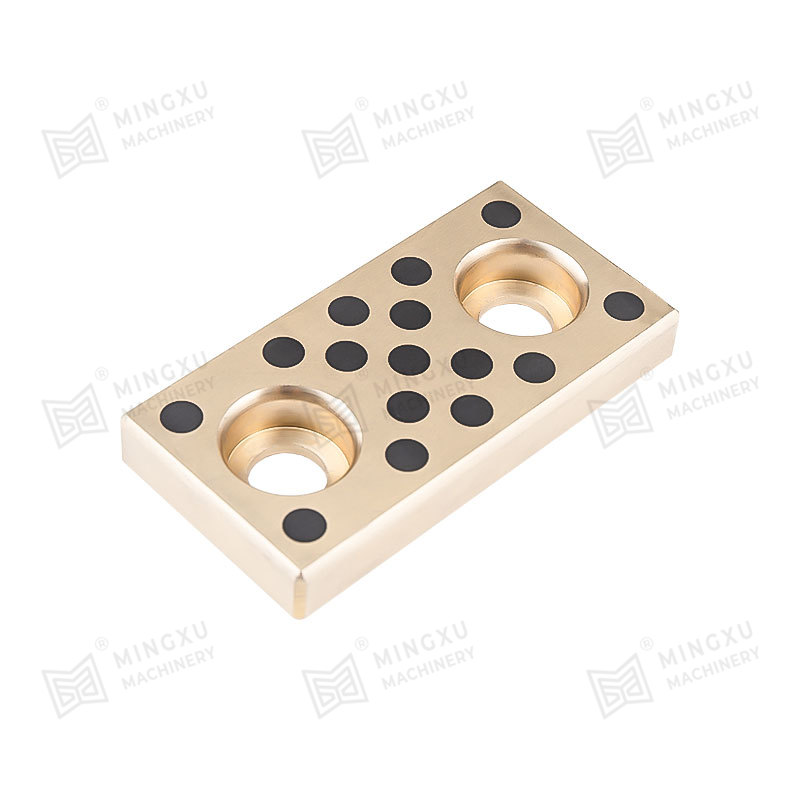
The microstructure of porous metal-based self-lubricating bushings plays a critical role in oil retention and long-term wear resistance by determining how lubricant is stored, released, and redistributed during operation. Here’s how different aspects of the microstructure influence performance:
1. Pore Size & Distribution
-
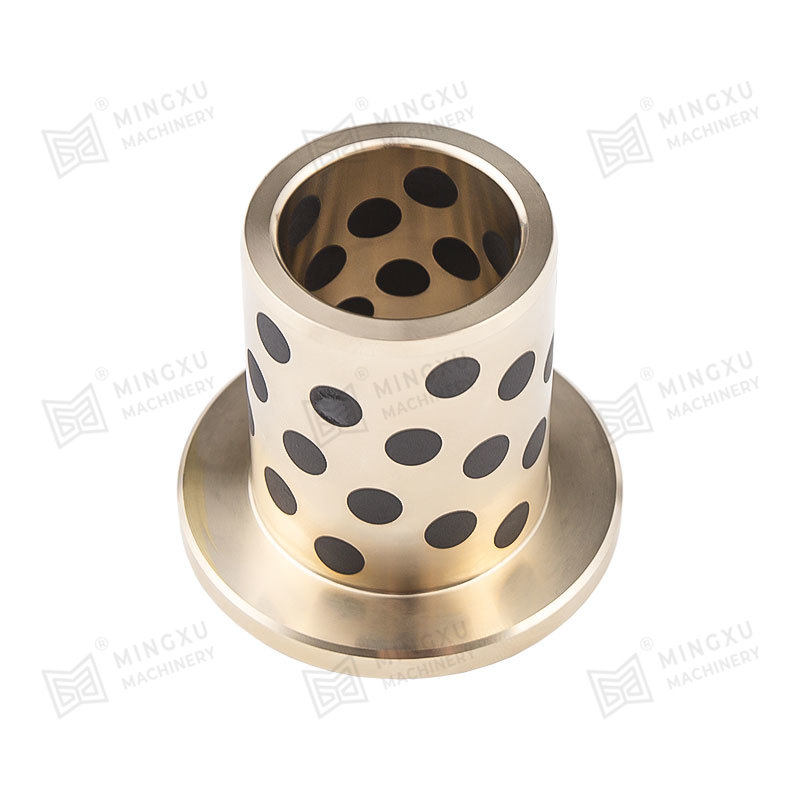
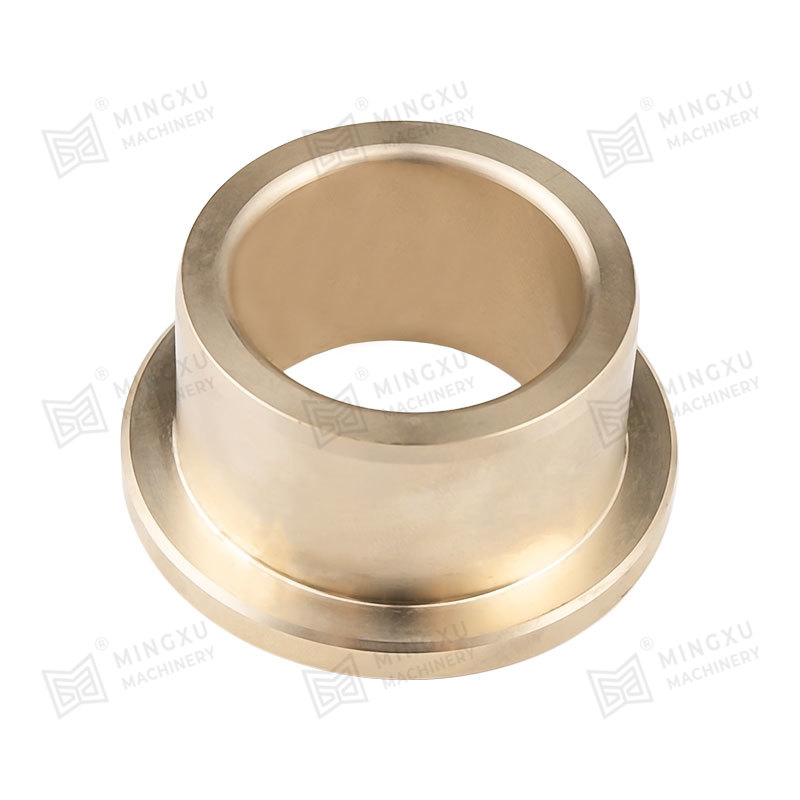
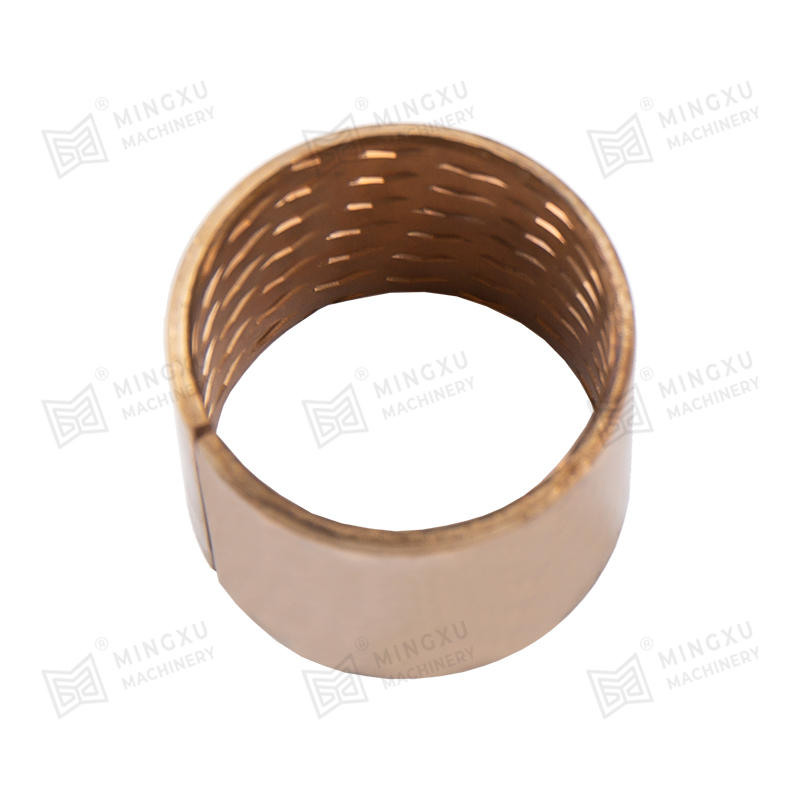
Oil Retention: The interconnected porosity in sintered metal bushings (such as bronze or iron-based materials) allows for the absorption and retention of lubricants. A uniform, well-distributed pore network ensures consistent oil distribution over the contact surface.
-
Wear Resistance: If the pores are too large, lubricant depletion can occur more quickly, reducing effectiveness over time. On the other hand, excessively small pores may hinder the capillary action required for efficient oil release.
2. Pore Volume Fraction (Porosity Level)
-
A higher porosity level (typically 15-30%) increases oil storage capacity, extending lubrication intervals and reducing maintenance needs.
