MXB-JFFB Self-Lubricating Half Bearing
Cat:Self-Lubricating Bearing
MXB-JFFB self-lubricating half bearings refer to bearings that cover only half of the circumference of a shaft or axle, providing support and reducing...
See DetailsGraphite bronze plates are widely used in industrial applications due to their excellent combination of strength, wear resistance, and self-lubricating properties. Commonly found in bearings, bushings, and sliding components, these plates are designed to reduce friction and improve the lifespan of machinery. Understanding what graphite bronze plates are and how they are manufactured is essential for engineers, designers, and maintenance professionals in multiple industries.
Content
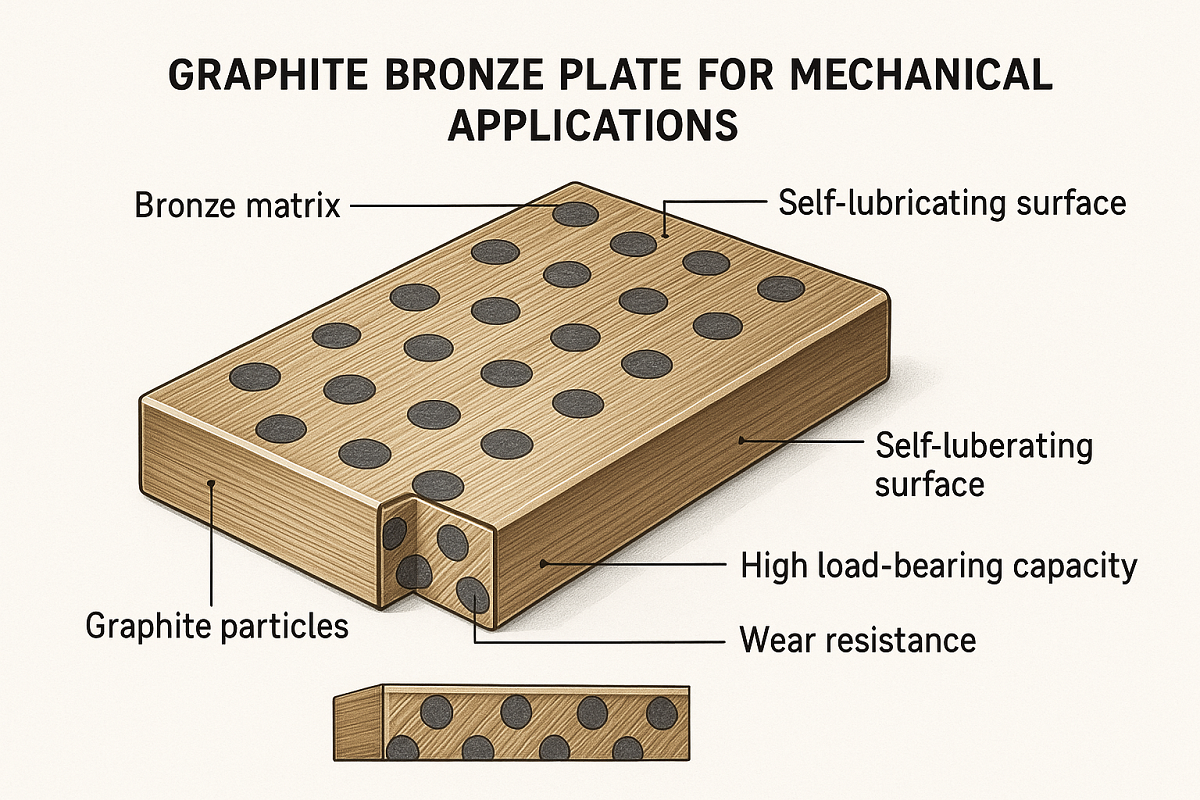
A graphite bronze plate is a composite material consisting of bronze embedded with graphite particles. The bronze provides structural strength, load-bearing capacity, and resistance to wear, while the graphite acts as a solid lubricant, reducing friction between moving parts. This combination makes graphite bronze plates ideal for applications where conventional lubrication is difficult or impossible.
High Load-Bearing Capacity: Bronze’s metallic structure supports heavy loads without deformation.
Self-Lubrication: Graphite particles form a lubricating layer between surfaces, reducing friction and wear.
