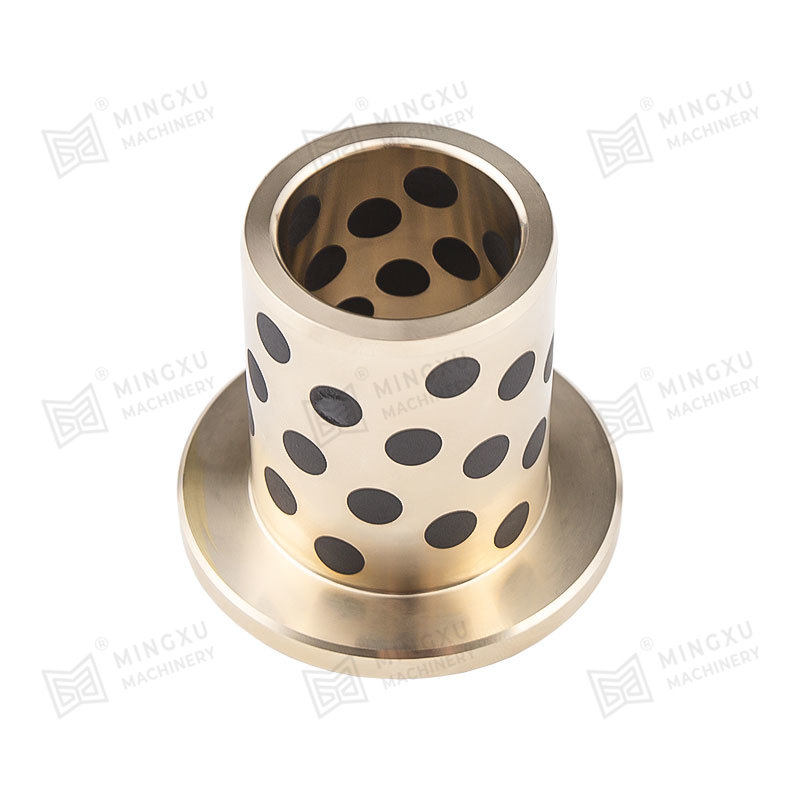
As critical components for connecting pipelines and equipment, Shoulder Bushing Flange Graphite Inlaid Self-Lubricating Bearings directly impact sealing performance, load-bearing efficiency, and application suitability. Square flanges, circular flanges, and trimmed flanges (irregular-shaped flanges) serve distinct industrial roles due to their geometric differences. In recent years, as demands for modular design and space constraints have intensified, proper flange selection has become pivotal in reducing installation costs and extending system lifespans.

Key Differences and Typical Applications of Three Flange Types
Square Flanges
Structural Features: Rectangular with four right-angled or rounded edges; bolt holes symmetrically distributed on all four sides.
Core Advantages:
l High Rigidity and Deformation Resistance: Square structures exhibit a 15%–20% higher section modulus against bending than circular flanges of the same size (ASME B16.5 comparative data), making them ideal for heavy-load or vibration-prone scenarios.
l Strong Spatial Adaptability: Right-angled edges facilitate seamless integration with equipment casings or frame structures, minimizing non-standard machining.
Typical Applications:
l Hydraulic pipelines in construction machinery (e.g., multi-way valve blocks in excavators).
l Inlet/outlet sealing for cabinet-style power distribution equipment (IP67 protection rating).
l Modular welding interfaces for shipbuilding segments (Hudong-Zhonghua Shipbuilding 2023 case study).

Circular Flanges
Structural Features: Standard ring-shaped with bolt holes uniformly distributed around the circumference, compliant with mainstream standards such as ASME, DIN, and GB.
Core Advantages:
l Uniform Stress Distribution and Sealing Performance: Circular symmetry ensures even stress distribution under pressure, improving sealing gasket compressibility consistency by 30% (Pressure Vessel 2021 experimental data).
l High Standardization: Over 80% of industrial pipelines adopt circular flanges, offering strong spare part interchangeability.
Typical Applications:
l High-pressure pipelines in petrochemical industries (PN40 and above ratings).
l Flange connections for wind turbine towers (large diameters exceeding DN2000).
l Clean pipelines in biopharmaceutical manufacturing (316L stainless steel + EPDM gaskets).

