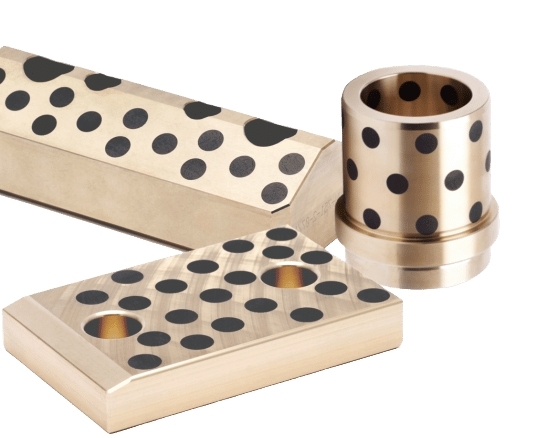
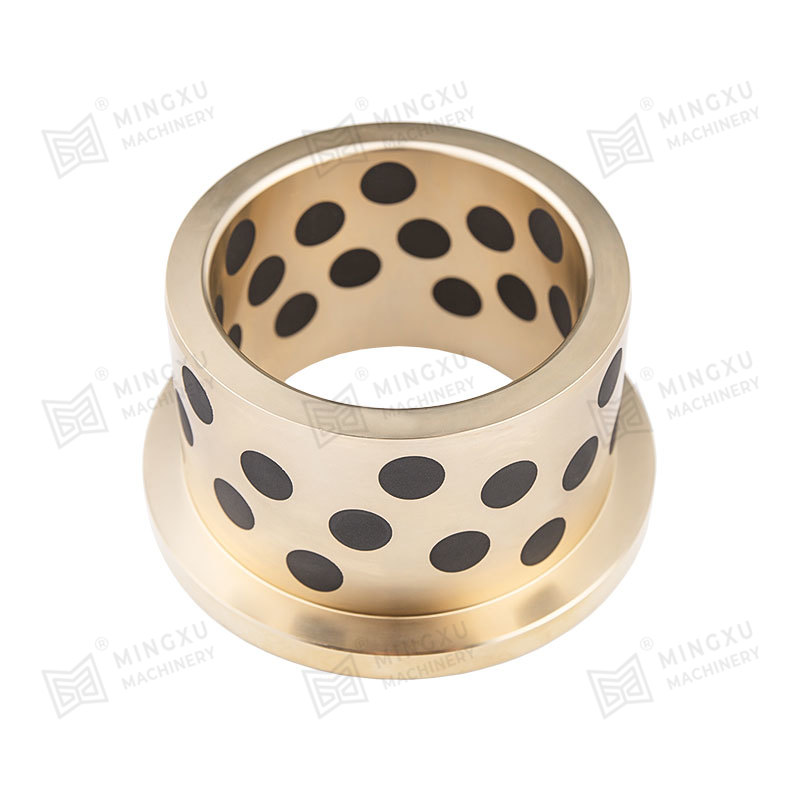
A solid-lubricating bearing is a type of bearing designed to provide smooth and efficient rotational or sliding motion between two parts without the need for external lubrication such as grease or oil. Instead of relying on liquid lubricants, these bearings incorporate solid lubricants embedded within the bearing material itself, offering long-lasting, maintenance-free performance under demanding operating conditions.
Solid-lubricating bearings are widely used in environments where traditional lubricants may be impractical or impossible to apply, such as in vacuum, extreme temperatures, dusty or corrosive atmospheres, or in sealed equipment where contamination risks are high. By integrating lubrication directly into the bearing structure, these bearings reduce friction and wear, improve reliability, and extend service life.
What Are Solid-Lubricating Bearings?
Solid-lubricating bearings combine a bearing substrate with solid lubricant materials that provide continuous lubrication during operation. The solid lubricant can be made from materials such as graphite, molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂), polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), or other self-lubricating polymers.
These bearings function by releasing or exposing the solid lubricant gradually as the bearing surface slides or rotates. This embedded lubrication mechanism means that solid-lubricating bearings do not require periodic lubrication maintenance, which is a significant advantage in many industrial applications.
Key Characteristics of Solid-Lubricating Bearings
The defining characteristics of solid-lubricating bearings differentiate them from traditional lubricated bearings and make them suited for specialized applications. Some important features include:
Self-Lubrication: Lubrication is integral, reducing or eliminating the need for external greasing or oiling.