-
However, too high porosity may weaken the structural integrity of the bushing, leading to mechanical failure under high loads.

3. Lubricant Release Mechanism
-
Capillary Action: The porous structure enables oil to move through the material due to capillary forces, ensuring a steady self-lubrication process.
-
Temperature-Activated Lubrication: When the bushing operates, frictional heat causes thermal expansion, allowing oil to be released more effectively onto the bearing surface.
-
Dynamic Lubricant Flow: During high-speed applications, the lubricant is drawn toward wear areas, reducing friction and wear rates dynamically.
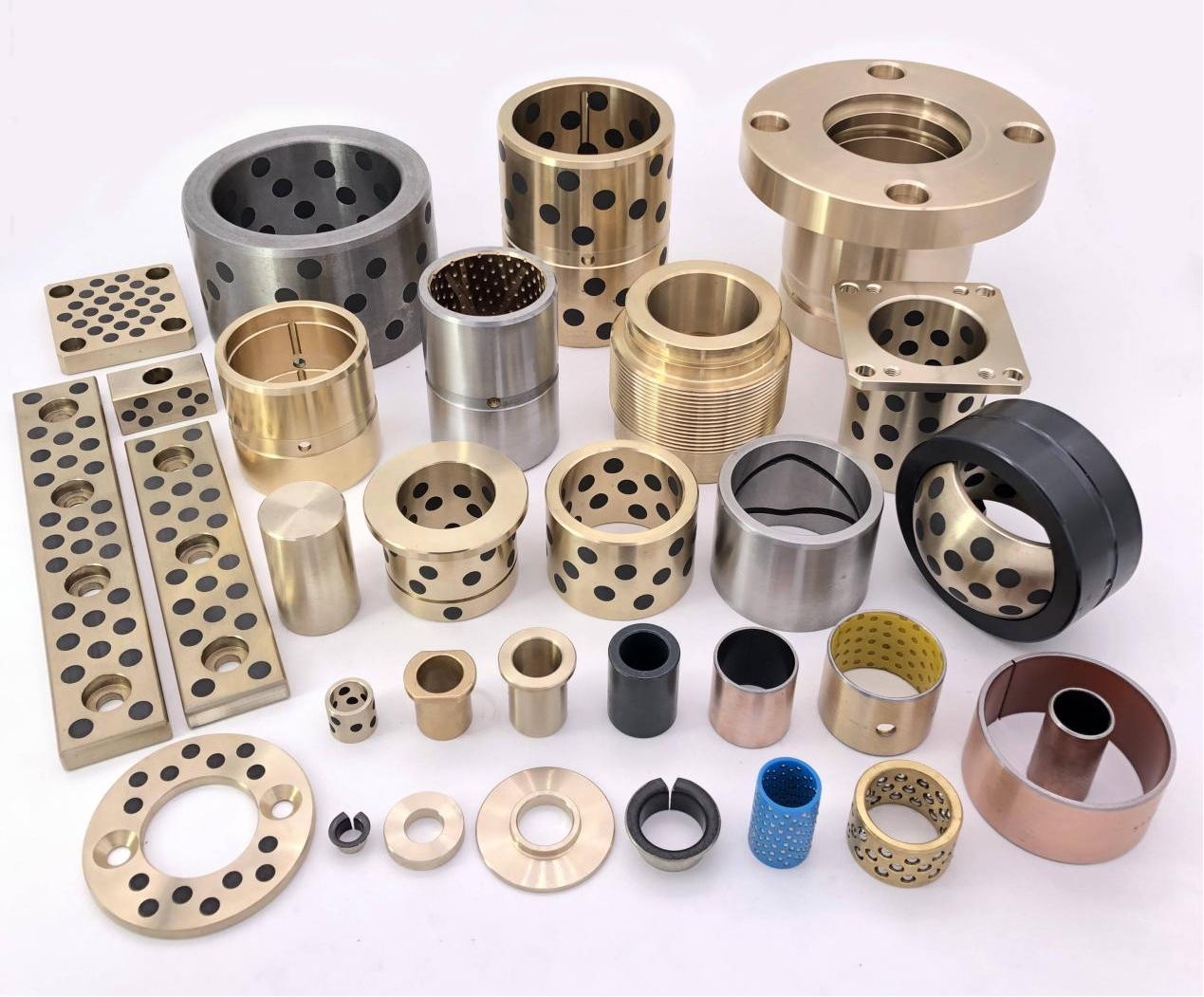
4. Material Composition & Hardness
-
Bronze-based sintered bushings (e.g., Cu-Sn or Cu-Pb alloys) exhibit superior anti-friction and wear resistance due to their ability to retain oil effectively.
