MXB-JTW Metric Thrust Washer For Vehicle Transmissions
Cat:Self-Lubricating Bearing
MXB-JTW metric thrust washers are based on high-strength brass (ZCuZn25Al6), with solid lubricant (graphite or molybdenum disulfide) embedded in the m...
See DetailsHydraulic machinery operates under harsh conditions involving prolonged water immersion, sediment scouring, and intermittent heavy loads. Traditional bearings often suffer from lubricant loss, corrosion-induced seizing, and reduced equipment reliability. Self-lubricating bearings, renowned for their maintenance-free operation, corrosion resistance, and abrasion resistance against sediment, have emerged as the preferred solution for critical installations such as sluice gates and pumping stations. This article analyzes typical application scenarios and core selection criteria for self-lubricating bearings in hydraulic machinery, drawi

I. Typical Applications of Self-Lubricating Bearings in Hydraulic Machinery
Sluice Gate Hoist Sliders and Guide Wheels
l Slider Bearings: Sluice gate hoists are continuously immersed in sediment-laden water. A Yangtze River hydraulic project adopted 316L stainless steel-based self-lubricating bearings with a surface-composite PTFE coating. After five years of continuous operation in water with a sediment concentration of 2 kg/m³, the wear depth was only 0.25 mm, quadrupling the lifespan compared to traditional bronze bushings and reducing hoisting force fluctuations by 30%.
l Guide Wheel Shaft Systems: Graphite-copper alloy bearings exhibit stable friction coefficients of 0.08–0.12 in humid environments. Field tests at the Three Gorges Ship Lock demonstrated a reduction in hoisting noise from 85 dB to 72 dB and a 20% improvement in synchronization accuracy.
Pump and Turbine Shaft Systems
l Deep-Well Pump Guide Bearings: Engineering plastic-based self-lubricating bearings (e.g., PEEK + carbon fiber) withstand high linear velocities (up to 10 m/s) and axial vibrations. Field measurements at a South-to-North Water Diversion pumping station recorded shaft vibration values ≤2.5 μm, a 60% reduction compared to metal bearings.
l Turbine Guide Vane Shafts: Ceramic-based self-lubricating bearings (SiC + graphite) in water flows containing micro-quartz particles (≤0.1 mm diameter) exhibited annual wear depths <0.05 mm. Post-retrofit testing at a Yunnan hydropower station shortened guide vane adjustment response times by 15%.
Articulated Mechanisms in River Dredging Equipment
l Dredger Cutterhead Bearings: Multi-layer composite bearings (steel backing + copper alloy + MoS₂ coating) withstand transient impact loads exceeding 50 MPa. A case study by a Dutch dredging company reported a 6,000-hour service life in sediment containing shell fragments, tripling maintenance intervals.
l Hydraulic Grab Joints: Self-lubricating spherical bearings (e.g., GE-type) resist saltwater immersion and high-frequency oscillations. Field tests on Zhoushan Port dredging vessels demonstrated a 70% improvement in seawater corrosion resistance compared to conventional bearings.
Actuators for Water Pipeline Valves
l Valve Stem Guide Bushings: Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE)-based bearings with friction coefficients as low as 0.05 reduced valve hoisting torque from 1,200 N·m to 800 N·m in a major water transfer project, achieving significant energy savings.
l Butterfly Valve Shaft Supports: PTFE fiber-reinforced composite bearings, operating at 30 cycles/day, exhibited wear depths <0.1 mm after 100,000 cycles, meeting ISO 5208 leakage class A requirements.

II. Key Selection Factors and Technical Specifications
Water Corrosion Resistance and Biofouling Prevention
l Freshwater Environments: Prioritize copper-based or engineering plastic bearings.
l Seawater Environments: Require 316L stainless steel or Hastelloy substrates compliant with ASTM G48 salt spray corrosion standards (720 hours without pitting).
l Algae Resistance: Research indicates that bearings with surface roughness Ra ≤ 0.2 μm reduce microbial adhesion by 80%.
Silt Abrasion Resistance
|
Sediment Concentration |
Recommended Bearing Material |
Surface Treatment Technology |
|
Low (≤1 kg/m³) |
PTFE composite materials |
Laser micro-texturing for drag reduction |
|
Medium (1–5 kg/m³) |
Copper-based WC spray coating |
Plasma nitriding hardening |
|
High (>5 kg/m³) |
Ceramic-based (Al₂O₃/ZrO₂) |
Diamond coating |
Temperature and Pressure Adaptability
l Deep-well pump bearings must withstand water temperature variations from 0°C to 80°C and static water pressures of 10 MPa. A PEEK-based bearing exhibited a thermal expansion rate of only 0.3% at 80°C, significantly lower than nylon's 1.5%.
l According to ISO 4378-4 standards, hydraulic bearings must pass 500-hour high-pressure water jet tests (15 MPa pressure, 20 m/s flow velocity).