Maintenance-Free Operation: Ideal for hard-to-access or sealed environments where maintenance is difficult or impossible.
Wide Temperature Range: Effective in extreme temperatures, from cryogenic lows to high-temperature environments beyond the range of conventional lubricants.
Corrosion Resistance: Materials used are often resistant to chemicals and moisture, improving durability in harsh conditions.
Dust and Contaminant Tolerance: Since no liquid lubricant is present to attract dirt, these bearings perform well in dusty or dirty environments.
Low Friction and Wear: Solid lubricants provide consistent friction reduction, extending bearing life.
Noise Reduction: The smooth sliding action often results in quieter operation compared to traditional bearings.
Types of Solid-Lubricating Bearings
Solid-lubricating bearings are manufactured in various types to suit different mechanical configurations and load requirements. The most common types include:
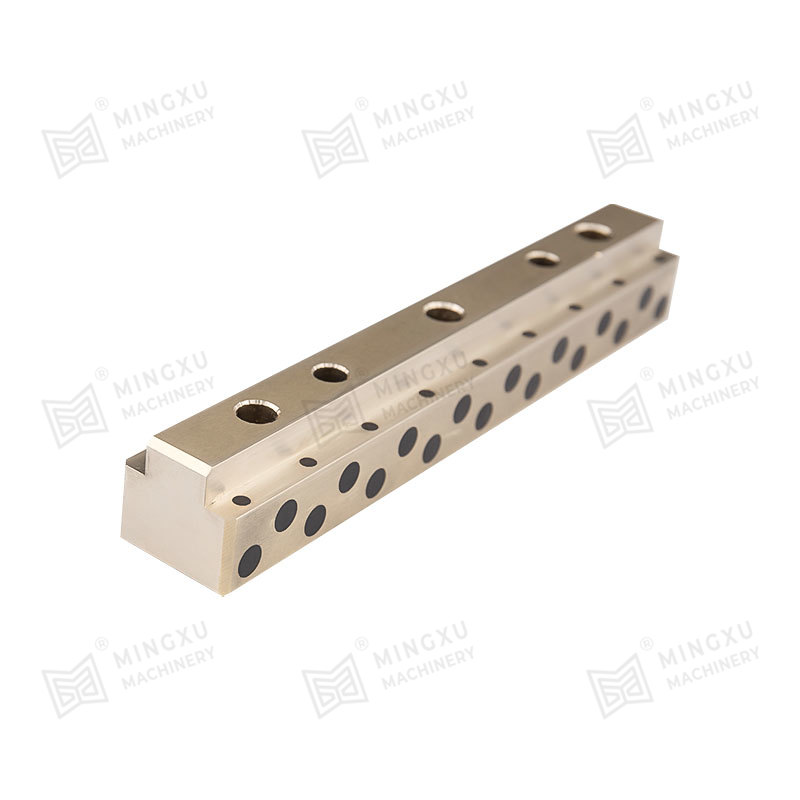
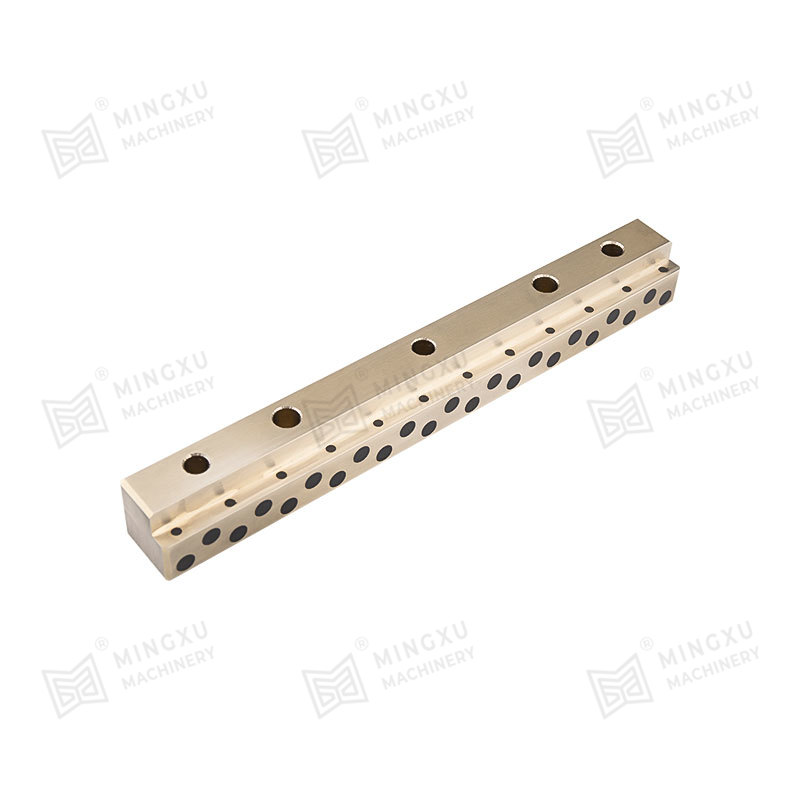
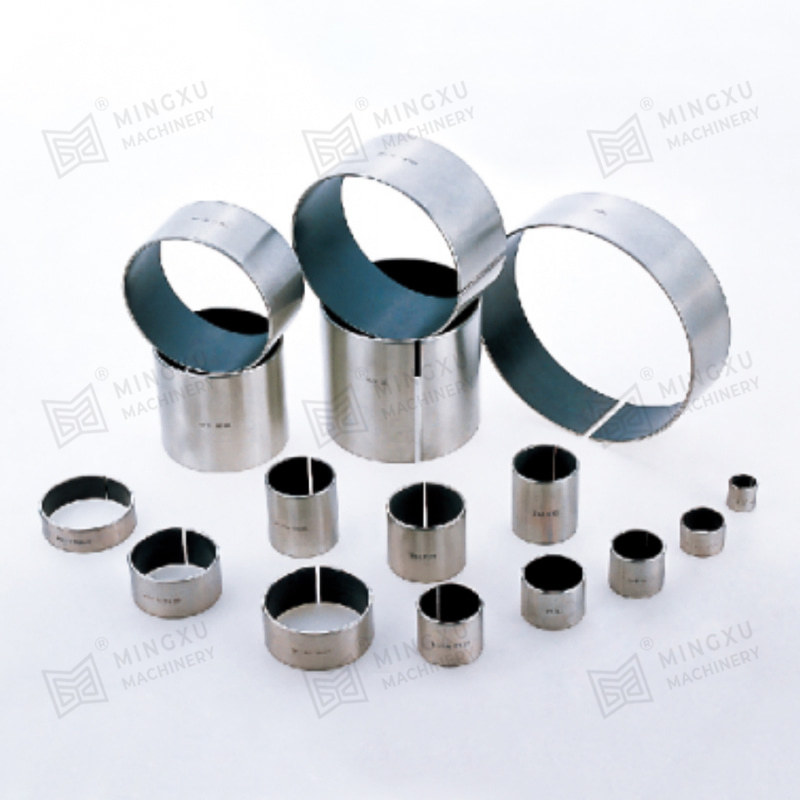
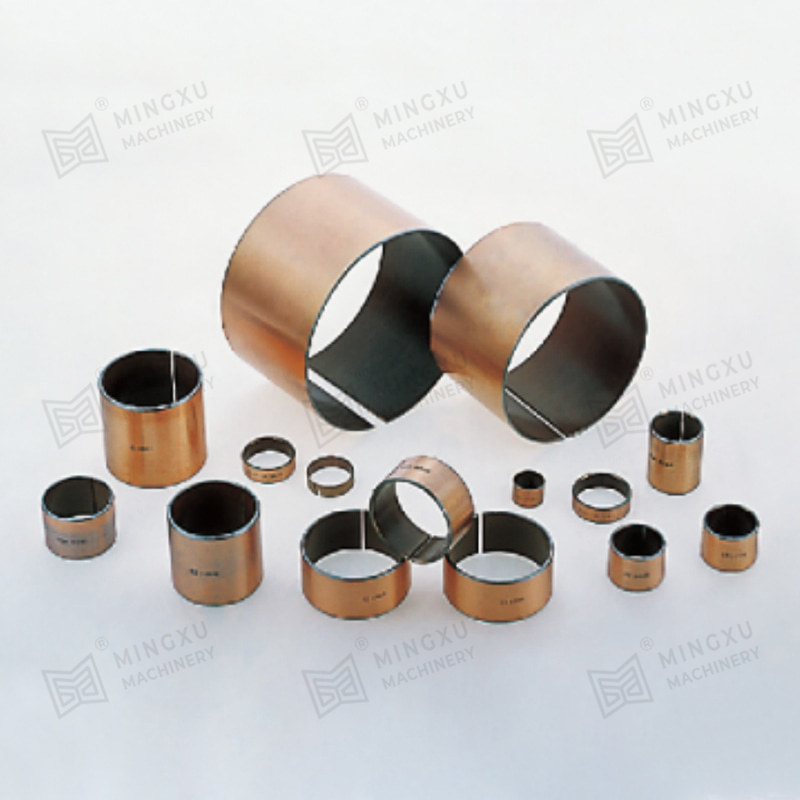
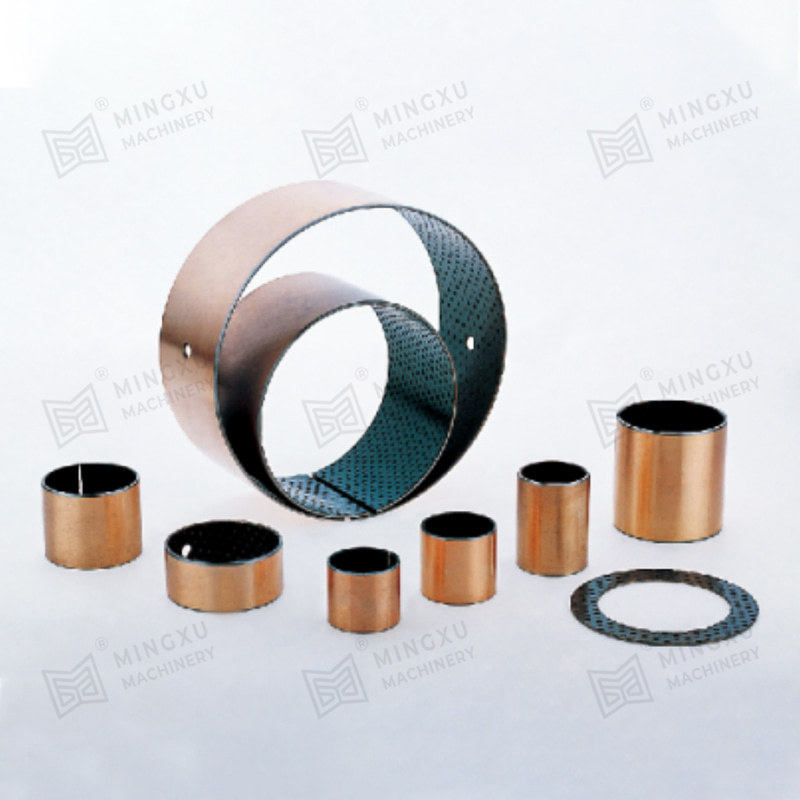
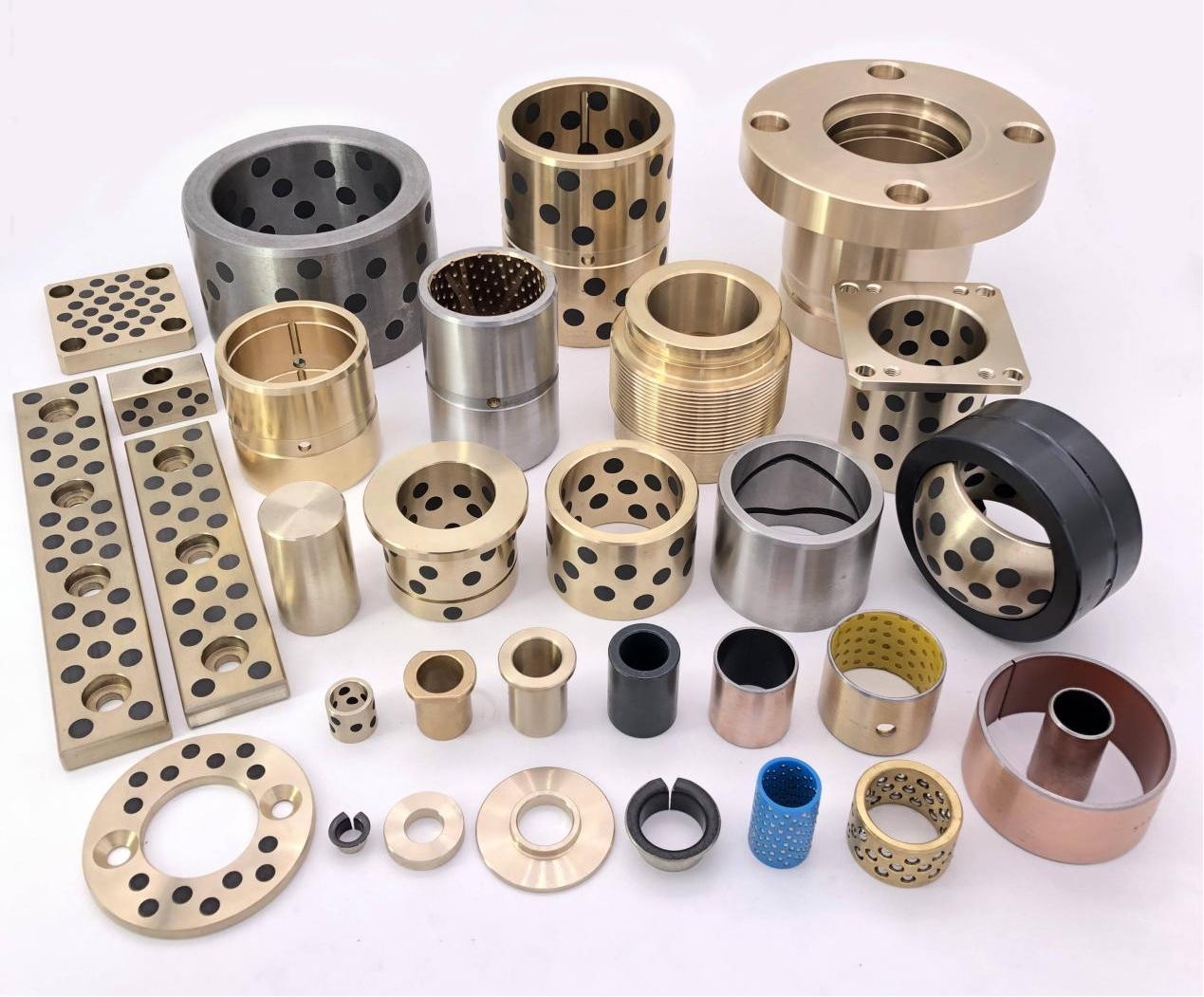
1. Composite Bearings
These bearings are made from a matrix of polymers or metals impregnated with solid lubricant particles such as graphite or