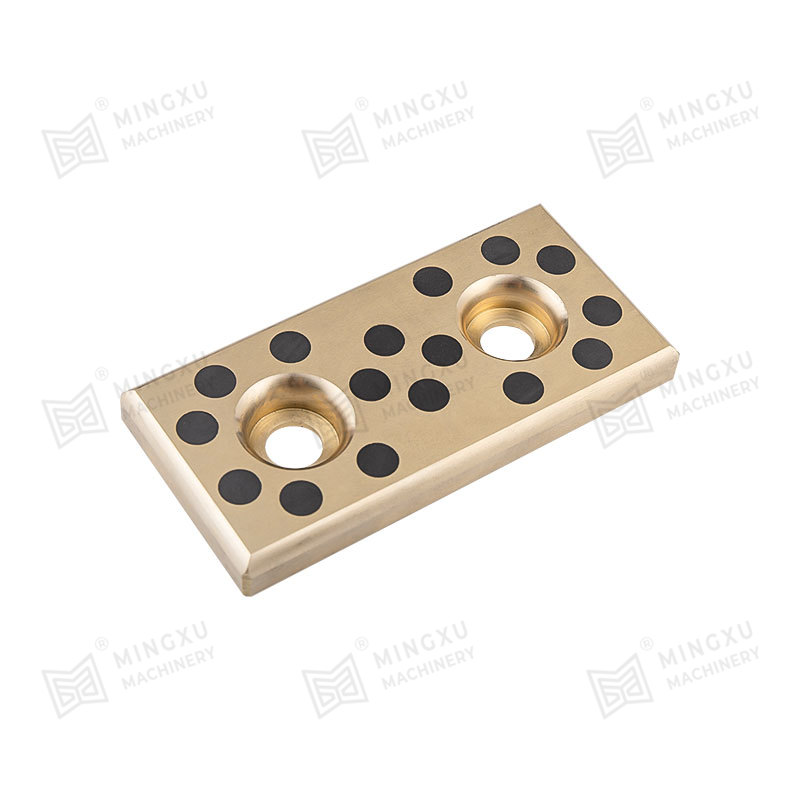
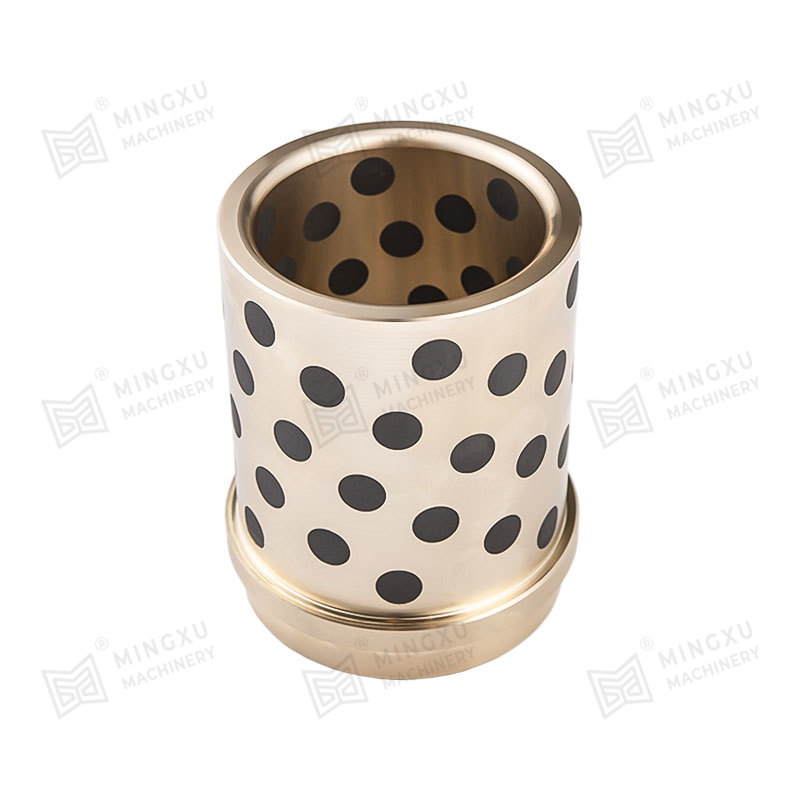
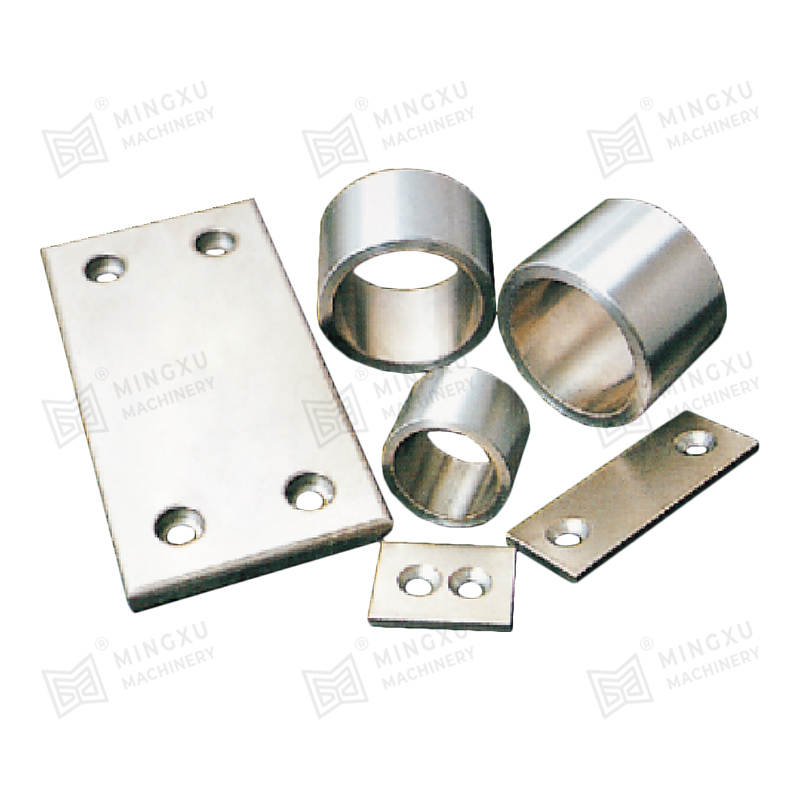
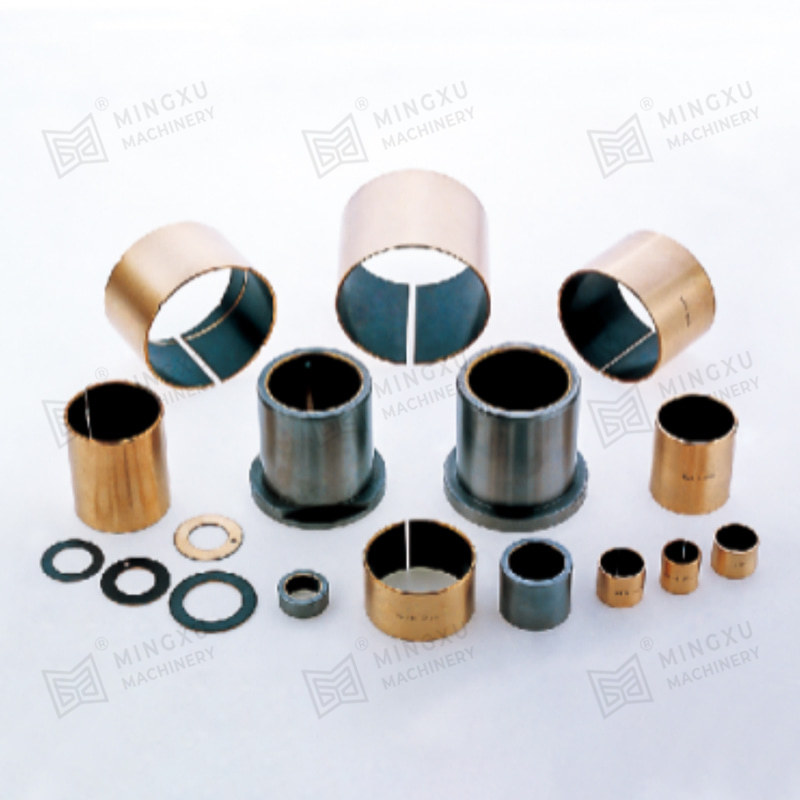
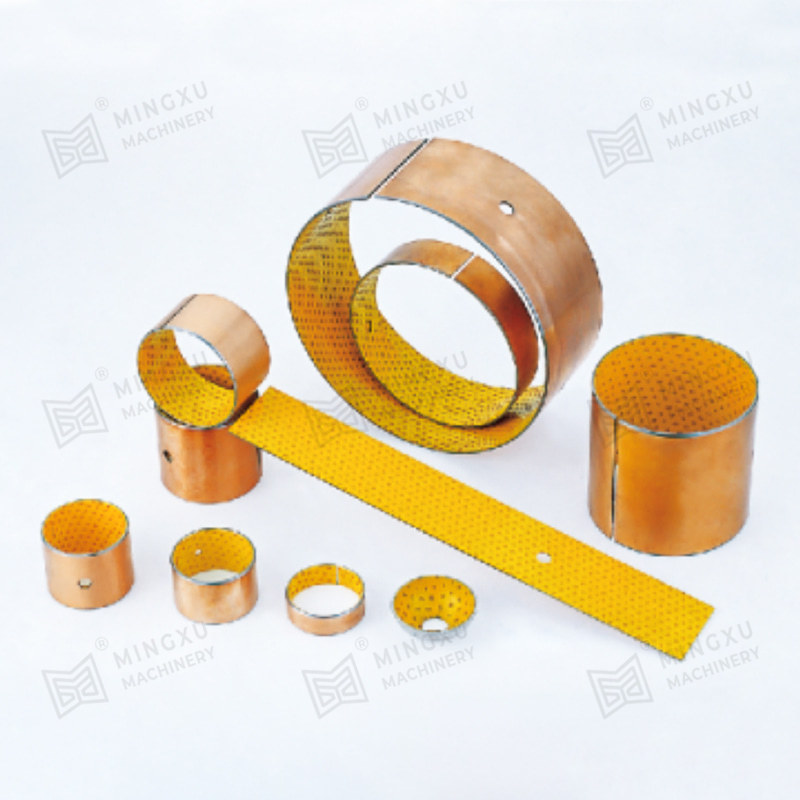
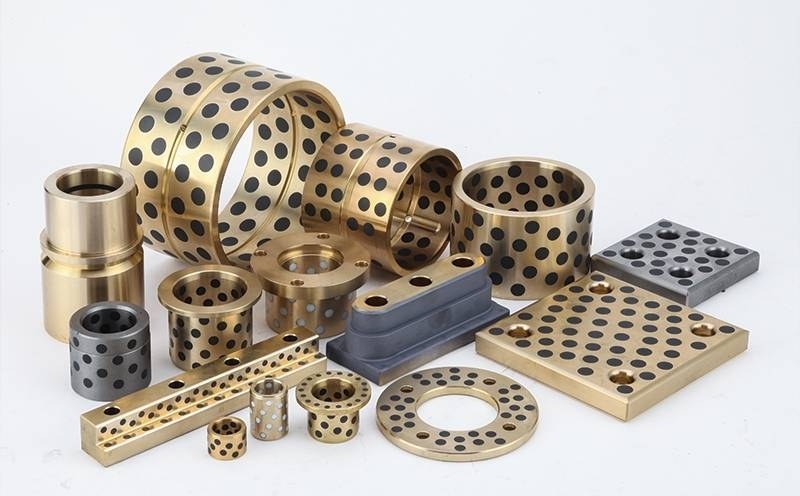
An oil-free bearing, also known as a self-lubricating bearing, is a type of bearing designed to operate without the need for external lubricants such as oil or grease. These bearings are typically made from materials with low friction properties, such as bronze, PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), or composite polymers. Oil-free bearings are engineered to reduce maintenance requirements, prevent contamination, and operate reliably in environments where traditional lubricants are unsuitable.
How Oil-Free Bearings Work
Oil-free bearings achieve smooth operation through self-lubricating materials or embedded solid lubricants. These materials create a low-friction surface that allows the bearing to function efficiently under load without additional lubrication. In some designs, microscopic pores within the bearing material release lubricants slowly over time, ensuring long-term performance without external maintenance.
Material Selection
Common materials used for oil-free bearings include:
- Bronze alloys impregnated with solid lubricants such as graphite.
- Composite polymers that combine strength with self-lubricating properties.
- PTFE coatings or inserts that reduce friction and wear.
Advantages of Oil-Free Bearings
Oil-free bearings provide multiple benefits, especially in applications where contamination, maintenance, and environmental factors are concerns.
Maintenance-Free Operation
Since these bearings do not require regular lubrication, they reduce maintenance intervals and operational downtime. This is particularly beneficial in hard-to-reach installations or continuous operation machinery.
