The Bronze-Based Solid Inlaid Self-Lubricating Spherical Bearing offers several distinct tribological advantages over conventional lubricated bearings, particularly in applications involving oscillating or angular motion where lubrication challenges are more pronounced. These advantages stem from both the inherent properties of the bronze alloy and the integration of solid lubricant materials into the bearing structure.
In traditional lubricated bearings, the formation of a hydrodynamic or elastohydrodynamic film is essential to minimize direct metal-to-metal contact. However, in oscillating or reciprocating motion—where the movement is limited in angle and speed—this lubricating film often breaks down or fails to form altogether. This leads to increased friction, wear, and ultimately, reduced service life. Conventional lubricants such as oils and greases can also degrade over time due to oxidation, contamination, or evaporation, particularly in high-temperature or inaccessible environments, necessitating regular maintenance.
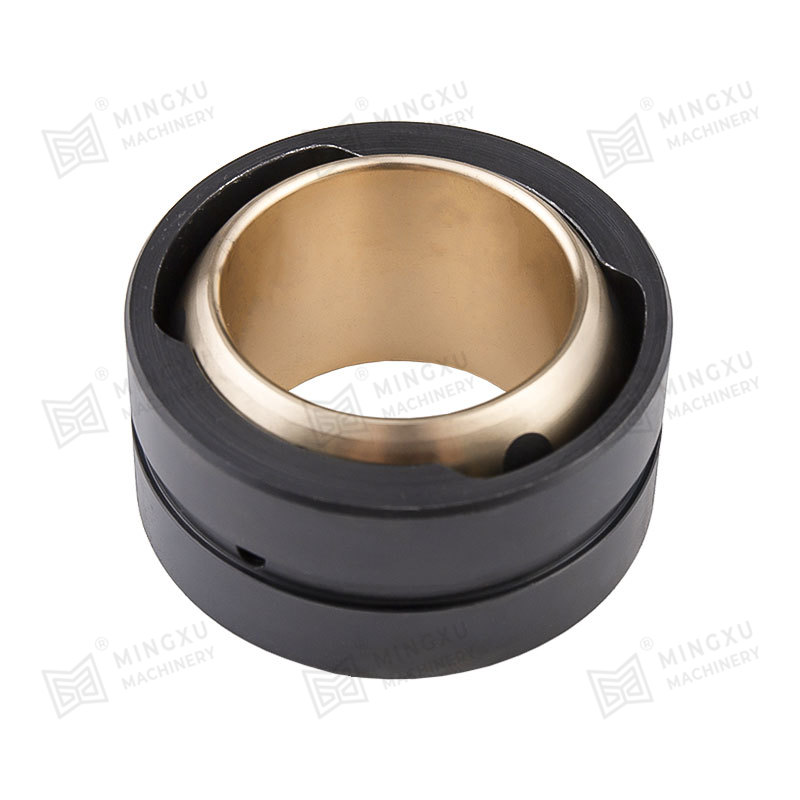
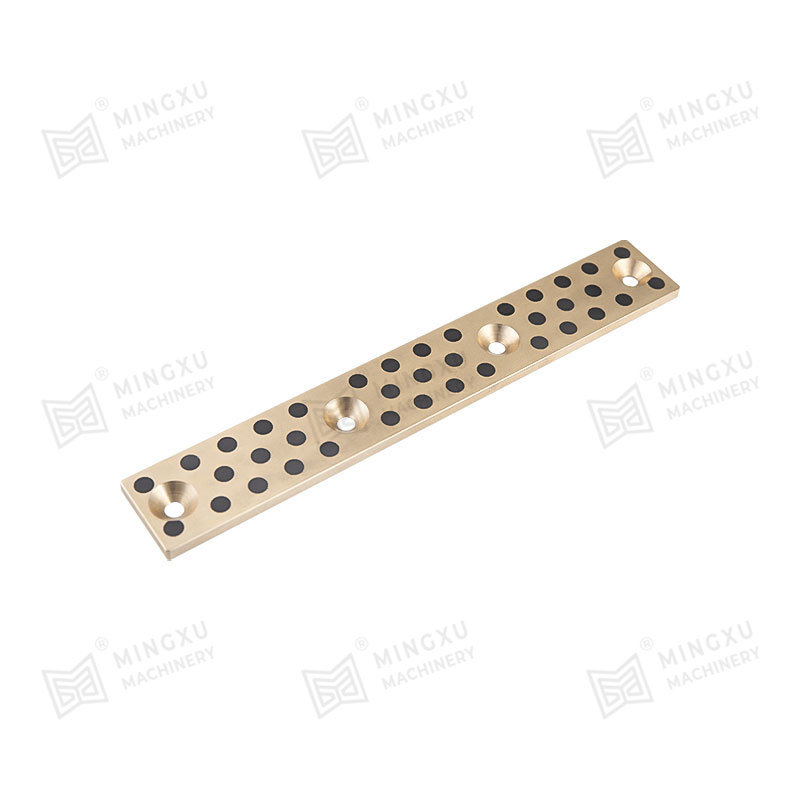
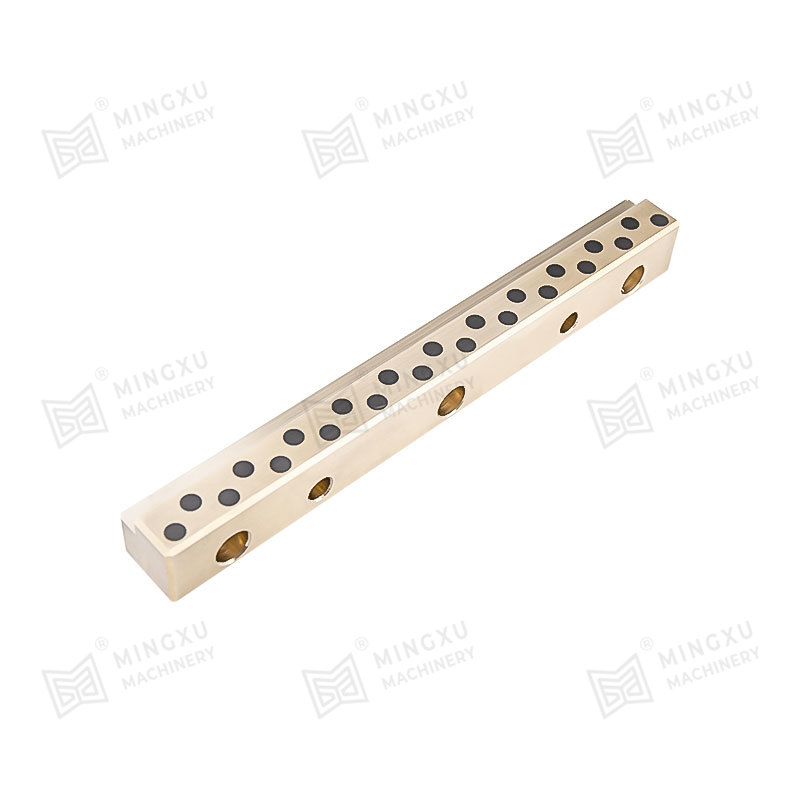
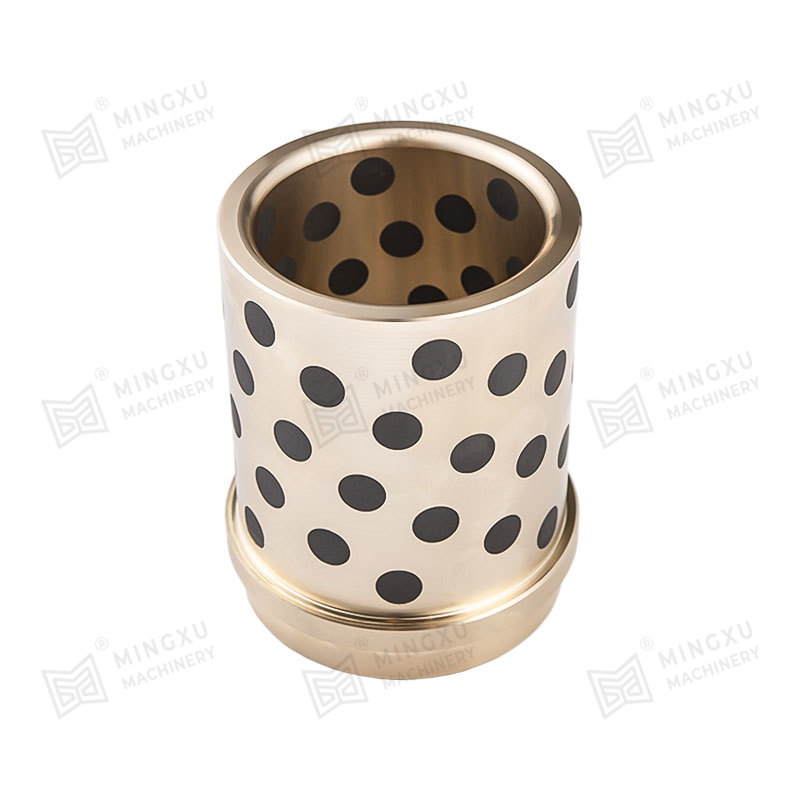
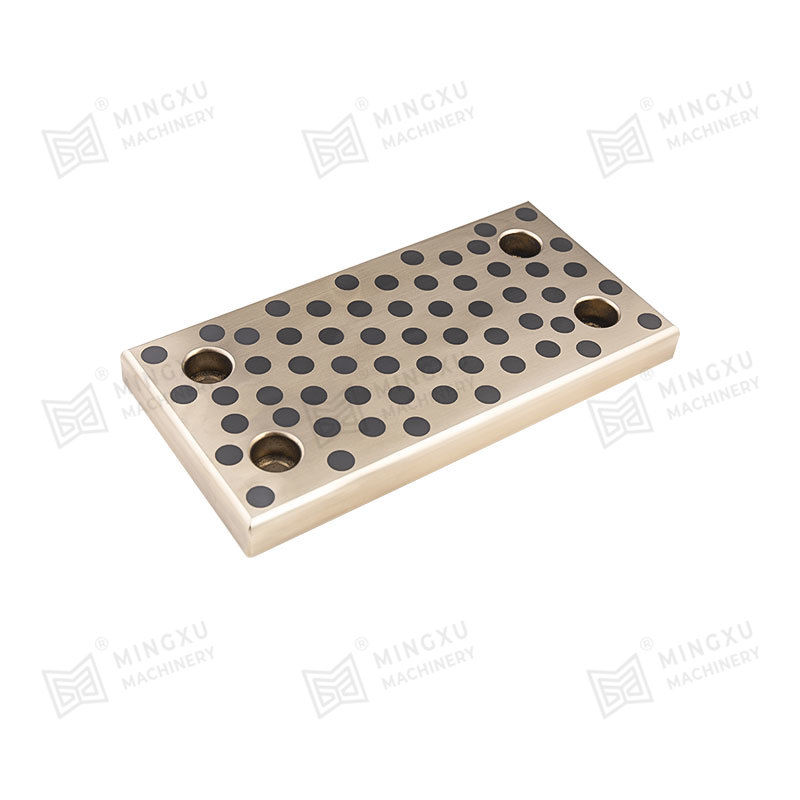
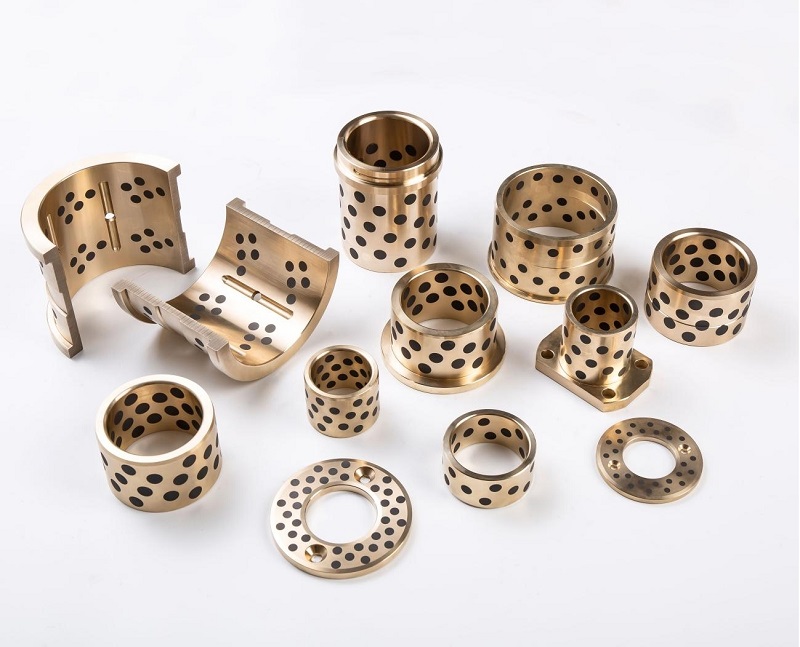
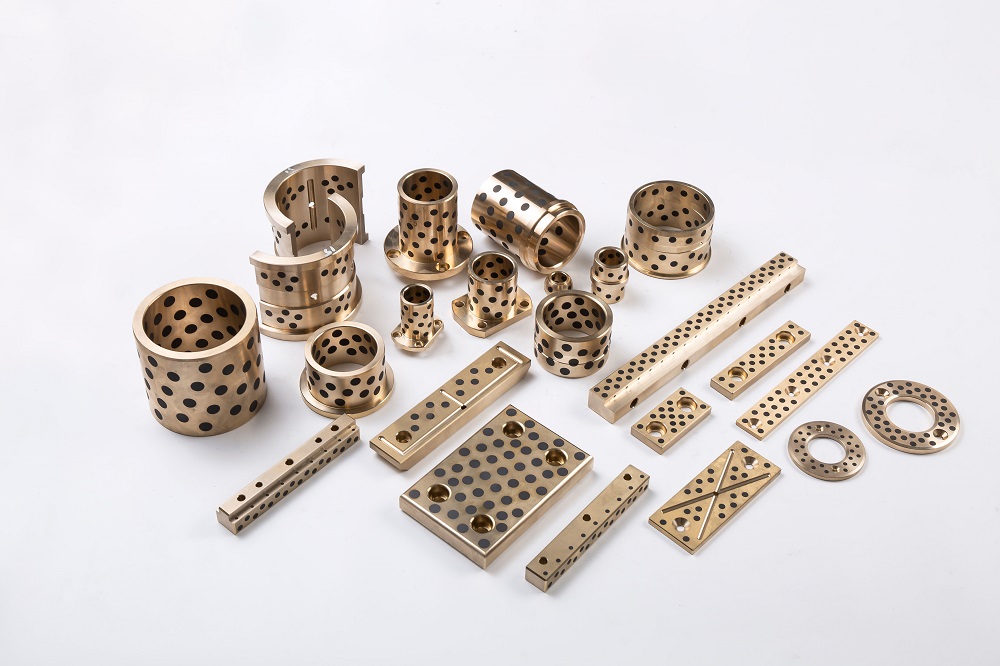
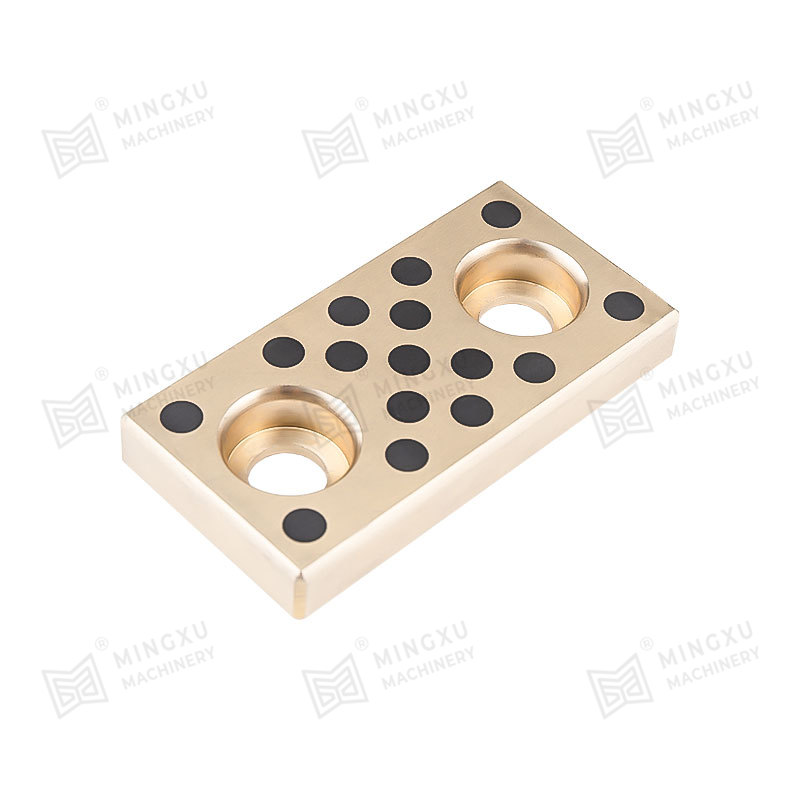
In contrast, Bronze-Based Solid Inlaid Self-Lubricating Spherical Bearings are designed to function effectively under such conditions without the need for external lubrication. These bearings consist of a bronze alloy matrix, often using materials such as tin-bronze or aluminum-bronze for their high strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. Into this bronze matrix, solid lubricant plugs—typically made of graphite, molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂), or polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)—are embedded in a uniform and strategically distributed pattern.