PTFE. They combine strength and low friction and are often used in automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery.
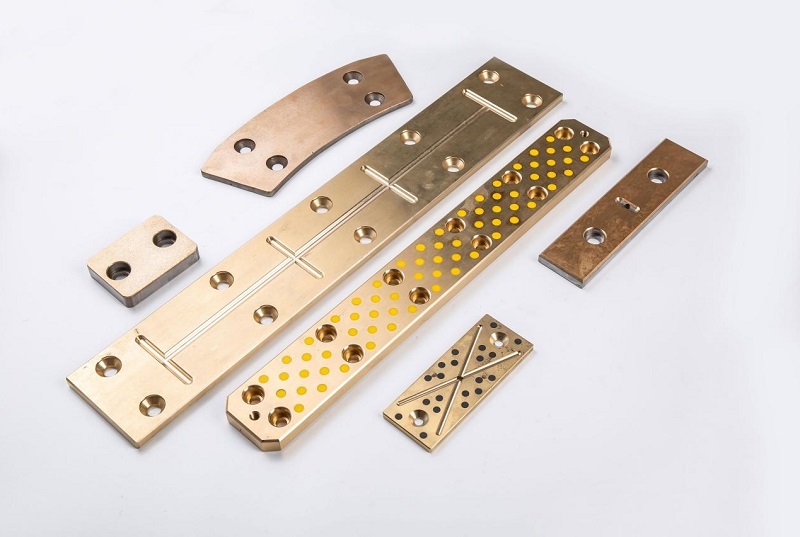
2. Metal-Polymer Bearings
Metal backings or shells are bonded with a layer of self-lubricating polymer composites, providing good load capacity and corrosion resistance. These are suitable for heavy-duty applications and are often used in construction or agricultural equipment.