Contamination Prevention
Oil or grease can attract dust, dirt, and other contaminants. Oil-free bearings eliminate the risk of lubricant-related contamination, making them ideal for cleanroom, food processing, medical, and semiconductor industries.
Environmental and Safety Benefits
Eliminating the need for lubricants reduces the risk of chemical spills, environmental contamination, and fire hazards. Oil-free bearings contribute to more sustainable and safer industrial operations.
Applications of Oil-Free Bearings
Oil-free bearings are widely used across industries where traditional lubrication is undesirable or impractical. Typical applications include:
- Food and beverage processing equipment.
- Medical devices and laboratory machinery.
- Cleanroom and semiconductor manufacturing equipment.
- Electric motors and pumps where maintenance access is limited.
- Automotive components such as alternators, tensioners, and HVAC systems.
Performance Considerations
Although oil-free bearings offer many advantages, selecting the right material and design is critical for optimal performance. Factors to consider include load capacity, speed, temperature range, and environmental conditions. In high-load or high-speed applications, careful evaluation ensures that wear rates and friction levels remain within acceptable limits.
Load and Speed Limitations
Oil-free bearings typically handle moderate loads and speeds. Exceeding their design limits can lead to increased friction, wear, or thermal expansion. Engineers must match the bearing material and design to the operational demands of the machinery.
Temperature and Environment
Different oil-free bearing materials tolerate different temperature ranges. Some polymers perform well at low to moderate temperatures, while metal-based bearings can handle higher temperatures. Exposure to chemicals, moisture, or abrasive particles also influences material selection and service life.
Maintenance and Longevity
While oil-free bearings reduce routine lubrication needs, they still require monitoring for wear and alignment. Regular inspection ensures that bearing surfaces remain intact, and replacement schedules are followed to prevent machinery downtime. Proper installation and load distribution are also key factors in extending the life of oil-free bearings.
Conclusion
Oil-free bearings provide a reliable, maintenance-free solution for a variety of industrial and commercial applications. By combining self-lubricating materials with robust design, these bearings reduce contamination risks, lower operational costs, and enhance safety. Understanding their properties, limitations, and applications allows engineers and manufacturers to optimize machinery performance while simplifying maintenance routines.


 English
English Español
Español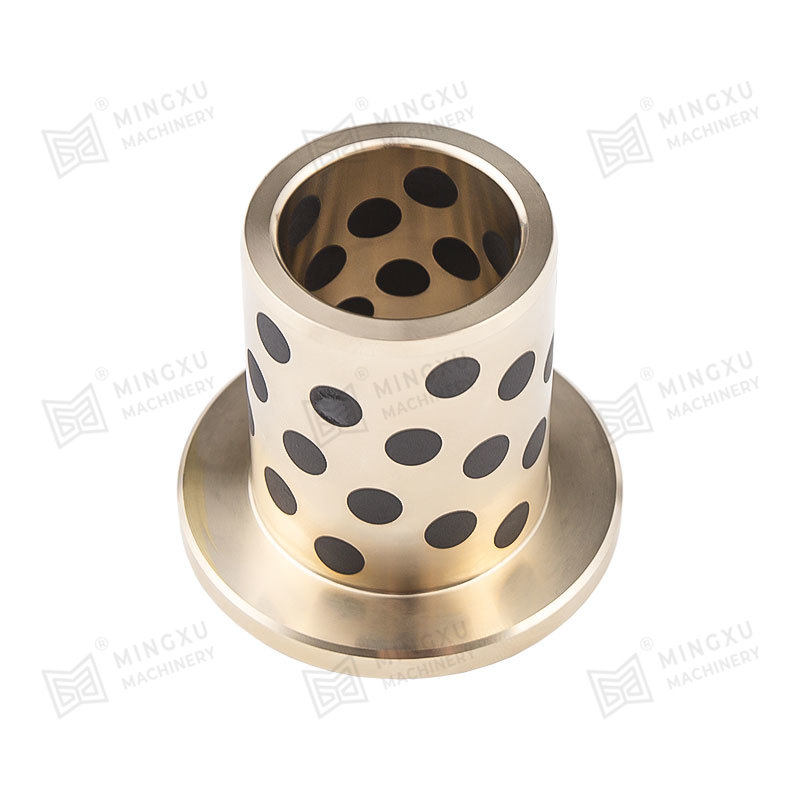
















Contact Us