In many industrial and mechanical applications, the choice between grease bearings and oil bearings significantly impacts the performance, durability, and maintenance requirements of a system. Each lubrication method comes with its own advantages and limitations, depending on the working environment, load conditions, and operational speeds. While grease bearings are widely used for their ease of application and lower maintenance needs, oil bearings are favored in situations requiring more efficient heat dissipation and high-speed performance. However, with the advancement of tribological materials, a third alternative — the oilless bearing — is gaining attention for its unique capabilities.
Understanding Grease Bearings and Oil Bearings
Grease bearings are lubricated using a semi-solid lubricant, which stays in place and provides a lasting protective film on the bearing surfaces. This type of lubrication is ideal for applications where frequent maintenance is not practical, as the grease does not require constant replenishment. Grease also helps to seal the bearing from external contaminants such as dust, moisture, or chemicals, making it suitable for moderate-speed and moderate-load conditions.
On the other hand, oil bearings are lubricated with liquid oil, which circulates through the bearing components, reducing friction and carrying away heat. Oil is more suitable for high-speed and high-temperature applications, as it provides better cooling and more consistent film thickness. However, oil lubrication systems are generally more complex, often requiring pumps, reservoirs, and filtration systems. This increases both the initial setup cost and the ongoing maintenance demands.
Comparing Performance in Practical Use
When deciding whether a grease bearing is better than an oil bearing, the answer largely depends on the specific operational context. For example, in low- to medium-speed machinery with limited access for routine maintenance — such as electric motors or agricultural equipment — grease bearings offer a simple and reliable solution. In contrast, for high-speed spindles, turbines, or precision