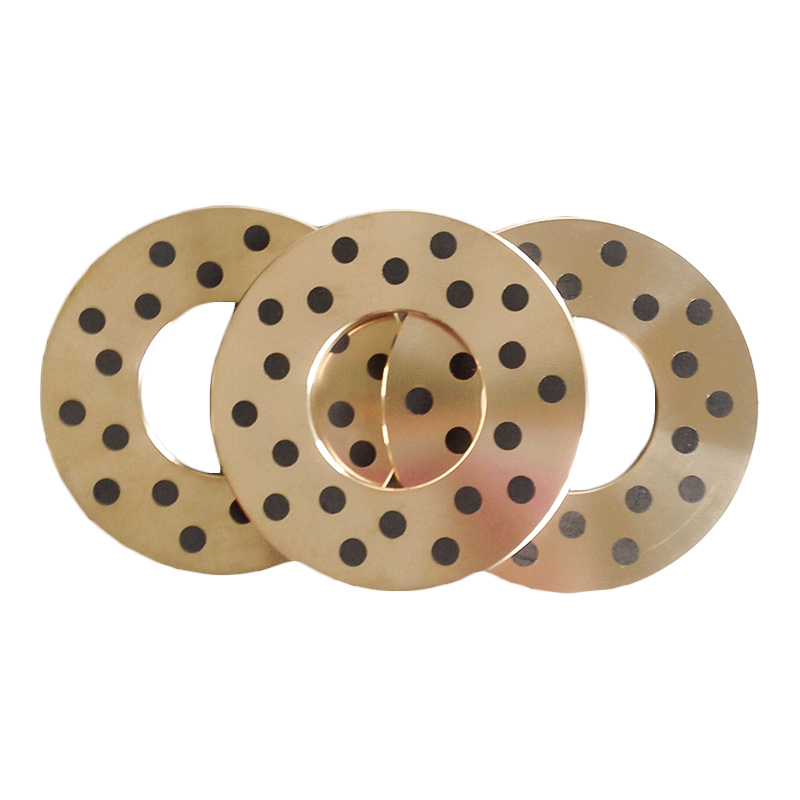
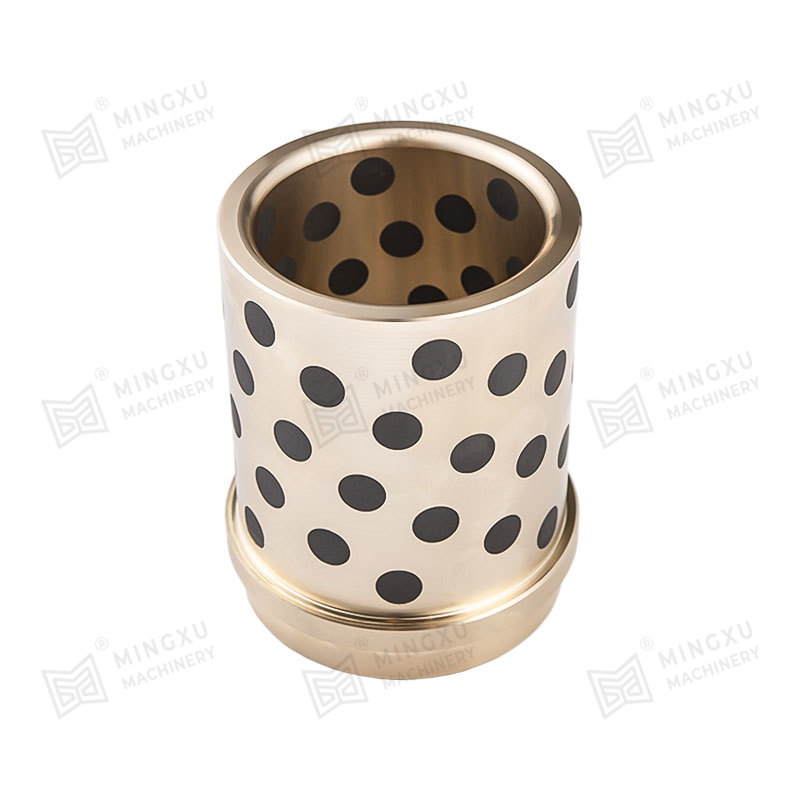
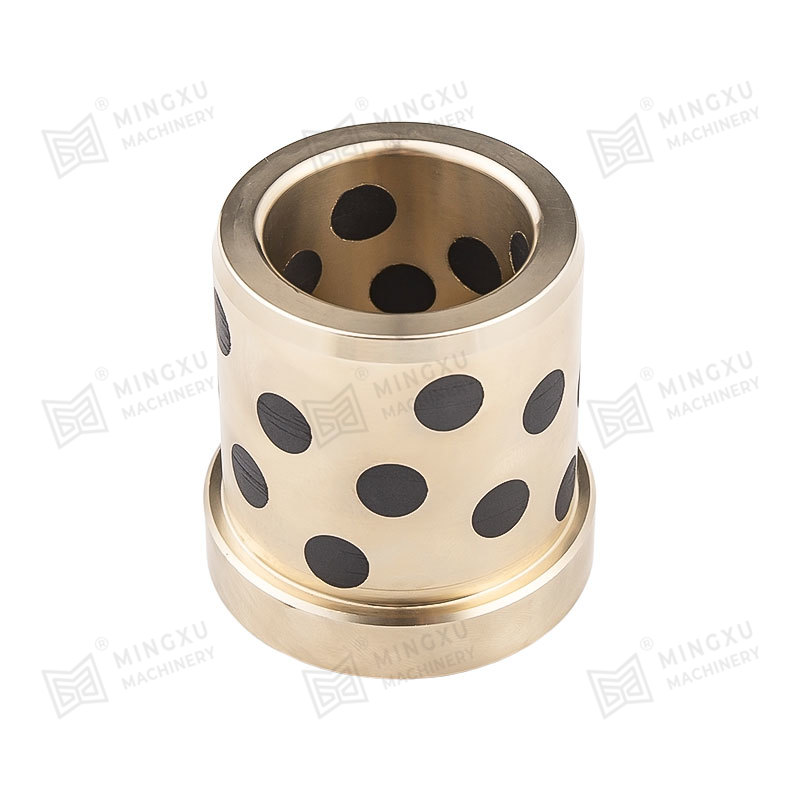
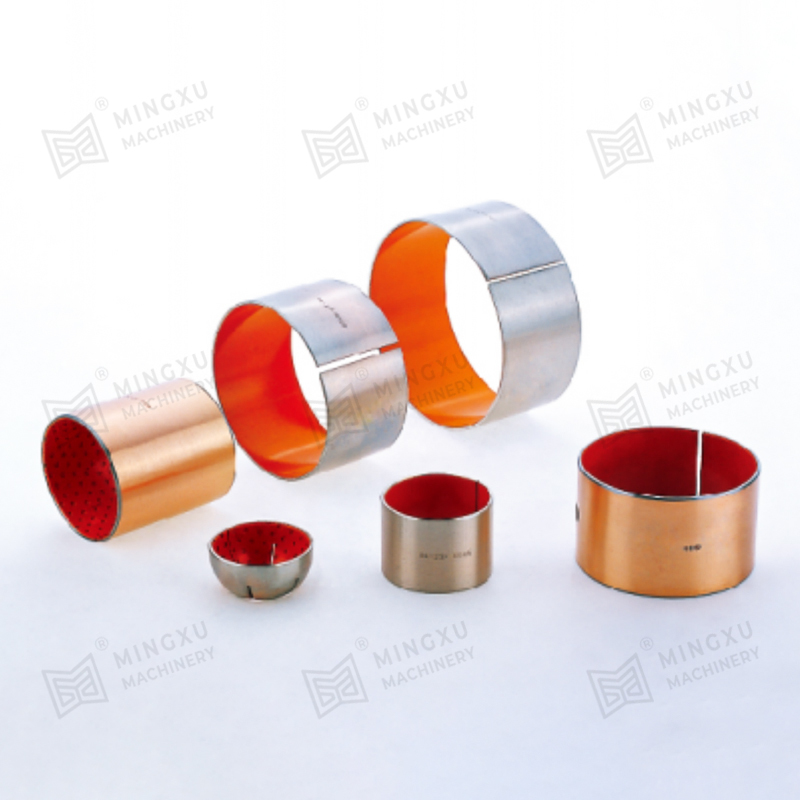
3. Sintered Bronze Bearings with Solid Lubricant
These bearings are porous bronze bearings impregnated with solid lubricants like MoS₂. The pores release the lubricant slowly during operation, making them suitable for moderate to high loads and speeds.
4. PTFE-Based Bearings
PTFE (Teflon) bearings are known for their low friction coefficient and excellent chemical resistance. Often used where chemical exposure or low friction is critical, PTFE bearings can operate without lubrication even under moderate load.
5. Graphite-Embedded Bearings
Graphite, a naturally lubricating material, can be embedded within bearing surfaces or coatings, offering excellent high-temperature and dry-running capabilities.
Installation of Solid-Lubricating Bearings
Installing solid-lubricating bearings generally follows standard bearing installation procedures but requires attention to preserve the bearing's integrated lubrication and ensure optimal performance:
-
Preparation: Clean the housing and shaft thoroughly to remove dirt, debris, or old lubricants. The surfaces must be smooth and free from burrs or corrosion.