Wear Resistance: The composite structure ensures durability under repeated sliding or rotational movements.
Temperature Resistance: Graphite’s stability at high temperatures allows the plate to operate efficiently in demanding environments.
Corrosion Resistance: Bronze’s natural corrosion resistance helps extend the lifespan of the plate in various environments.
Applications of graphite bronze plates include sliding bearings, pump bushings, industrial machinery components, and automotive parts, especially in situations where regular lubrication maintenance is challenging.
The performance of a graphite bronze plate depends on the quality and composition of its materials:
Bronze Matrix: Typically composed of copper and tin, sometimes with small amounts of other elements like lead or aluminum, which enhance mechanical properties.
Graphite Particles: Uniformly distributed within the bronze, graphite serves as the self-lubricating element. The size and concentration of graphite particles influence the friction, load capacity, and wear resistance of the plate.
Choosing the right combination of bronze alloy and graphite content is crucial for balancing mechanical strength, lubrication efficiency, and operational durability.
Graphite bronze plates are manufactured using specialized processes to ensure uniform distribution of graphite and high-quality performance. The main steps include:
Bronze alloys are melted in furnaces, and any required elements (tin, lead, or aluminum) are added to achieve the desired mechanical properties.
Graphite powder or granules are mixed into the molten bronze or added during casting to create a uniform distribution. The proportion of graphite is carefully controlled to achieve optimal lubrication without compromising strength.
The mixture is then cast into slabs or ingots and cooled under controlled conditions. Some manufacturers also use rolling or extrusion processes to achieve the desired thickness and surface finish.
Heat treatment is applied to relieve internal stresses and enhance the mechanical properties of the bronze matrix. This step ensures that the plate maintains stability under operational loads.
The plate is then cut, ground, or polished to precise dimensions and surface tolerances. This ensures smooth contact surfaces and consistent performance in bearing or sliding applications.
Finally, the plates undergo inspection for dimensional accuracy, hardness, graphite distribution, and surface quality. This step ensures that each plate meets the stringent requirements for industrial applications.
The combination of casting, heat treatment, and precision machining provides several advantages:
Uniform distribution of graphite for consistent self-lubricating performance.
Enhanced mechanical strength and wear resistance of the bronze matrix.
Ability to produce plates in various sizes and thicknesses for diverse industrial needs.
High reliability and long service life in heavy-duty or high-temperature applications.
Graphite bronze plates are engineered composite materials that combine the strength and durability of bronze with the self-lubricating properties of graphite. Their manufacturing involves careful alloy preparation, graphite incorporation, casting, heat treatment, and precision machining to ensure high performance. These plates are essential in industrial machinery, automotive components, and other applications where reduced friction, wear resistance, and durability are critical. Understanding the material composition and manufacturing process helps engineers and designers select the right graphite bronze plates for specific operational requirements.

MXB-JFFB self-lubricating half bearings refer to bearings that cover only half of the circumference of a shaft or axle, providing support and reducing...
See Details
SF stands for three-layer composite, namely steel plate layer, copper powder layer and plastic layer. The steel plate layer plays the role of assembly...
See Details
FB090 bronze bearings are made of tin bronze alloy CuSn8. The surface can be rolled with diamond or hemispherical oil holes and oil grooves according ...