machinery, oil bearings are typically superior due to their better thermal management and lubrication properties.
Yet, both types of bearings have inherent limitations. Grease can dry out or become contaminated over time, leading to increased wear. Oil systems can leak or require constant monitoring to maintain correct oil levels and cleanliness. In environments where maintenance is difficult or where contamination must be minimized — such as food processing, medical equipment, or cleanroom machinery — these issues become even more critical.
The Role of Oilless Bearings in Modern Applications
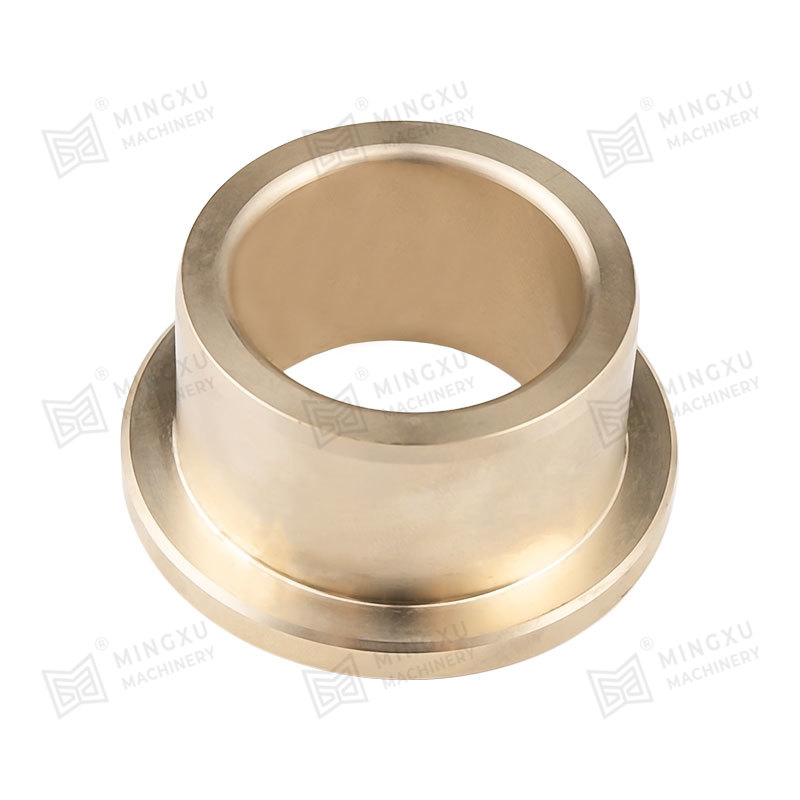
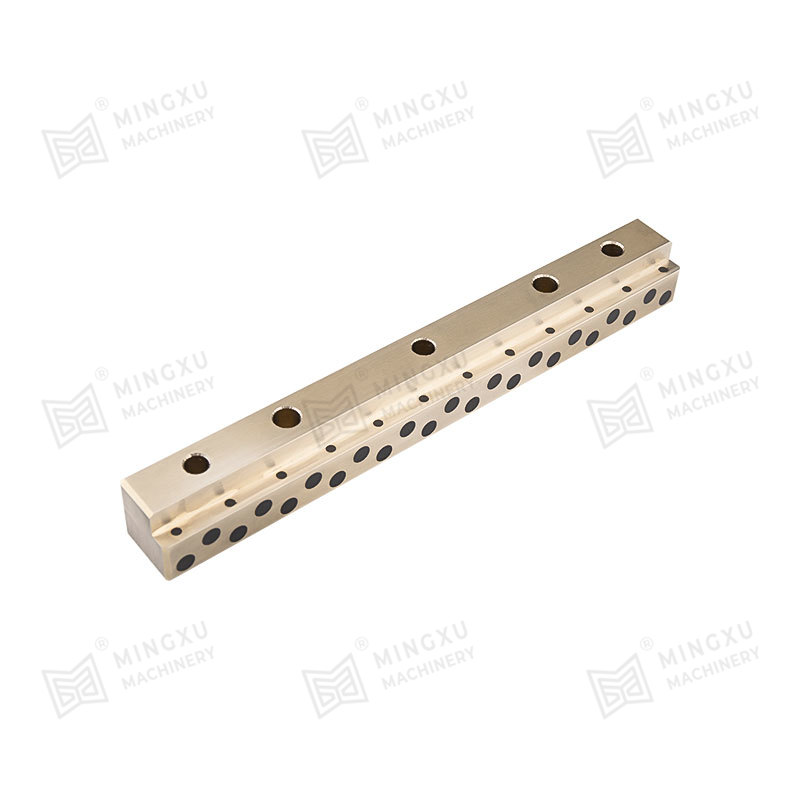
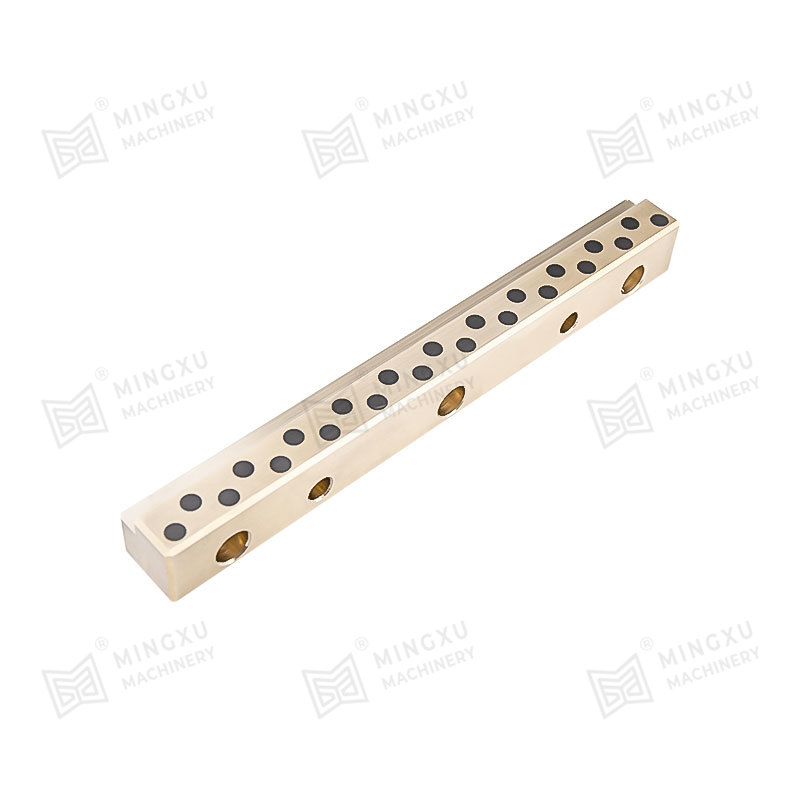
