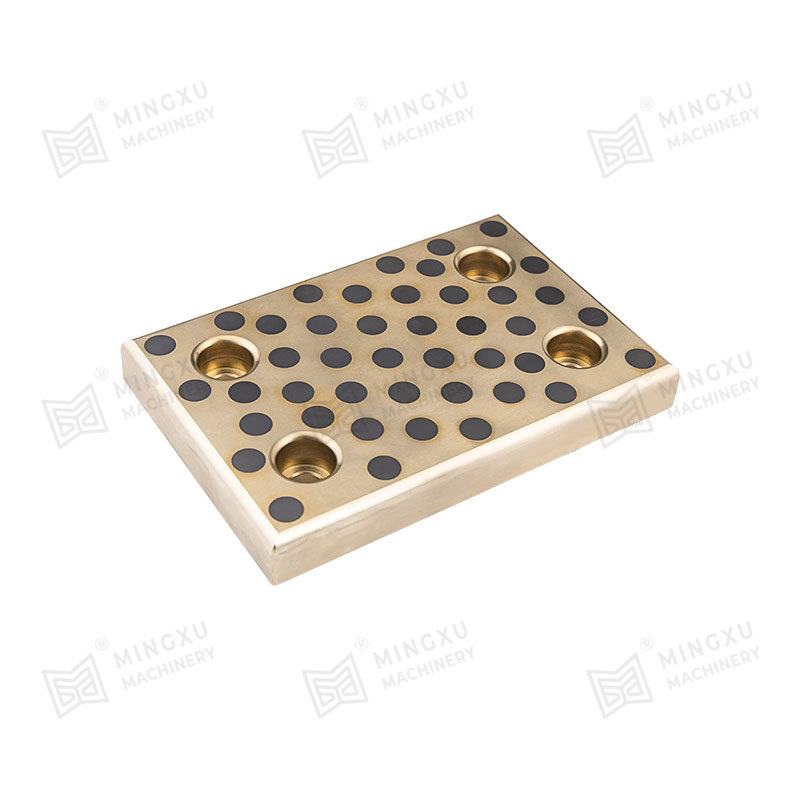
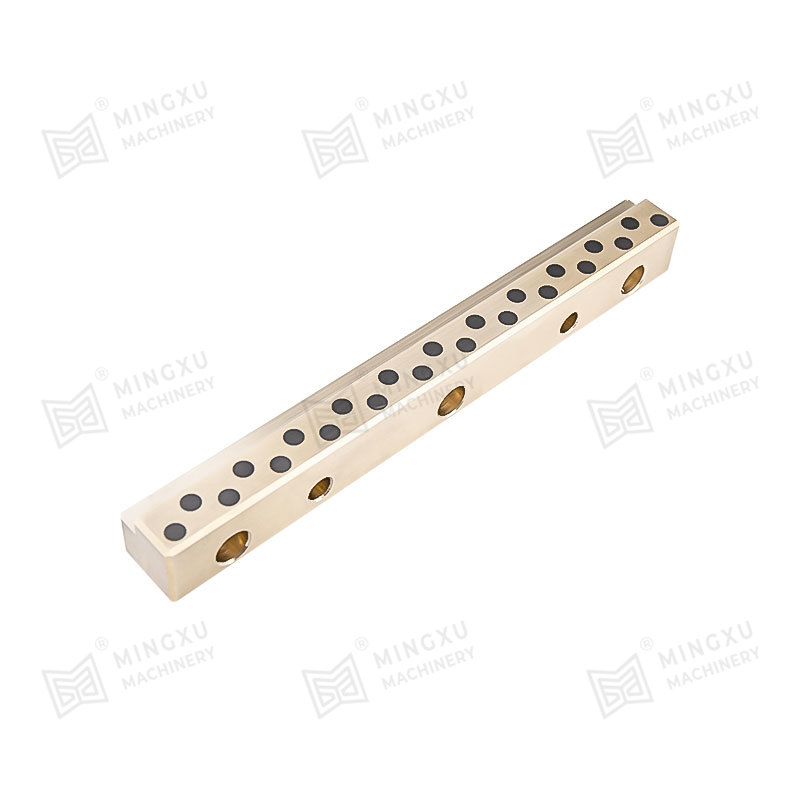
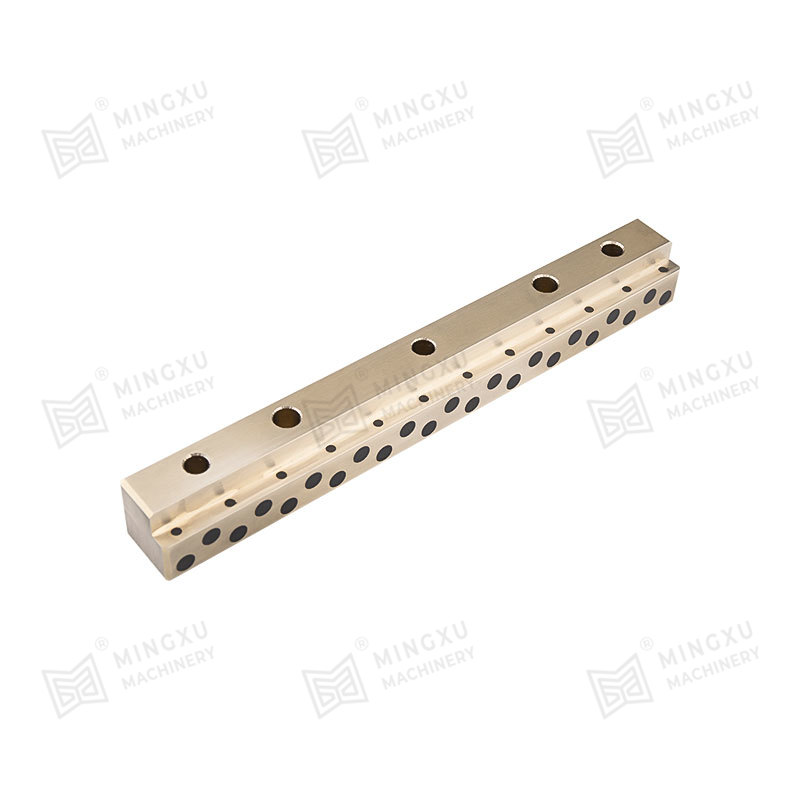
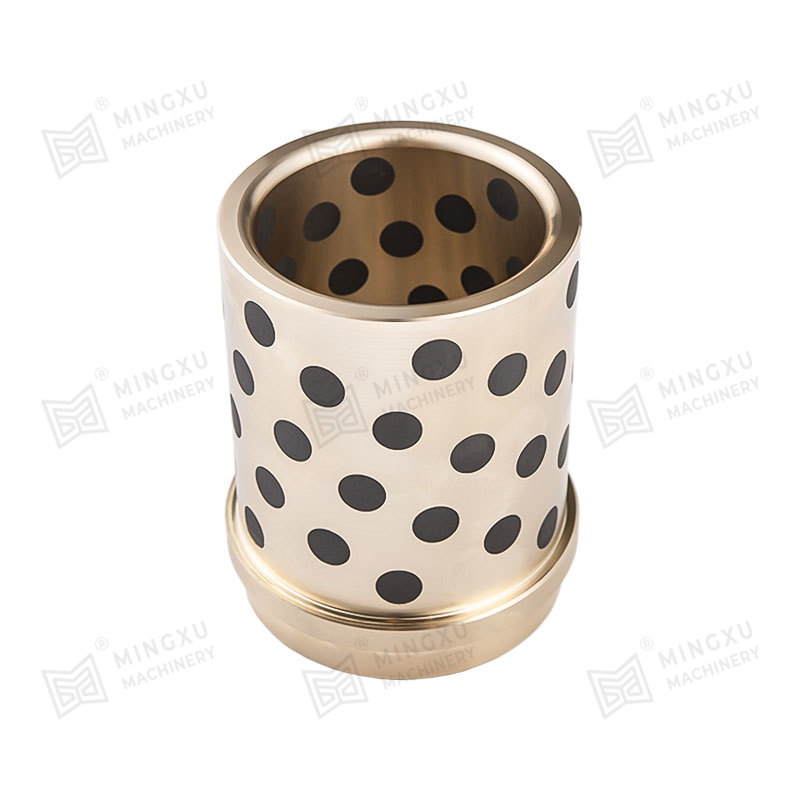
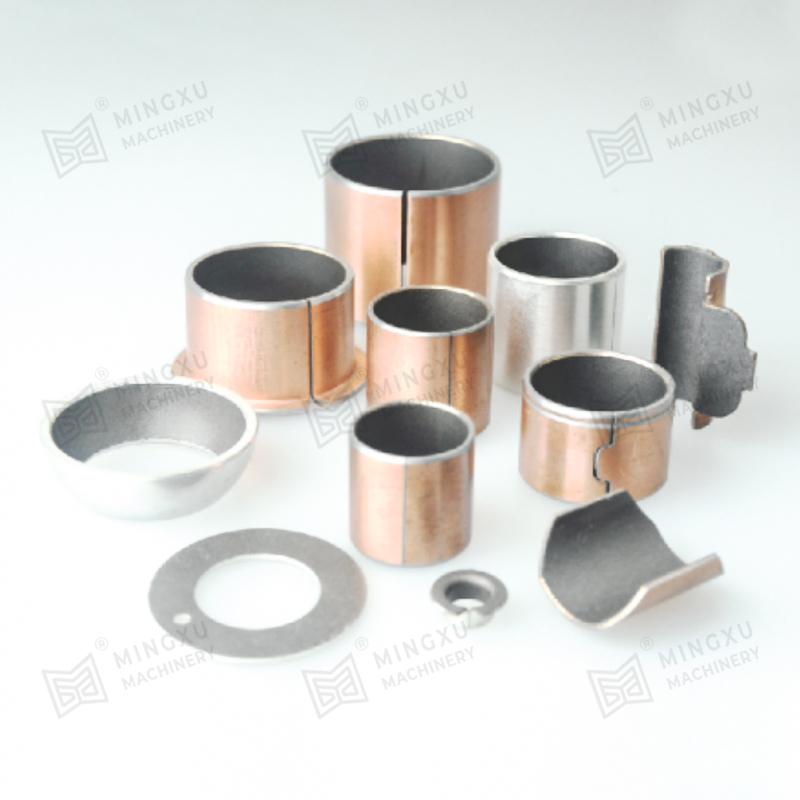