-
Avoid External Lubricants: Do not apply additional grease or oil unless specifically recommended by the manufacturer, as external lubricants can interfere with the solid lubricant's function.
-
Press-Fit or Slide-Fit: Depending on the bearing design, install the bearing by press-fitting into the housing or sliding onto the shaft. Ensure even pressure and alignment to avoid damage.
-
Check for Clearance: Proper clearance between the bearing and shaft must be maintained as per manufacturer specifications to avoid excessive wear or seizure.
-
Secure Fixing: Use retaining rings, set screws, or other fastening methods recommended to fix the bearing securely in place.
-
Avoid Contamination During Installation: Since the lubricant is embedded in the bearing material, contamination from dirt or moisture during installation can damage the bearing surface.

Maintenance of Solid-Lubricating Bearings
One of the major advantages of solid-lubricating bearings is their reduced maintenance requirements. However, proper maintenance is still essential to maximize service life:
Inspection: Regularly inspect the bearing and surrounding components for signs of wear, unusual noise, or vibration.
Cleaning: Remove any dust, debris, or corrosive substances that may accumulate around the bearing. Use non-lubricating cleaning methods to avoid interfering with the embedded lubricant.
Replacement: When wear or damage is detected, replace the bearing promptly to prevent damage to shafts or housings.
Environmental Control: Maintain operating conditions within the recommended temperature, load, and speed limits for the bearing to avoid premature failure.
Avoid Contaminants: While solid-lubricating bearings tolerate contaminants better than lubricated types, excessive abrasive particles can still cause wear.
How to Use Solid-Lubricating Bearings
Solid-lubricating bearings are used in applications where traditional lubrication is challenging or undesirable. Usage considerations include:
Dry or Contaminated Environments: Ideal for use in dusty, dirty, or abrasive environments where liquid lubricants attract contaminants.
Sealed or Enclosed Equipment: Equipment that cannot be frequently maintained or relubricated benefits greatly.
Extreme Temperatures: Suitable for use in cryogenic applications or high-heat environments where oils and greases would degrade.
Vacuum and Space Applications: Used in aerospace and semiconductor industries, where external lubrication is impractical.
Heavy Load and Shock Applications: Depending on the material, some solid-lubricating bearings handle shock loads better due to their composite structure.
Proper selection involves consulting manufacturer data to match load capacity, speed, temperature, and environmental conditions.
Advantages of Solid-Lubricating Bearings
Solid-lubricating bearings offer a range of benefits that make them attractive in many industries:
1. Maintenance Reduction
By embedding lubrication in the bearing, the need for regular greasing or oiling is eliminated, reducing downtime and labor costs.
2. Extended Service Life
Solid lubricants provide consistent friction reduction and wear protection over the bearing’s entire lifespan.
3. Environmental Friendliness
Reducing or eliminating liquid lubricants minimizes the risk of lubricant leaks and contamination, supporting green manufacturing initiatives.
4. Reliability in Harsh Conditions
They perform reliably in vacuum, corrosive, dusty, or extreme temperature environments where conventional bearings would fail.
5. Lower Operational Noise
The smooth sliding action of solid-lubricating materials reduces noise generation in moving parts.
6. Cost Effectiveness
Though initial costs may be higher than traditional bearings, the reduced maintenance and longer life reduce overall lifecycle costs.
7. Design Flexibility
Available in various materials and composites, solid-lubricating bearings can be tailored for specific applications, including heavy loads, high speeds, or chemical resistance.
Conclusion
Solid-lubricating bearings represent a significant advancement in bearing technology by integrating lubrication directly into the bearing structure. They provide long-term, maintenance-free operation and excel in demanding conditions that challenge traditional lubricated bearings. From aerospace and automotive applications to industrial machinery and harsh environmental conditions, solid-lubricating bearings improve reliability, reduce maintenance costs, and extend service life.
Selecting the right type of solid-lubricating bearing requires understanding application demands such as load, speed, temperature, and environmental exposure. Proper installation and periodic inspection ensure the bearing performs optimally.
As industries push the limits of performance and sustainability, solid-lubricating bearings will continue to play a vital role in enabling efficient, clean, and reliable mechanical systems worldwide.


 English
English Español
Español

















Contact Us