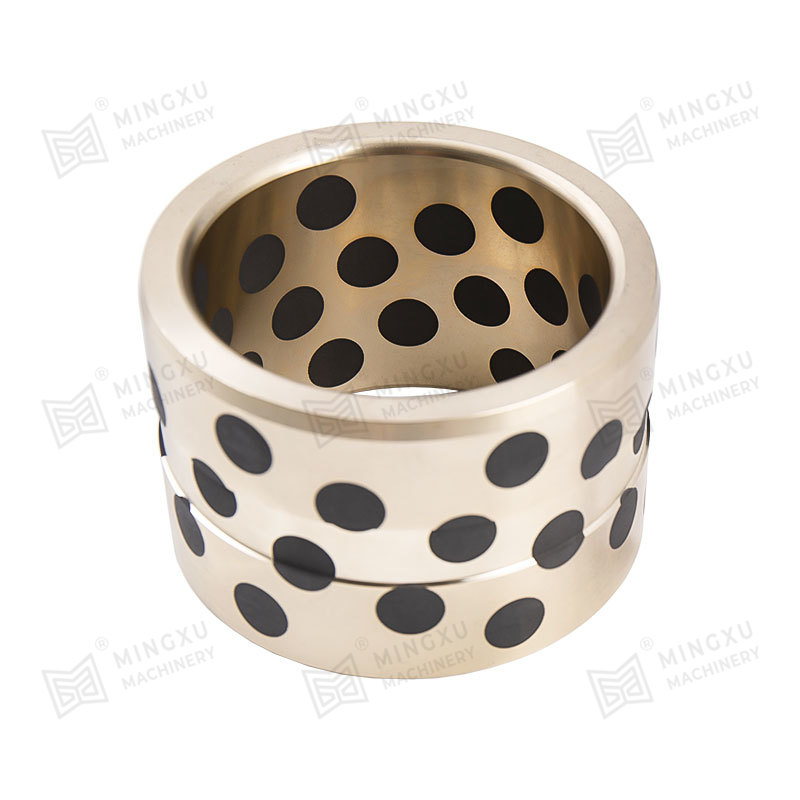
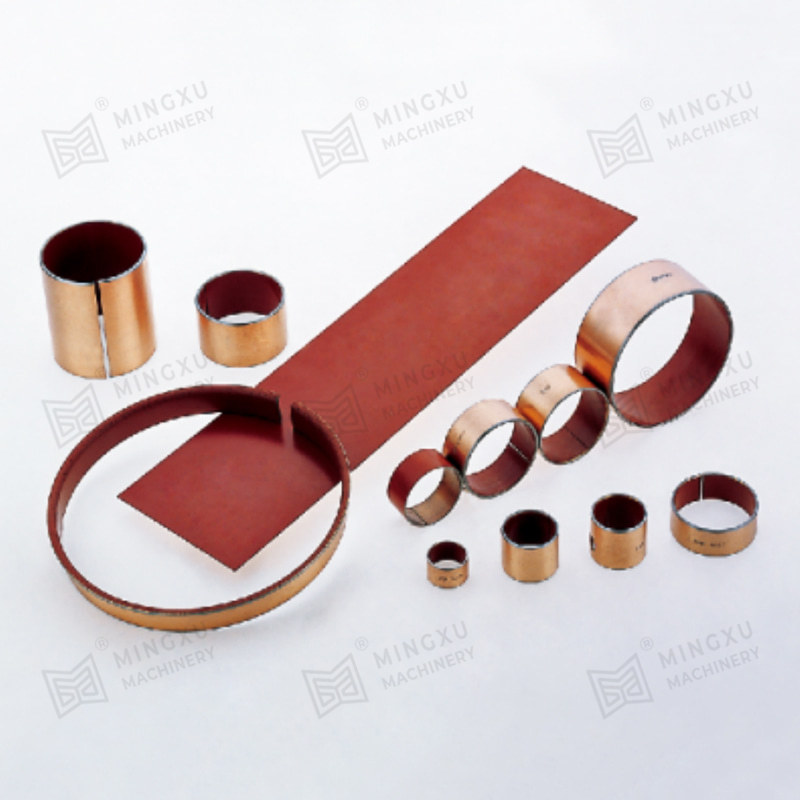
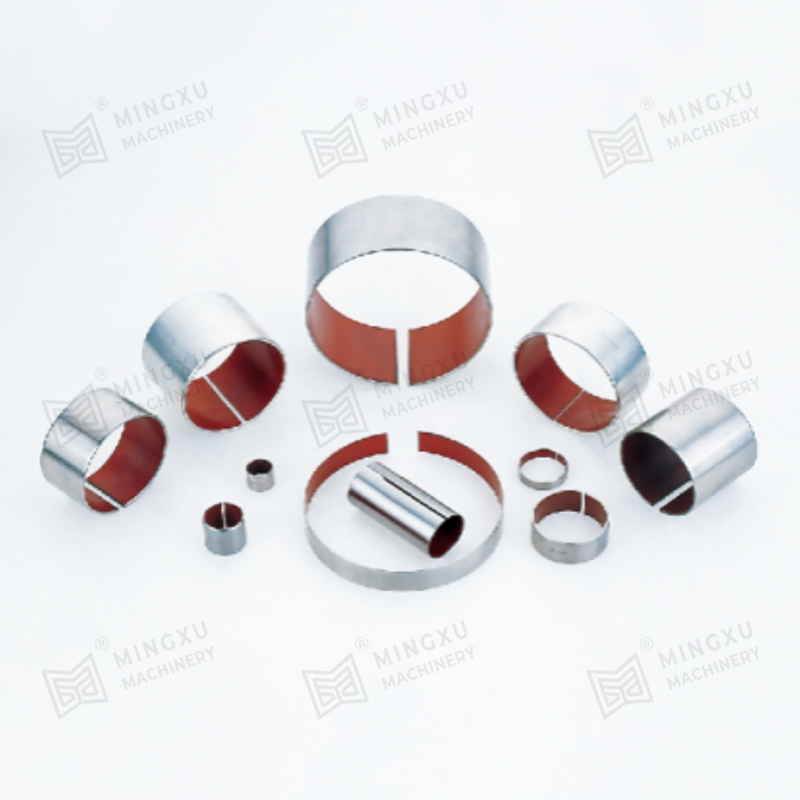
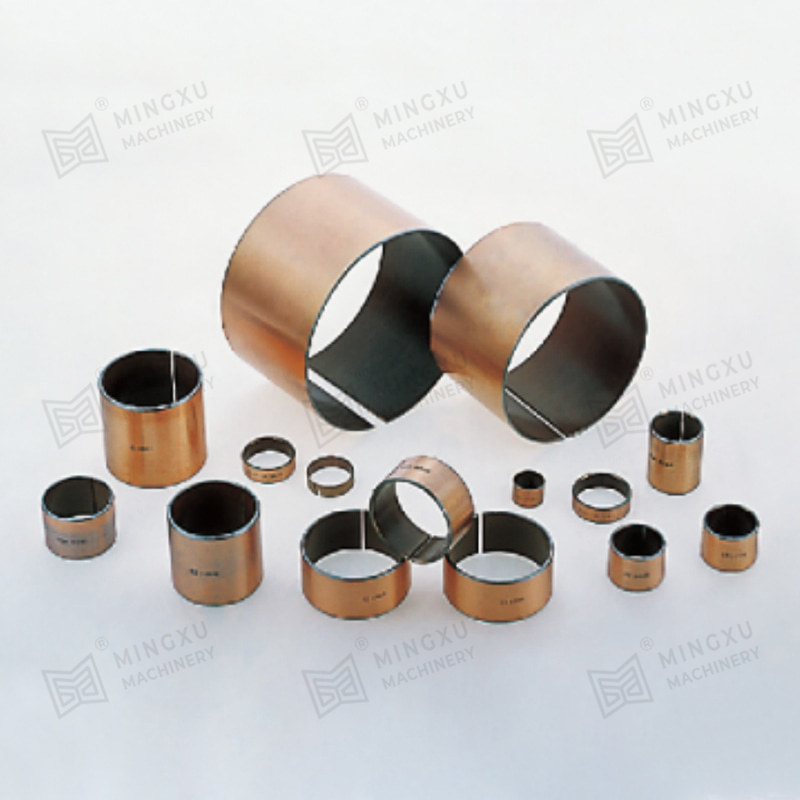
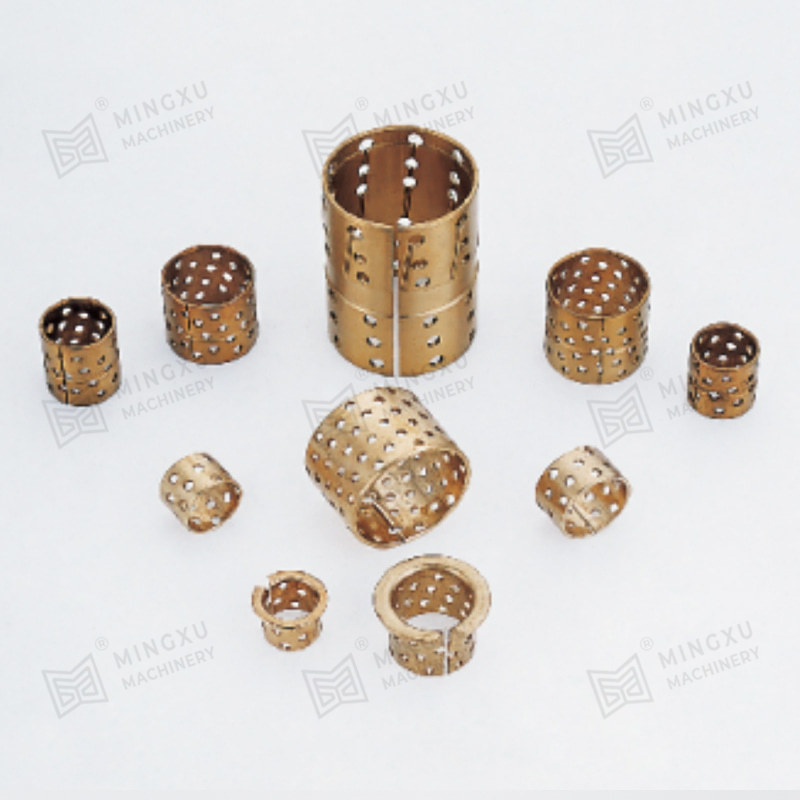
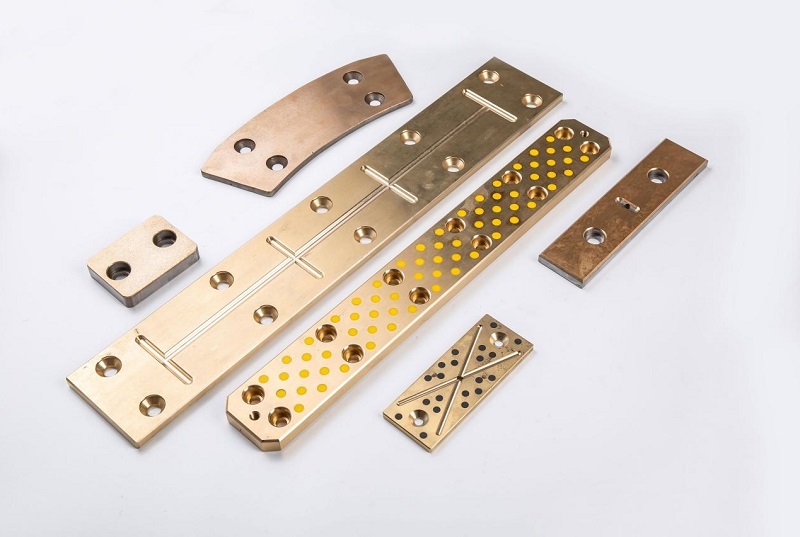
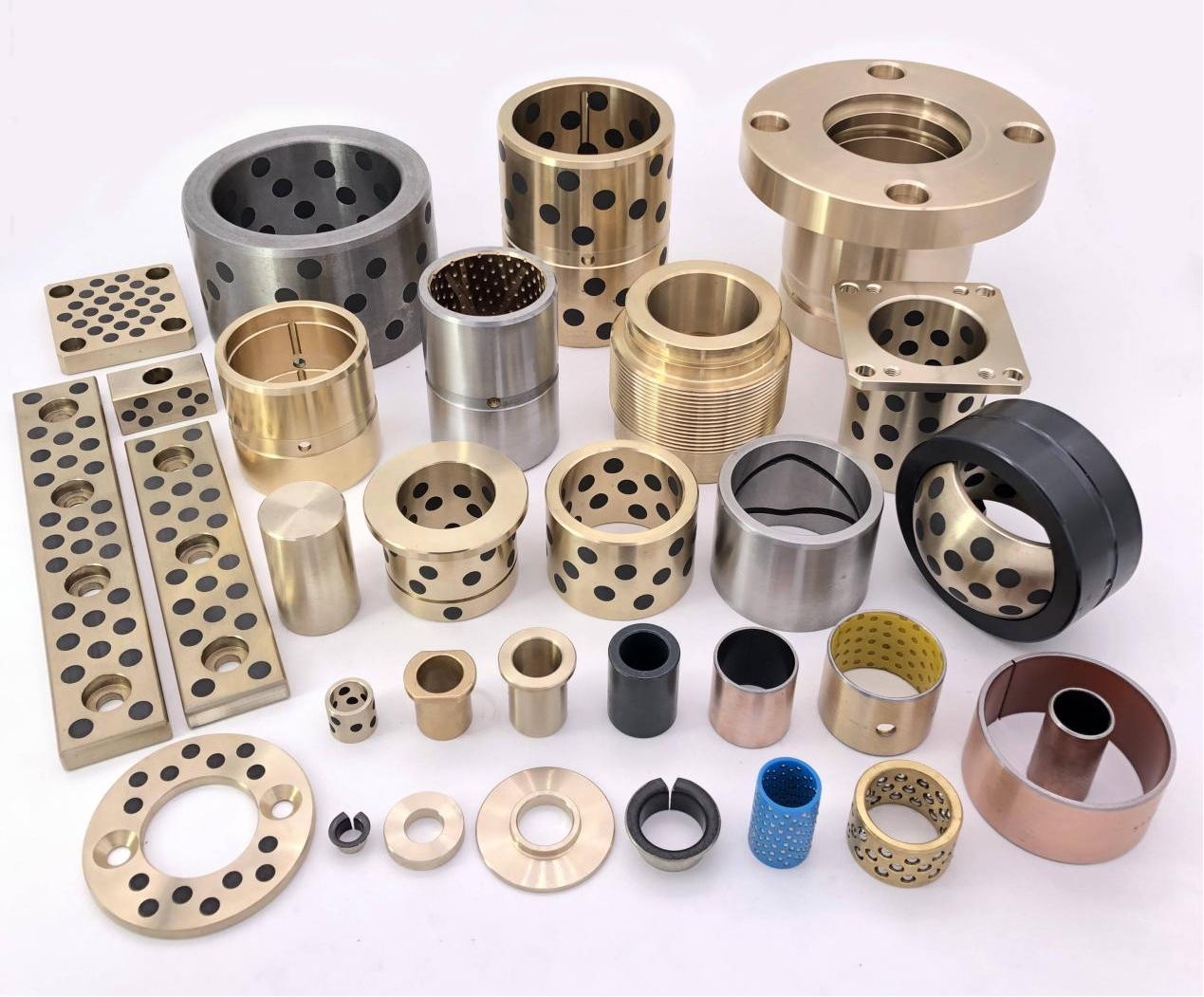
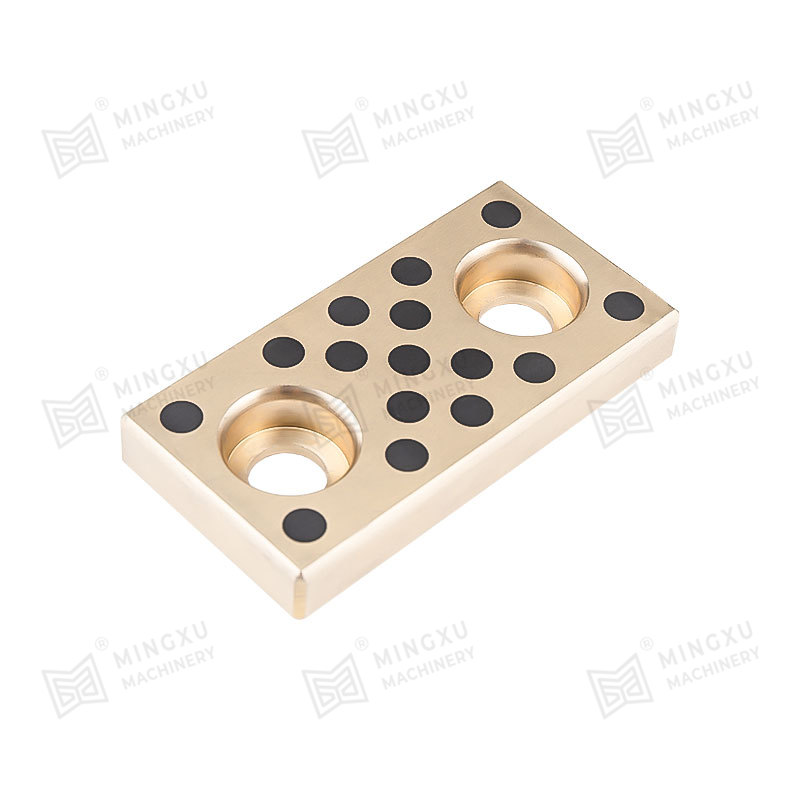
This is where oilless bearings present a compelling alternative. Oilless bearings are designed to operate without external lubrication, thanks to materials embedded with solid lubricants such as graphite, PTFE, or other specialized compounds. These self-lubricating bearings reduce maintenance needs, eliminate the risk of lubricant leakage, and offer long service life even in harsh environments.