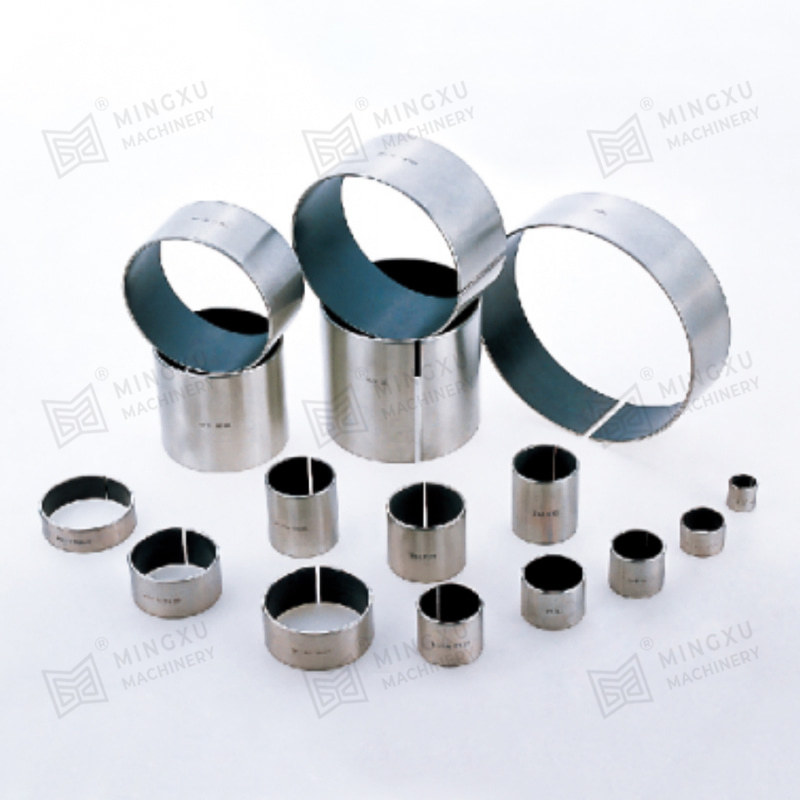
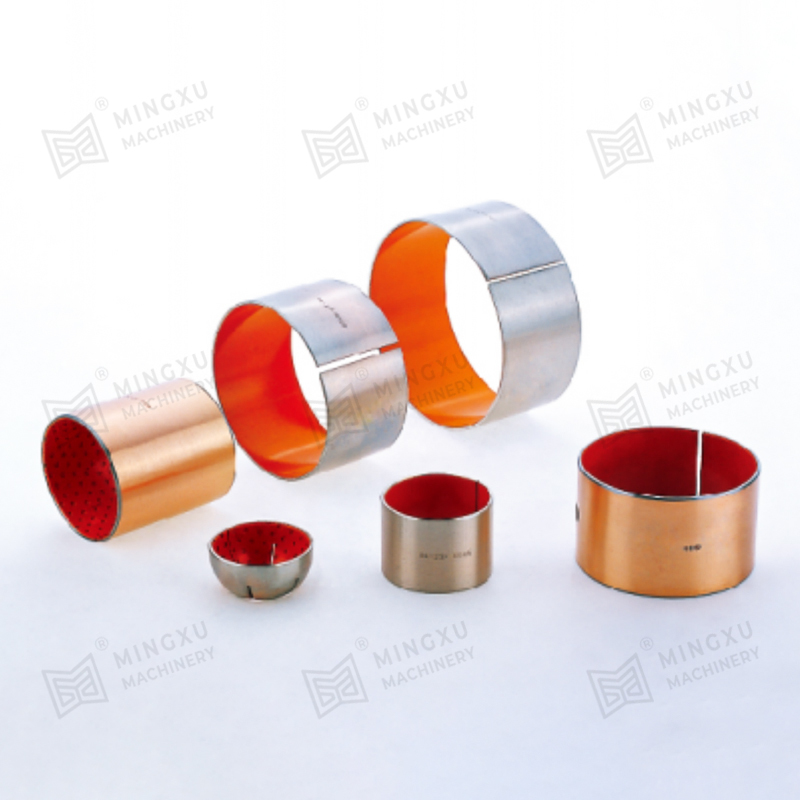
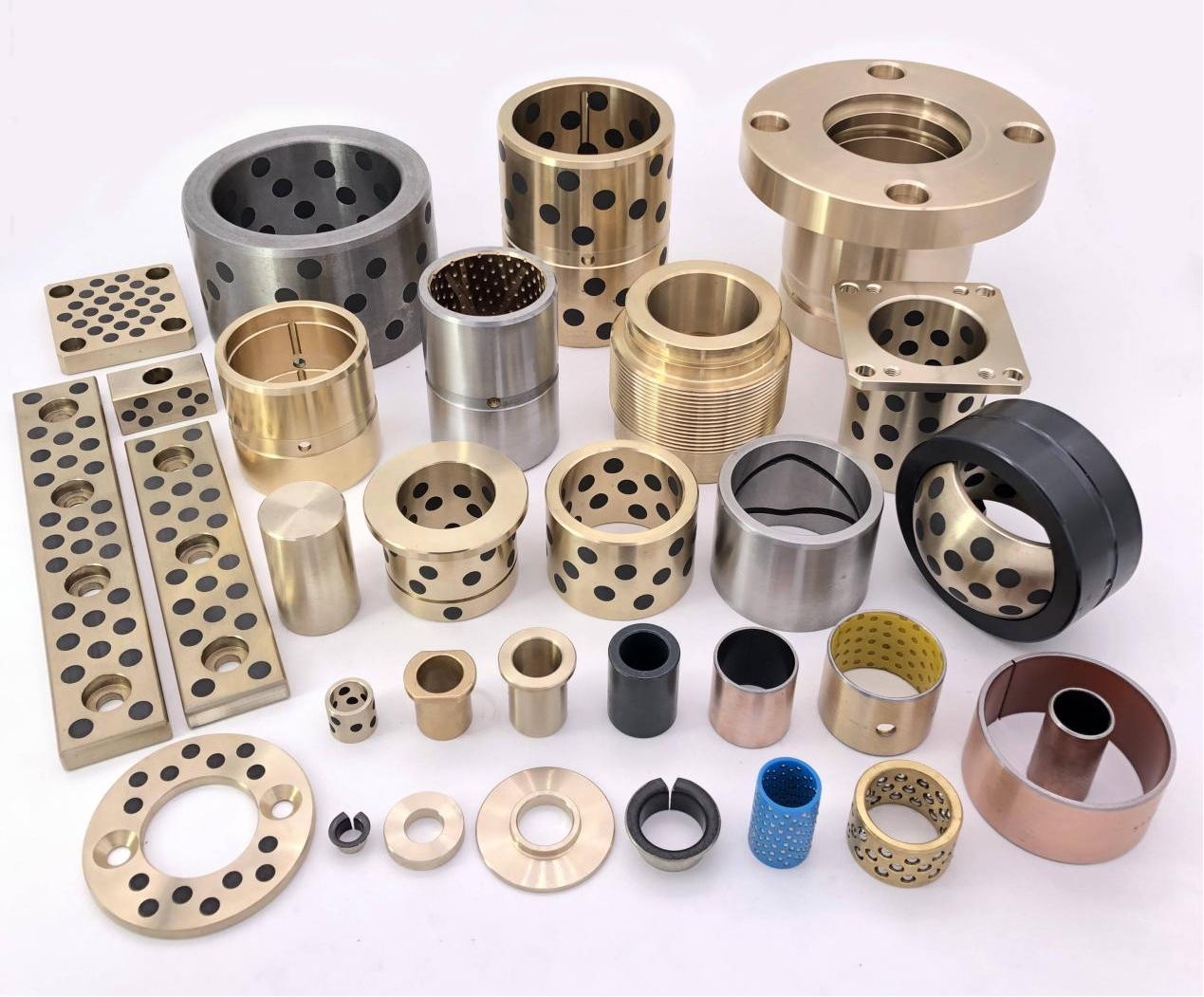
Bronze bushings are a fundamental component in many types of machinery, providing low-friction support between rotating or sliding parts. Known for their durability, corrosion resistance, and high load-bearing capacity, bronze bushings are widely used in automotive, industrial, agricultural, and construction equipment. However, despite their robustness, they are subject to wear over time, and understanding their types, wear mechanisms, and proper maintenance strategies is crucial for long-term performance.
Bronze bushings come in a variety of types, each designed to meet specific operational requirements:
-
Plain Bronze Bushings: These are solid bronze cylinders with no additional features. They are commonly used in low- to medium-load applications where external lubrication is applied.