-
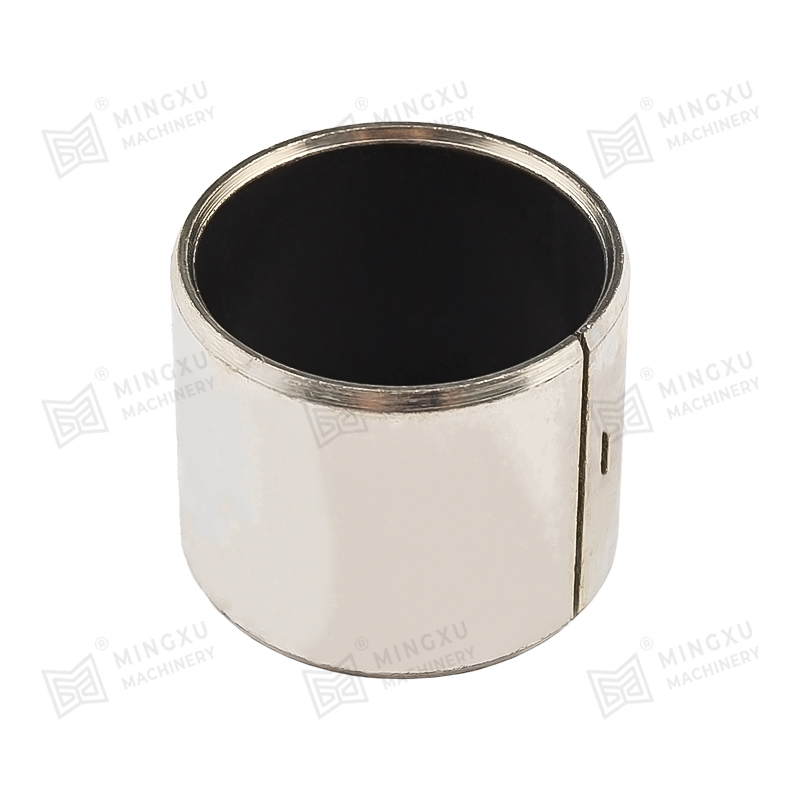
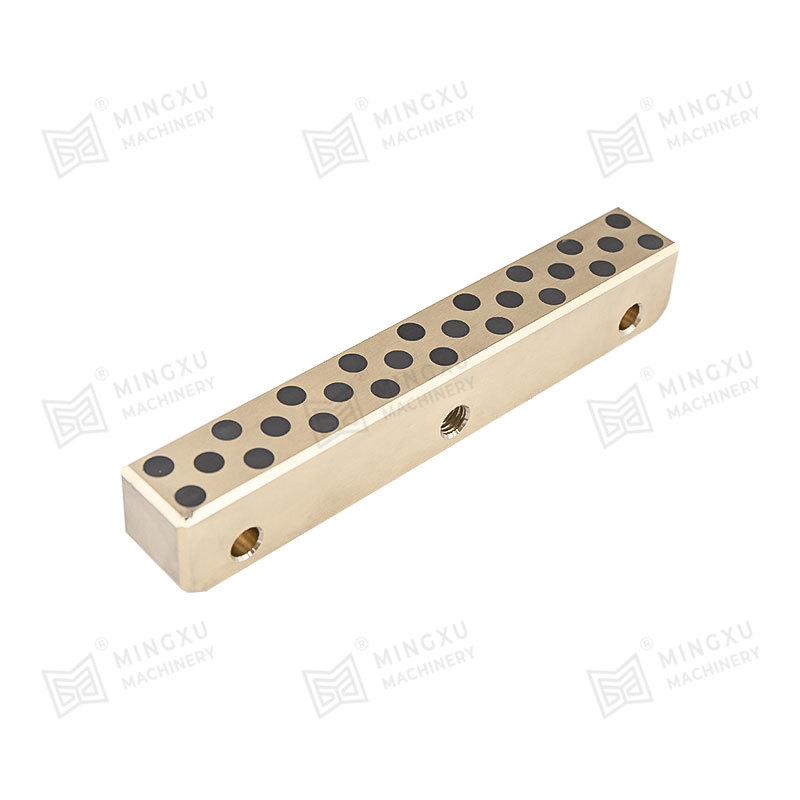
Iron-based porous bushings tend to be harder but may require additional impregnating agents (such as PTFE or graphite) to improve self-lubrication.
5. Surface Interaction & Film Formation
-
The microstructure influences how a stable lubricant film forms between the bushing and the shaft.
-
A well-optimized porosity level ensures a continuous oil film, reducing direct metal-to-metal contact and enhancing wear resistance over long-term operation.


 English
English Español
Español















Contact Us