Oilless bearing technology has seen wide adoption in industries such as automotive manufacturing, aerospace, textile machinery, and packaging equipment. They are particularly valued for applications involving high loads, intermittent motion, or environments where traditional lubrication would attract dust and debris. Moreover, oilless bearings are often made from composite materials or bronze alloys with embedded lubricants, offering excellent resistance to wear, corrosion, and high temperatures.
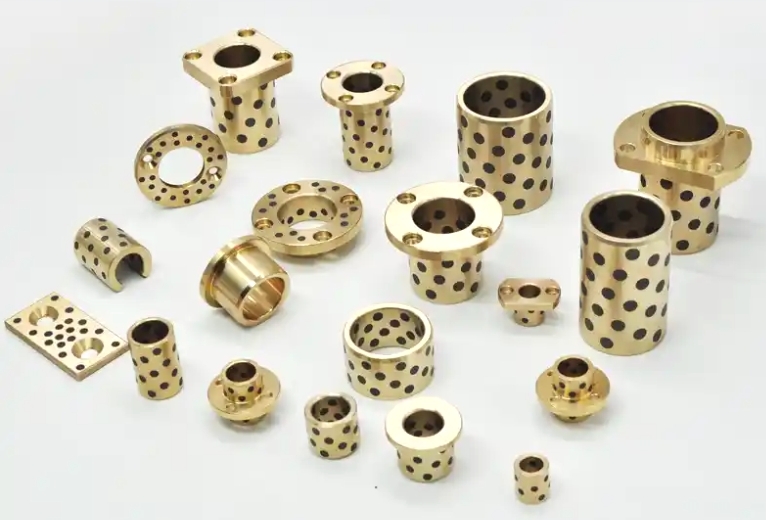

In comparing grease bearings and oil bearings, it is clear that each has its strengths based on specific application requirements. Grease bearings are cost-effective and simple to maintain, while oil bearings deliver superior performance under demanding conditions. However, with increasing demands for reliability, reduced maintenance, and environmental cleanliness, oilless bearings have emerged as a robust and efficient solution for many modern applications. Their ability to perform without additional lubrication makes them a strategic choice for engineers seeking long-term performance with minimal intervention.
As technology continues to evolve, and as industries push for more sustainable and maintenance-free designs, the role of oilless bearings will only grow in relevance and application scope.


 English
English Español
Español















Contact Us