-
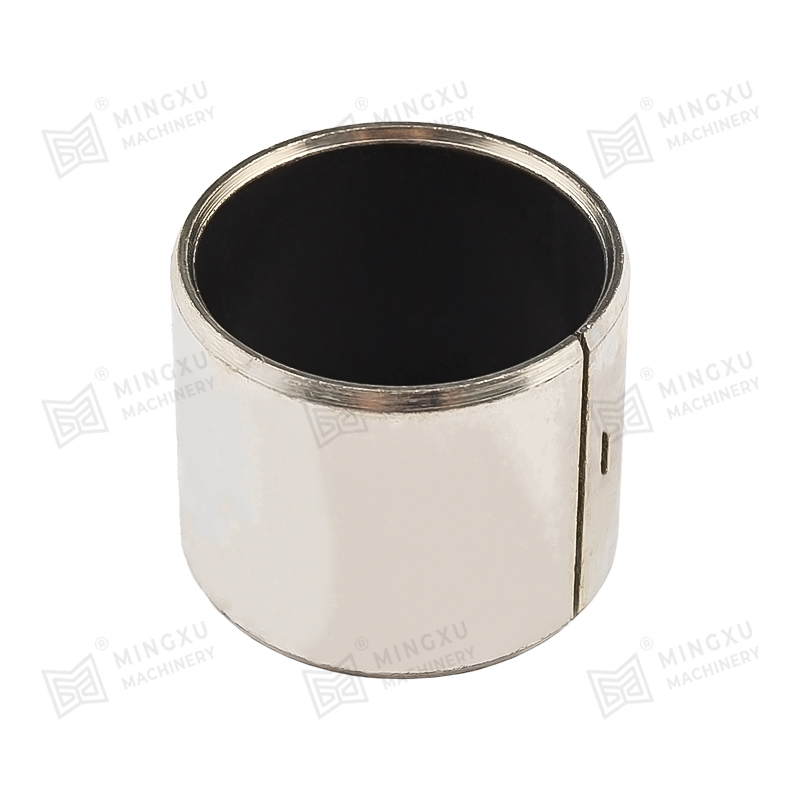
Oil-Embedded or Self-Lubricating Bushings: These bushings incorporate lubricants such as graphite or PTFE within the bronze matrix. They provide consistent lubrication without requiring frequent external maintenance, making them ideal for hard-to-reach or continuous-operation machinery.
-
Flanged Bushings: Featuring an extended flange on one end, these bushings provide axial location and prevent lateral movement, simplifying installation in assemblies that require precise positioning.
-
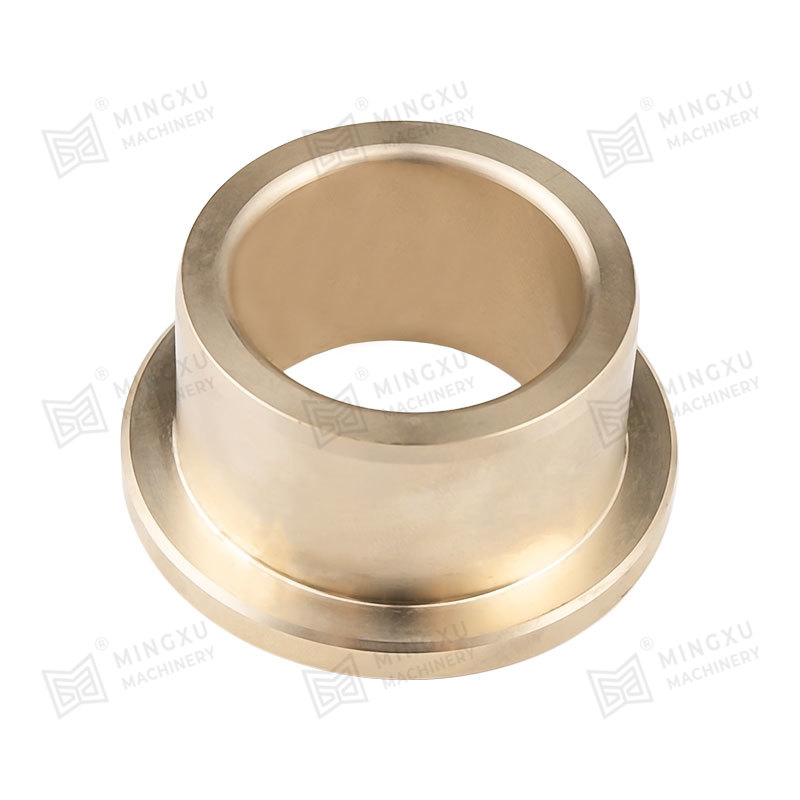
Split or Sleeve Bushings: These designs allow for easy replacement or installation in pre-existing shafts and housings without disassembling the machinery. Split bushings can also accommodate slight misalignments and thermal expansion.
-
Powdered Metal Bronze Bushings: Manufactured from compressed bronze powders, these bushings are often combined with lubricants and designed for high-precision applications where consistent material properties and tight tolerances are required.
2. Common Wear Mechanisms
Bronze bushings are durable, but they are subject to several wear mechanisms:
-
Adhesive Wear: Caused by direct metal-to-metal contact, usually under high loads or insufficient lubrication. Material may transfer between the shaft and bushing, leading to scoring or shiny patches.