As the bearing operates, the solid lubricant is gradually transferred from the inlaid plugs to the contact surfaces through a self-replenishing mechanism. This process ensures a consistent, low-friction interface even under dry running conditions or during start-stop motion. In angular or oscillating movement, where boundary lubrication dominates and where traditional lubricants might be wiped away or fail to redistribute effectively, the solid lubricant continues to function reliably. This greatly reduces the coefficient of friction and minimizes adhesive or abrasive wear mechanisms.
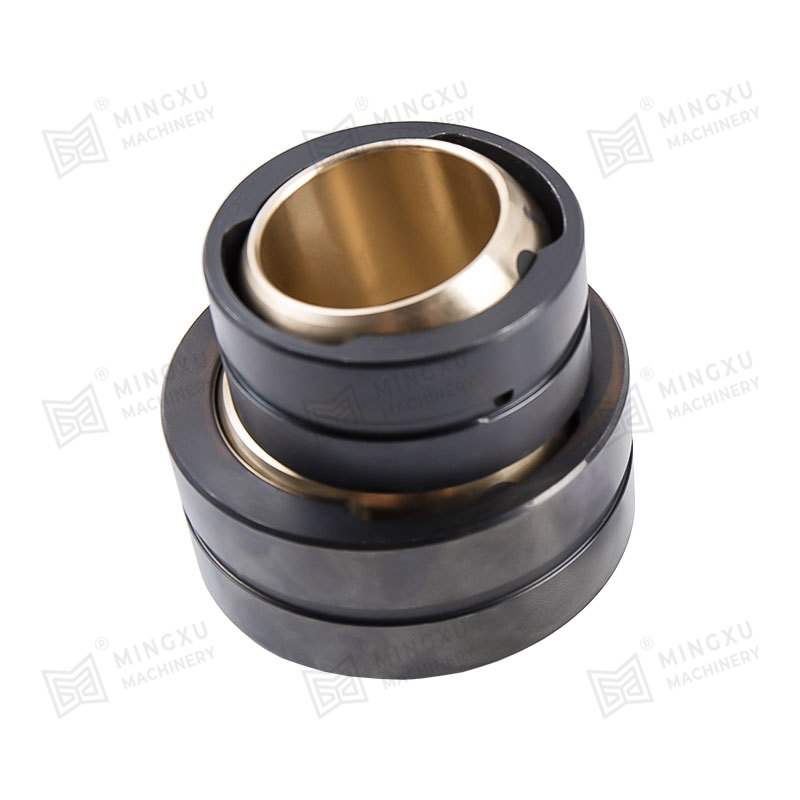

Another significant advantage is the bearing’s ability to operate in environments where conventional lubricants are not feasible, such as in high-temperature settings, vacuum applications, or areas where contamination by oil or grease must be avoided (e.g., food processing or cleanrooms). The bronze base provides mechanical strength and load capacity, while also allowing for effective heat dissipation, which helps prevent thermal degradation of both the bearing and the lubricant.
Furthermore, Bronze-Based Solid Inlaid Self-Lubricating Spherical Bearings are well-suited to compensate for misalignment and shaft deflection due to their spherical contact design. This geometry allows angular motion to occur while maintaining surface conformity and uniform stress distribution, which reduces localized wear and improves the overall stability of the system.
The primary tribological advantages of using Bronze-Based Solid Inlaid Self-Lubricating Spherical Bearings in oscillating or angular motion applications include maintenance-free operation, consistent lubrication without external grease or oil, resistance to lubricant loss under intermittent movement, superior performance under boundary lubrication, and extended service life under harsh operating conditions. These characteristics make them a preferred solution in sectors such as heavy machinery, hydraulic systems, construction equipment, aerospace components, and marine engineering—especially where reliability, durability, and reduced maintenance are critical.


 English
English Español
Español
















Contact Us