Metallurgical machinery operates under extreme conditions of high temperature, heavy loads, and severe dust contamination. Traditional lubricated bearings frequently fail due to oil volatilization, carbon deposition, and clogging, leading to unplanned equipment shutdowns. Self-lubricating bearings, leveraging their inherent lubrication properties, excel in maintenance-free operation, high-temperature resistance, and contamination immunity, making them a critical upgrade choice for metallurgical equipment.
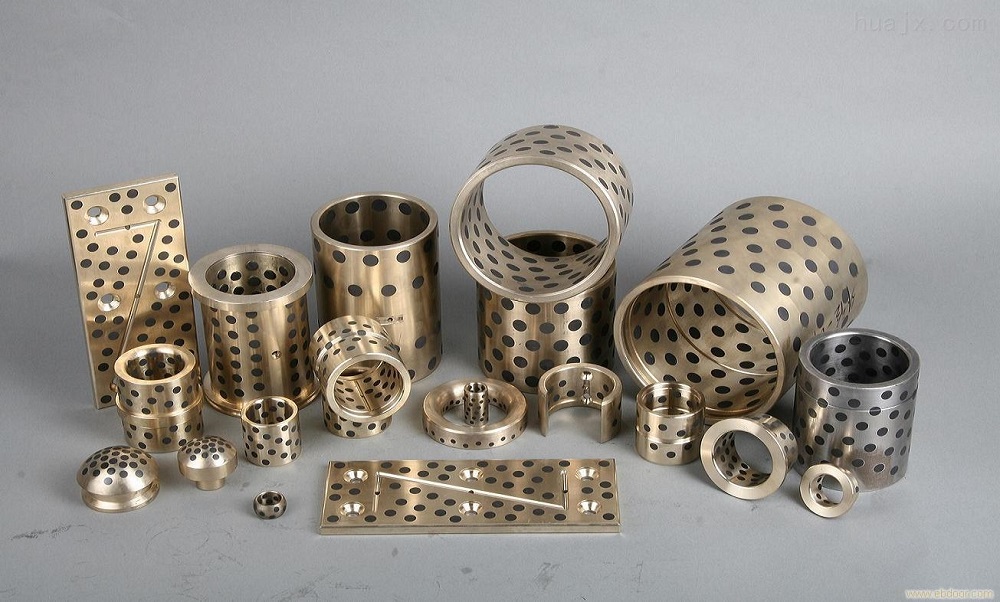

1. Typical Applications in Metallurgical Machinery
1.1 Continuous Casting Machine Segment Guide Rollers
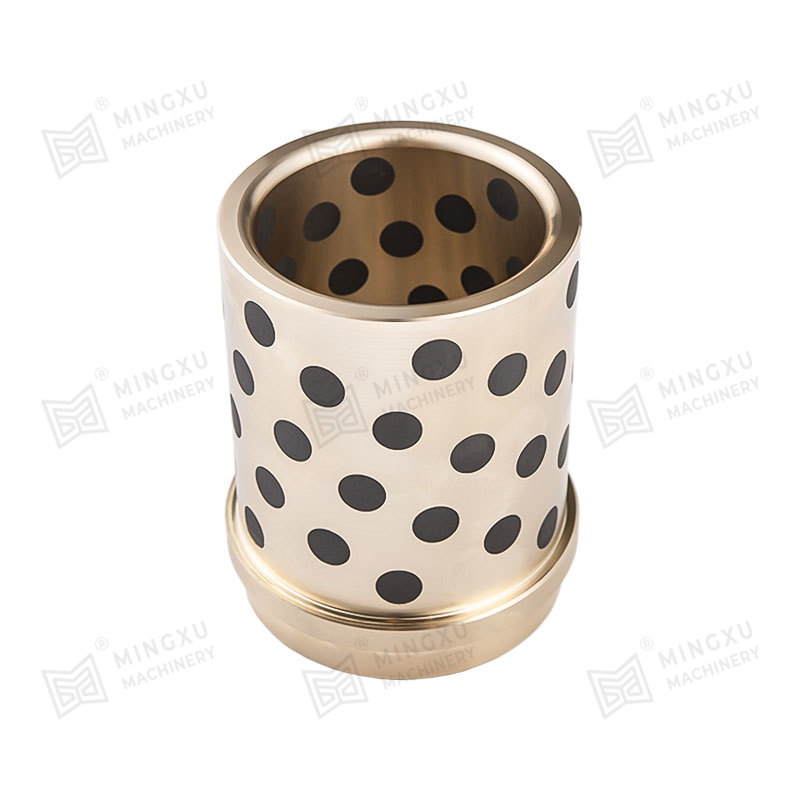
Casting roller temperatures often reach 400–600°C, causing conventional grease-lubricated bearings to carbonize and fail. A domestic steel mill adopted graphite-inlaid copper-based self-lubricating bearings (CuSn10 + 20% graphite). After six months of continuous operation in the secondary cooling zone of a continuous caster, wear was only 0.3 mm—three times longer than grease-lubricated bearings—with no need for oil replenishment.
Data from a Spanish steel mill shows that under high-temperature conditions, these bearings maintain a stable friction coefficient of 0.12–0.15, reducing surface scratching defects in cast slabs by 45%.
1.2 Hot Rolling Mill Roll Bearings
Under rolling pressures exceeding 2,000 tons, metal-based self-lubricating bearings (e.g., steel-backed copper alloy) can withstand surface pressures up to 80 MPa. ThyssenKrupp’s 2,250 mm hot strip mill case study demonstrated that support roll bearing replacement cycles extended from 3 weeks to 12 weeks, saving €1.2 million annually in maintenance costs.
Impact-Resistant Design: A multi-layer composite structure (steel back + copper powder layer + PTFE coating) tolerates peak impact loads of 120 MPa during rolling.
1.3 Blast Furnace Top Distributors
In high-temperature, dusty gas environments (300°C, 200 g/m³ dust concentration), ceramic-based self-lubricating bearings (e.g., Si₃N₄ + BN) excel. Baosteel’s 2022 retrofit showed that distributor bearing life increased from 2 months to 8 months, with dust-wear resistance improving by 60%.
1.4 Cold Rolling Mill Tension Roller Groups
Precision cold rolling demands low-vibration bearings. A Japanese company employed PI (polyimide)-based self-lubricating bearings, achieving vibration values ≤1.5 μm at 1,200 m/min line speed—50% lower than conventional solutions—ensuring strip thickness tolerance of ±0.5 μm.