Load and Start-Stop Characteristics
l Static Load with Prolonged Immersion (e.g., Gate Supports): Select sintered copper-based bearings with surface pressure capacities ≥50 MPa (GB/T 23894 standard).
l High-Frequency Start-Stop (e.g., Pump/Valve Controls): Use PI-based bearings capable of 10⁶ start-stop cycles (five times higher than metal bearings).
Economic and Environmental Considerations
l According to the 2023 Global Hydraulic Machinery Bearing Market Report, self-lubricating bearings reduce total lifecycle costs by 30%–40% compared to traditional solutions:
l Annual maintenance costs for a large pumping station decreased from RMB 480,000 to RMB 180,000.
l Gate bearing replacement time was reduced from 8 hours to 2 hours per instance.
l Potable water contact scenarios require NSF/ANSI 61 certification, prohibiting materials containing lead, cadmium, or other hazardous substances.
III. Industry Trends and Selection Recommendations
Technological Frontiers
l Bionic Surface Technology: Bearings with sharkskin-inspired groove structures reduce hydraulic drag by 15%, applied in energy-efficient retrofits of large pumping stations.
l Integrated Smart Monitoring: NMB's waterproof vibration sensor bearings enable real-time monitoring of shaft misalignment and wear conditions.
Practical Selection Recommendations
l Prioritize products certified under ISO 4378 (sliding bearing testing) and AWWA C540 (water industry standards).
l Hydraulic bearings should incorporate drainage channels or self-cleaning structures to prevent sediment buildup and seizing.
l Require manufacturers to provide sediment-laden water bench test reports (recommended: 500-hour high-pressure water jet + 10⁶ start-stop cycle tests).

Zhejiang Mingxu Machinery Manufacturing Co., Ltd., with over a decade of expertise in self-lubricating bearing R&D and manufacturing, has earned positive feedback from hydraulic machinery manufacturers. For inquiries, please contact: [email protected].

MXB-JTW metric thrust washers are based on high-strength brass (ZCuZn25Al6), with solid lubricant (graphite or molybdenum disulfide) embedded in the m...
See Details
JTWN thrust washers adopt self-lubricating inlay technology, which further improves self-lubricating performance based on its high strength and wear r...
See Details
MXB-JDB self-lubricating bearings, also known as graphite inlaid bronze bushings, are novel lubricating bearings that have both the characteristics of...
See Details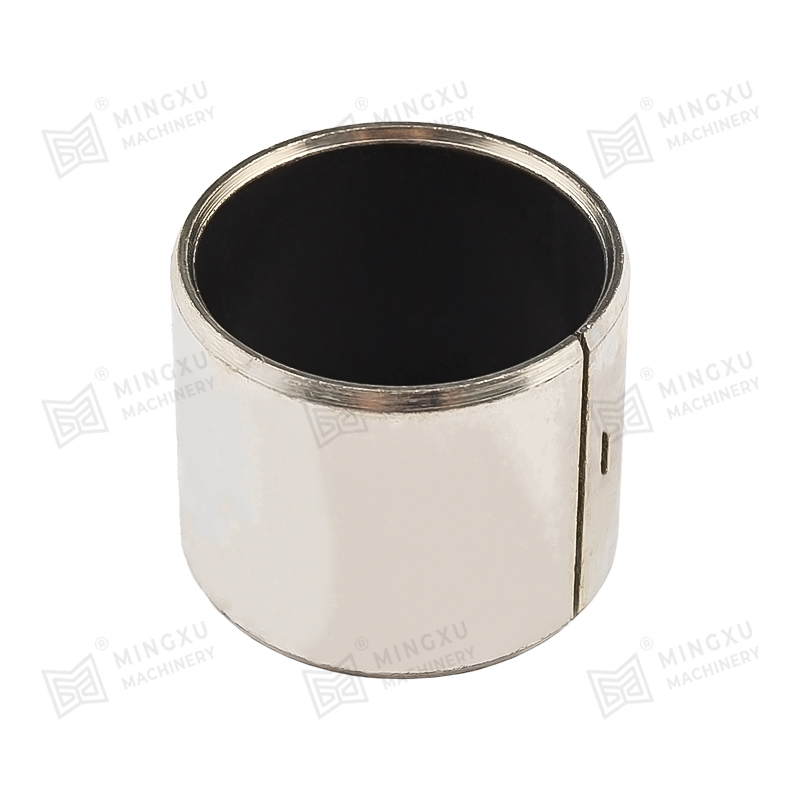
SF stands for three-layer composite, namely steel plate layer, copper powder layer and plastic layer. The steel plate layer plays the role of assembly...