See Details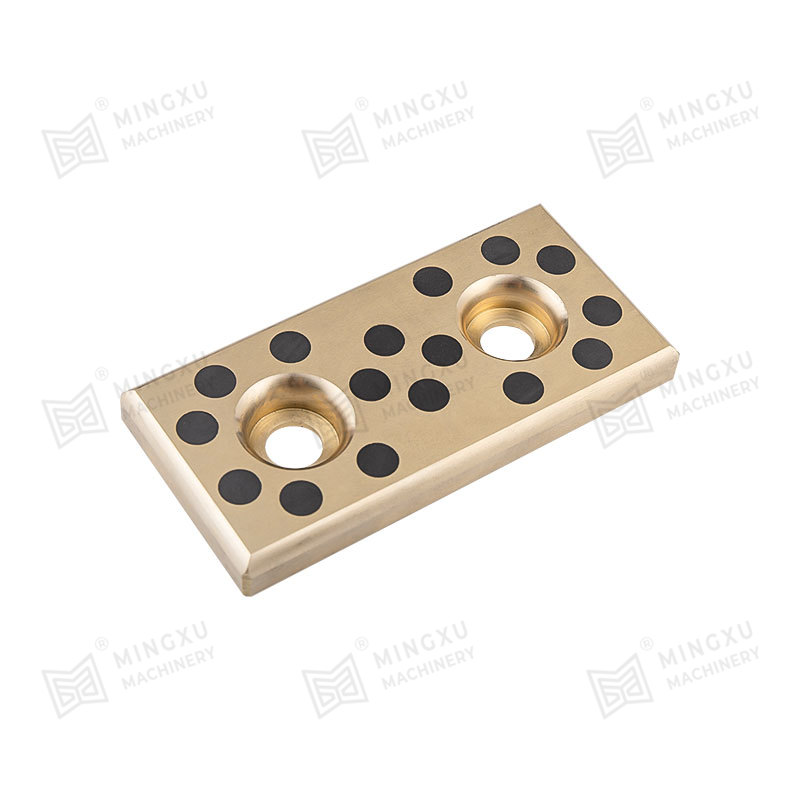
Mining machinery and equipment are very easy to wear during use. In order to extend the service life of the equipment, Mingxu Machinery recommends tha...
See Details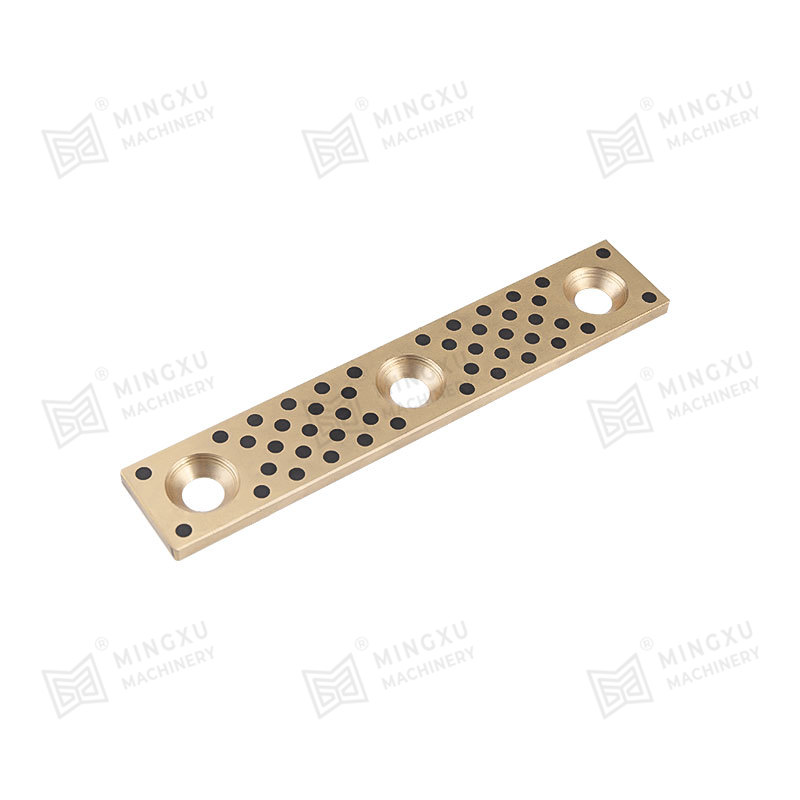
MXB-JUWP self-lubricating wear-resistant plate is a 5mm thick self-lubricating graphite inlaid wear-resistant plate developed and produced by Mingxu M...