Mitigation: Use proper lubricants, select self-lubricating bronze bushings, and maintain smooth shaft surfaces.
-
Abrasive Wear: Occurs when hard particles or debris become trapped between the bushing and shaft. This creates scratches and grooves, accelerating material loss.
Mitigation: Install seals to prevent contamination, use hard bronze alloys or surface coatings, and maintain clean operating environments.
-
Corrosive Wear: Chemical reactions with moisture, acids, or other substances degrade the bronze material over time, causing pitting or oxidation.
Mitigation: Apply corrosion-resistant coatings, use lubricants with inhibitors, and select bronze alloys designed for harsh environments.
-
Fatigue Wear: Repeated stress cycles lead to micro-cracks, flaking, or spalling of the bushing surface. This is common under high load or vibration.
Mitigation: Choose alloys with high fatigue strength, maintain loads within recommended limits, and use bushings with adequate wall thickness.
-
Fretting Wear: Small oscillations or vibrations between the bushing and mating surface cause localized surface degradation and particle formation.
Mitigation: Use tight-fitting bushings, vibration-damping designs, and lubricants resistant to squeeze-out.

3. Lubrication Practices
Proper lubrication is essential for bronze bushings to reduce friction, wear, and heat buildup:
- External Lubrication: Oils or greases are applied directly to the bushing surface. This is suitable for accessible locations and allows easy replenishment.
- Self-Lubricating Bushings: Contain embedded lubricants such as graphite or PTFE, providing consistent lubrication without manual intervention. Ideal for continuous operation or inaccessible areas.
- Lubricant Selection: Use lubricants compatible with bronze alloys and the operating temperature, load, and environment. Anti-wear and corrosion-inhibiting additives can extend service life.
4. Material and Alloy Selection
Bronze bushings are manufactured from a range of alloys, each with unique properties:
- Tin Bronze (CuSn): High strength and wear resistance; suitable for high-load, low-speed applications.
- Aluminum Bronze (CuAl): Exceptional corrosion resistance, high strength, and fatigue resistance; commonly used in marine and industrial environments.
- Phosphor Bronze (CuSnP): Excellent wear resistance and fatigue strength; widely used in electrical and precision machinery.
- Lead Bronze (CuPb): Improved machinability and anti-seizure properties; useful for heavy-load applications with moderate speeds.
Selecting the right alloy depends on operating conditions such as load, speed, temperature, and exposure to moisture or chemicals.
5. Maintenance and Installation Tips
Proper installation and maintenance are critical to maximize bushing life:
- Proper Fit: Ensure accurate inner diameter sizing and shaft alignment to reduce uneven wear.
- Lubrication Schedule: For externally lubricated bushings, maintain a consistent lubrication interval. For self-lubricating bushings, monitor wear and replace when necessary.
- Clean Operating Environment: Prevent contamination with dust, dirt, or metal particles, which accelerate abrasive wear.
- Periodic Inspection: Check for signs of wear such as scoring, pitting, or vibration. Replace bushings showing significant degradation.
- Avoid Overloading: Maintain operating loads within manufacturer specifications to prevent fatigue and adhesive wear.
6. Applications
Bronze bushings are used across numerous industries:
- Automotive: Suspension components, steering linkages, and transmission systems.
- Industrial Machinery: Gearboxes, conveyors, presses, and pumps.
- Marine: Propeller shafts, rudder linkages, and other components exposed to corrosive environments.
- Construction Equipment: Heavy-duty machines requiring high-load capacity and wear resistance.
Conclusion
Bronze bushings are essential components in machinery due to their strength, durability, and ability to reduce friction. Understanding the types of bronze bushings, common wear mechanisms, lubrication practices, and material selection is crucial for ensuring long service life and reliable operation. Proper installation, maintenance, and protection against contamination and overloading further enhance performance. By selecting the right alloy and implementing effective maintenance strategies, bronze bushings can provide years of trouble-free operation in demanding industrial, automotive, and marine applications.


 English
English Español
Español

















Contact Us