See Details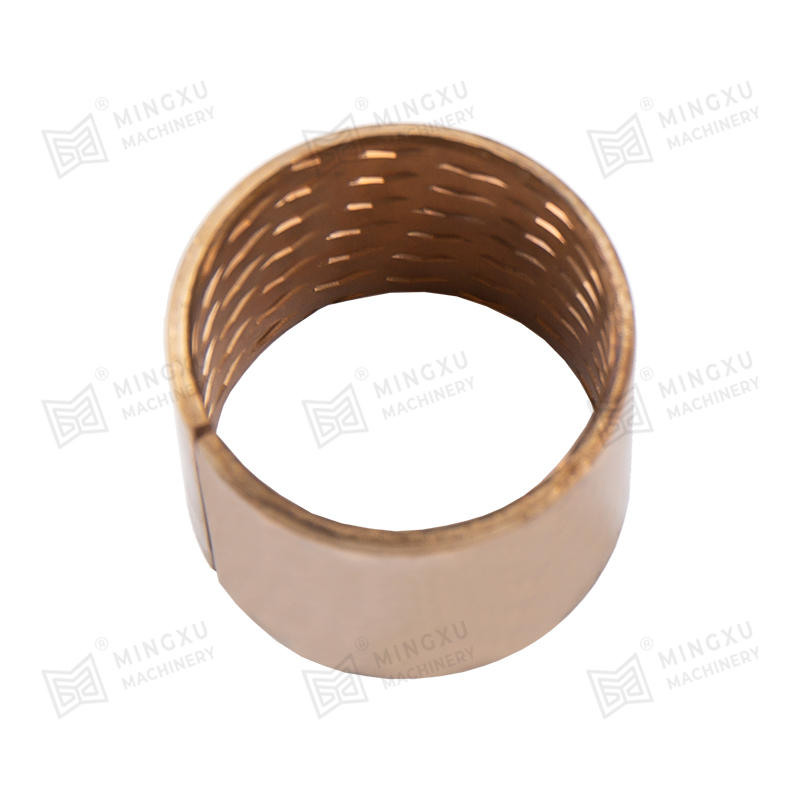
FB090 bronze bearings are made of tin bronze alloy CuSn8. The surface can be rolled with diamond or hemispherical oil holes and oil grooves according ...
See Details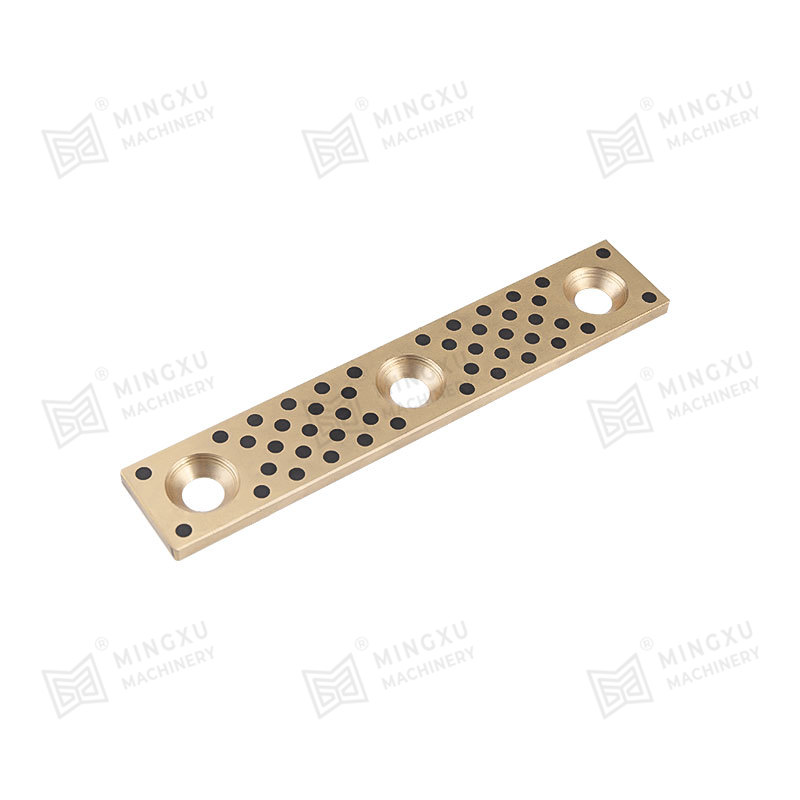
MXB-JUWP self-lubricating wear-resistant plate is a 5mm thick self-lubricating graphite inlaid wear-resistant plate developed and produced by Mingxu M...
See Details
MXB-JOLP self-lubricating wear plates have good self-lubricating properties and require no external lubrication. This product has good load-bearing ca...