2. Key Selection Criteria and Technical Specifications
2.1 High-Temperature Resistance
|
Material Type
|
Maximum Temperature
|
Suitable Applications
|
|
Graphite-copper composite
|
500°C (600°C transient)
|
Continuous casting, reheating furnace rollers
|
|
Ceramic bearings
|
800°C
|
Blast furnace gas systems
|
|
Steel-backed PTFE composite layer
|
260°C
|
Cold rolling equipment
|
2.2 Contamination Resistance and Wear Resistance
Metallurgical dust (Fe₃O₄, SiO₂) has a Mohs hardness of 6, requiring materials with surface hardness ≥HB200. Third-party tests show that WC-coated self-lubricating bearings reduce wear rates by 70% compared to standard bearings in environments with 10% alumina dust.
Per ISO 4378-1, metallurgical bearings must pass ≥100-hour quartz sand erosion tests (flow rate 15 m/s).
2.3 Load Capacity Verification
Static Load: Sintered copper-based bearings must withstand static surface pressures ≥100 MPa (GB/T 23894 standard).
Dynamic Load: Rolling mill bearings must meet dynamic load factors ≥3.0 (DIN 732 standard).
2.4 Thermal Expansion Compatibility
Metallurgical equipment often experiences thermal deformation. Control the difference in thermal expansion coefficients between bearings and substrates:
Steel substrate (CTE 12×10⁻⁶/°C) pairs well with copper-based bearings (CTE 18×10⁻⁶/°C).
Ceramic bearings (CTE 3×10⁻⁶/°C) require expansion compensation structures.
2.5 Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
According to the 2023 Metallurgical Machinery Bearing Market Report, self-lubricating bearings cost 30–50% more initially but reduce total maintenance costs by 60%:
A medium-sized steel mill cut continuous casting line maintenance costs from ¥820,000 to ¥350,000 annually.
Rolling mill bearing replacement time dropped from 16 hours to 4 hours per instance.

3. Industry Trends and Selection Recommendations
3.1 Technological Trends
Extreme-Condition Materials: Titanium diboride (TiB₂)-reinforced aluminum bearings withstand 1,000°C and weigh 1/3 of steel.
Smart Condition Monitoring: Sweden’s SKF offers bearings with integrated temperature/vibration sensors for real-time overload or wear alerts.
3.2 Practical Selection Tips
Prioritize products certified to ISO 4378 (sliding bearing testing) and ASTM E228 (thermal expansion coefficient testing).
Increase bearing clearances by 20–30% over standard designs to compensate for thermal expansion in metallurgical applications.
Request vendor-provided dust environment bench test reports (preferably with combined high-temperature wear + impact load testing).
Zhejiang Mingxu Machinery Manufacturing Co., Ltd. has specialized in self-lubricating bearing R&D and manufacturing for over a decade, earning positive feedback from metallurgical machinery clients. For inquiries, contact: [email protected].


 English
English Español
Español



















Contact Us