See Details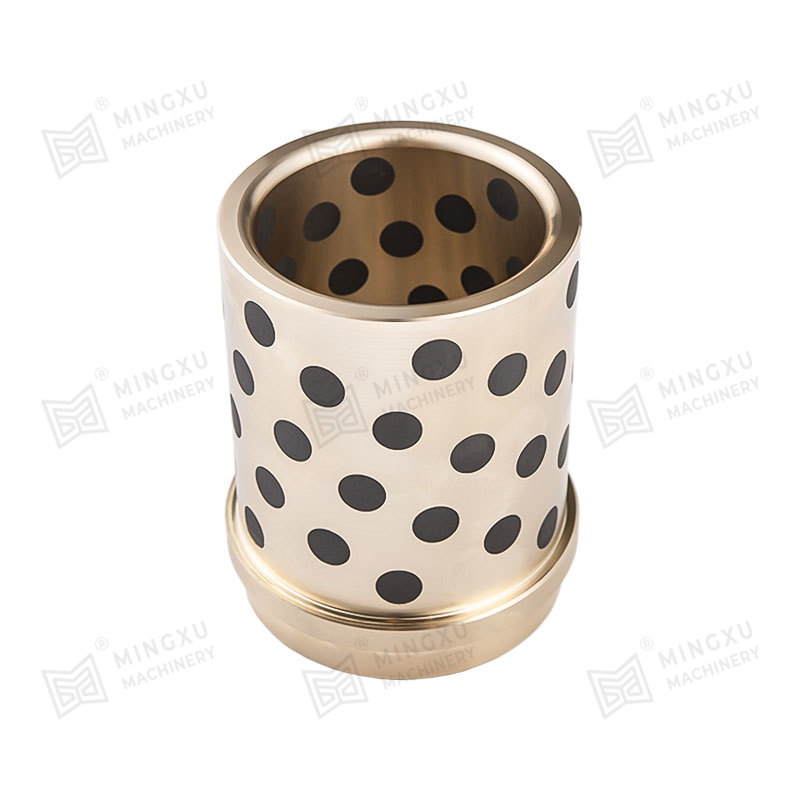
MGB61 NAAMS Standard Guide Bushing is a reliable solution for precise, smooth guide applications. This guide bushing is designed to meet NAAMS standar...
See Details
Circular guides are frequently used in automobile panel molds and large stamping molds. The mold base and unloading plate guides usually use self-lubr...
See Details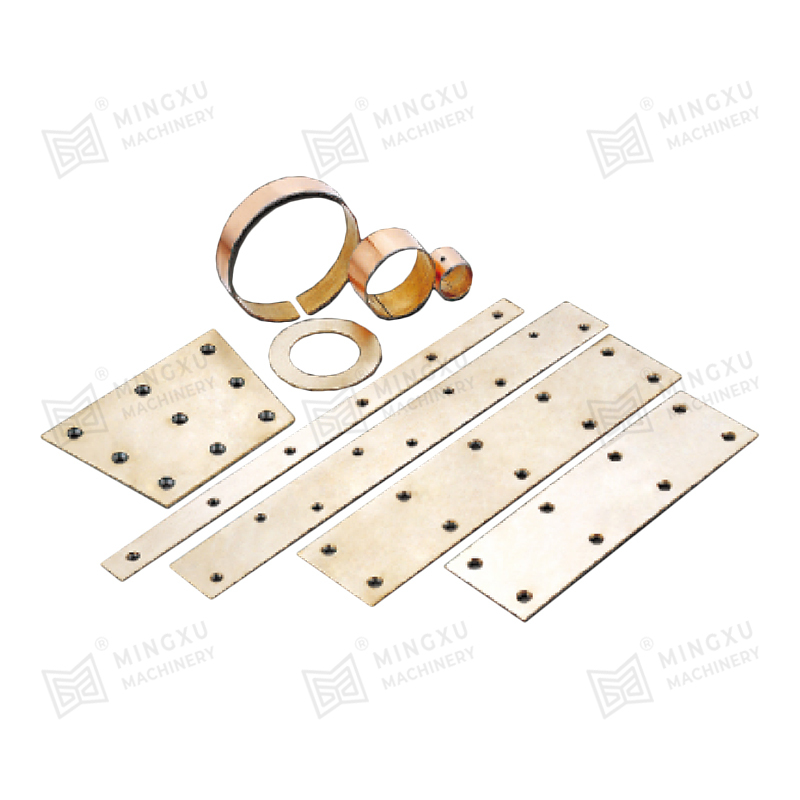
MX2000-1 graphite embedded alloy bearing, MX2000-1 graphite scattered alloy bearing is an improved product of JF800 bimetallic bearing. It has the pre...