See Details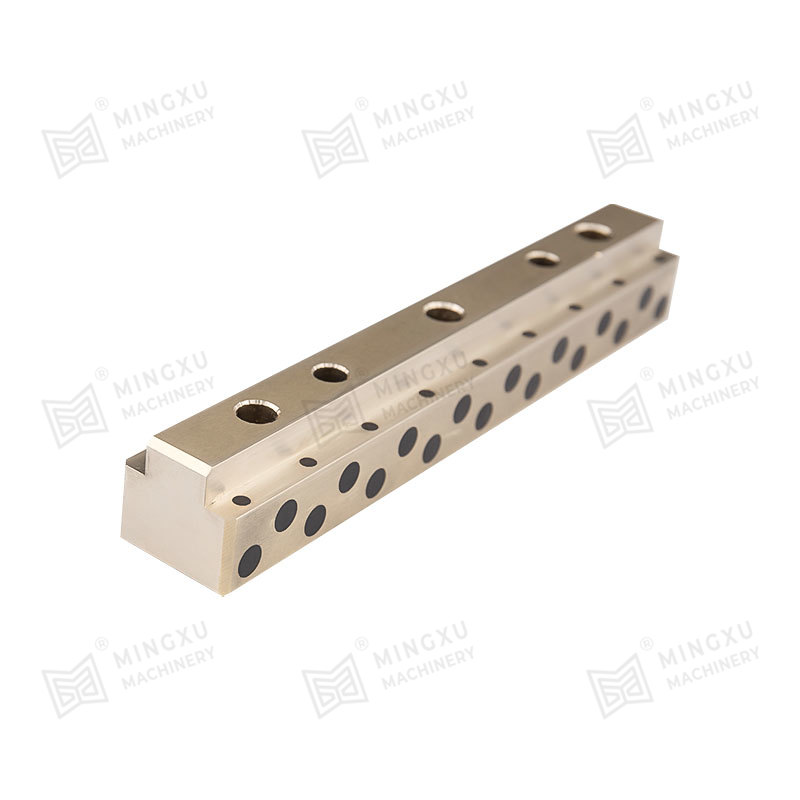
MXB-JTGLW self-lubricating guide rails provide resistance and reduce friction, ensuring extended durability and enhanced performance. This product pro...
See Details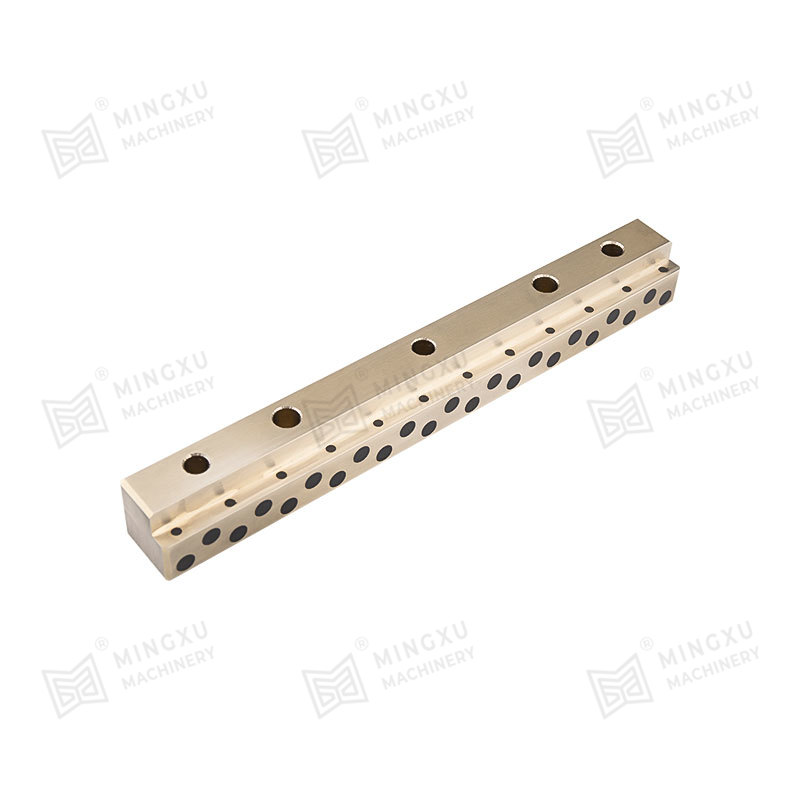
MXB-JSOL self-lubricating guide rail is an L-shaped guide groove type self-lubricating guide rail, which is made of a combination of high-strength bra...
See Details
MX2000-2 nickel graphite dispersed alloy bearing is a new product among solid lubricating bearings. Compared with TF-1, this product has the character...
See Details
Contact Us