Trimmed Flanges
Structural Features: Circular flanges with locally cut or stamped asymmetric edges, commonly featuring single-side or multi-side flattened designs.
Core Advantages:
l Space-Saving Optimization: Trimmed sections avoid interference with adjacent components, reducing installation clearances to within 5 mm (e.g., automotive exhaust pipes bypassing turbos).
l Lightweight Material Reduction: Weight savings of 10%–25% after trimming, suitable for mobile equipment (e.g., fuel pipelines in drones).
Typical Applications:
l Compact pipelines in automotive engine compartments (e.g., Volkswagen MQB platform EA888 engines).
l Asymmetric layouts in aviation hydraulic systems (e.g., Airbus A350 fuselage piping).
l Internal connections for semiconductor equipment chambers (trimmed to avoid wafer-handling robotic arms).

Selection Logic (Based on ISO 5211 and GB/T 9119 Standards)
Step 1: Prioritize Operating Conditions
Load Types:
l Vibration/impact scenarios → Opt for square flanges (high bending rigidity).
l Uniform pressure/high sealing requirements → Circular flanges (standardized sealing surfaces).
l Space constraints/lightweight needs → Trimmed flanges (customized clearance avoidance).
Medium Characteristics:
l Corrosive fluids → Circular flanges (mature lining/plating processes).
l High-temperature gases → Square flanges (superior bolt thermal expansion compensation).
Step 2: Match Installation Conditions
Connected Object Morphology:
l Square containers/frames → Square Solid-Lubricating Bearing flange(reduced transition pieces).
l Circular pipelines/rotating equipment → Circular flanges (high coaxiality).
l Irregular equipment chambers → Trimmed flanges (localized fitting).
Maintenance Frequency:
l High-frequency disassembly → Circular flanges (standard tool compatibility).
l One-time encapsulation → Trimmed flanges (space utilization prioritized).
Step 3: Evaluate Cost and Supply Chain
l Mass Production: Circular flanges (standardized inventory, procurement lead time ≤3 days).
l Small-batch Customization: Square/trimmed flanges (CNC machining, lead time 7–15 days).
l Extreme Environments: Deep-sea/aerospace → Circular flanges (mature titanium alloy forging processes).
Industry Application Data Comparison (2020–2024)
|
Metric
|
Square Flanges
|
Circular Flanges
|
Trimmed Flanges
|
|
Market Share
|
12% (heavy industry-dominated)
|
73% (general-purpose)
|
15% (specialty customization)
|
|
Max. Pressure Rating
|
PN64
|
PN420 (nuclear-grade)
|
PN25 (lightweight)
|
|
Typical Weight Reduction
|
-
|
-
|
10%–25%
|
|
Installation Tolerance
|
±1.5°
|
±0.5°
|
±2.0° (requires tooling)
|
|
Leading Suppliers
|
WIKA Group
|
Flowserve
|
Swagelok custom line
|
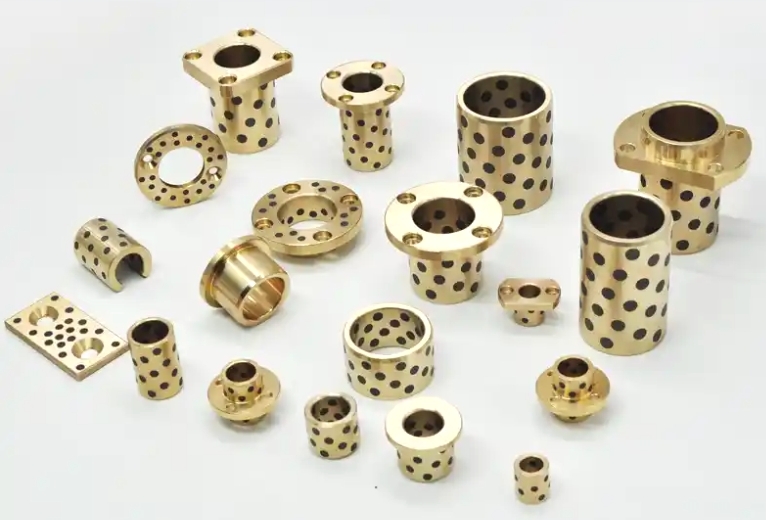

Zhejiang Mingxu Machinery Manufacturing Co., Ltd., a professional manufacturer of sliding bearings, can design flanges in various forms tailored to your operating conditions, safeguarding your production needs. For custom product inquiries, please contact us at [email protected].


 English
English Español
Español





















Contact Us