See Details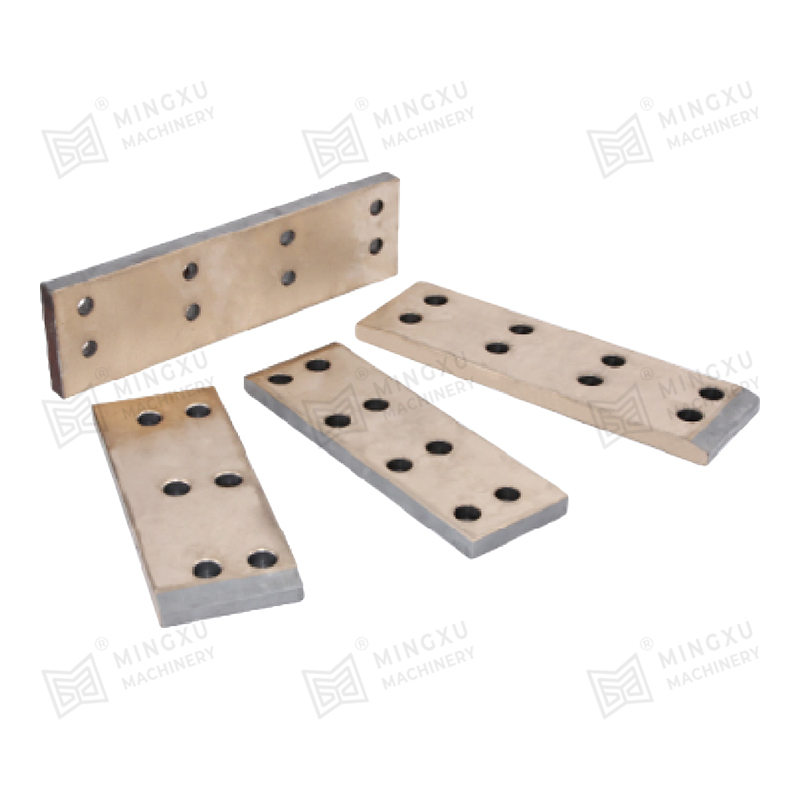
The bimetallic slide plate with wear-resistant alloy sintered on three sides is a new type of self-lubricating plate. Compared with the general single...
See Details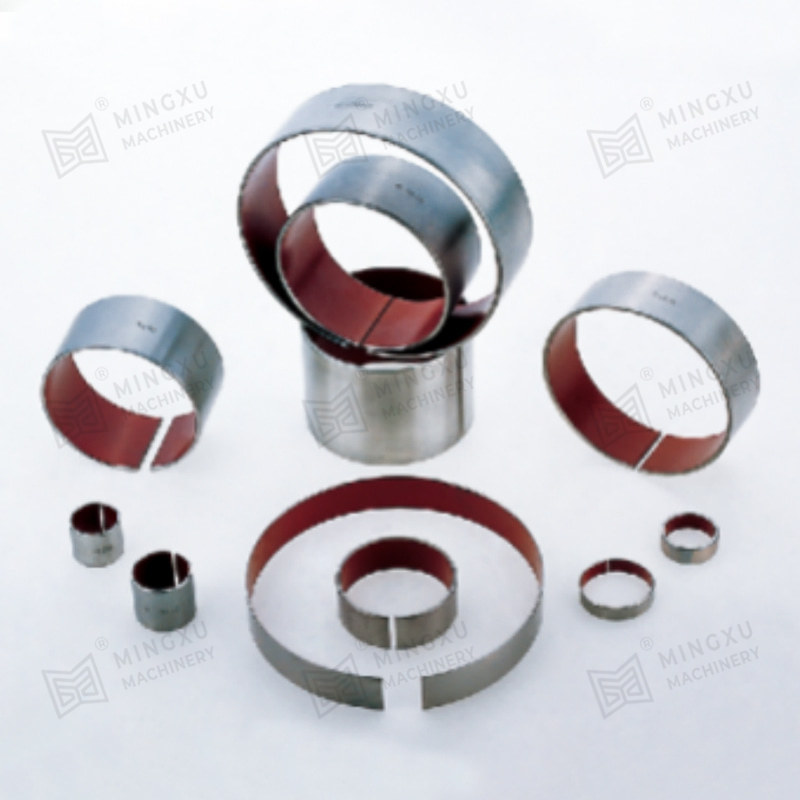
SF-1S stainless steel corrosion-resistant bearing is a very effective corrosion-resistant material that is formed by rolling with stainless steel as t...
See Details
Contact Us