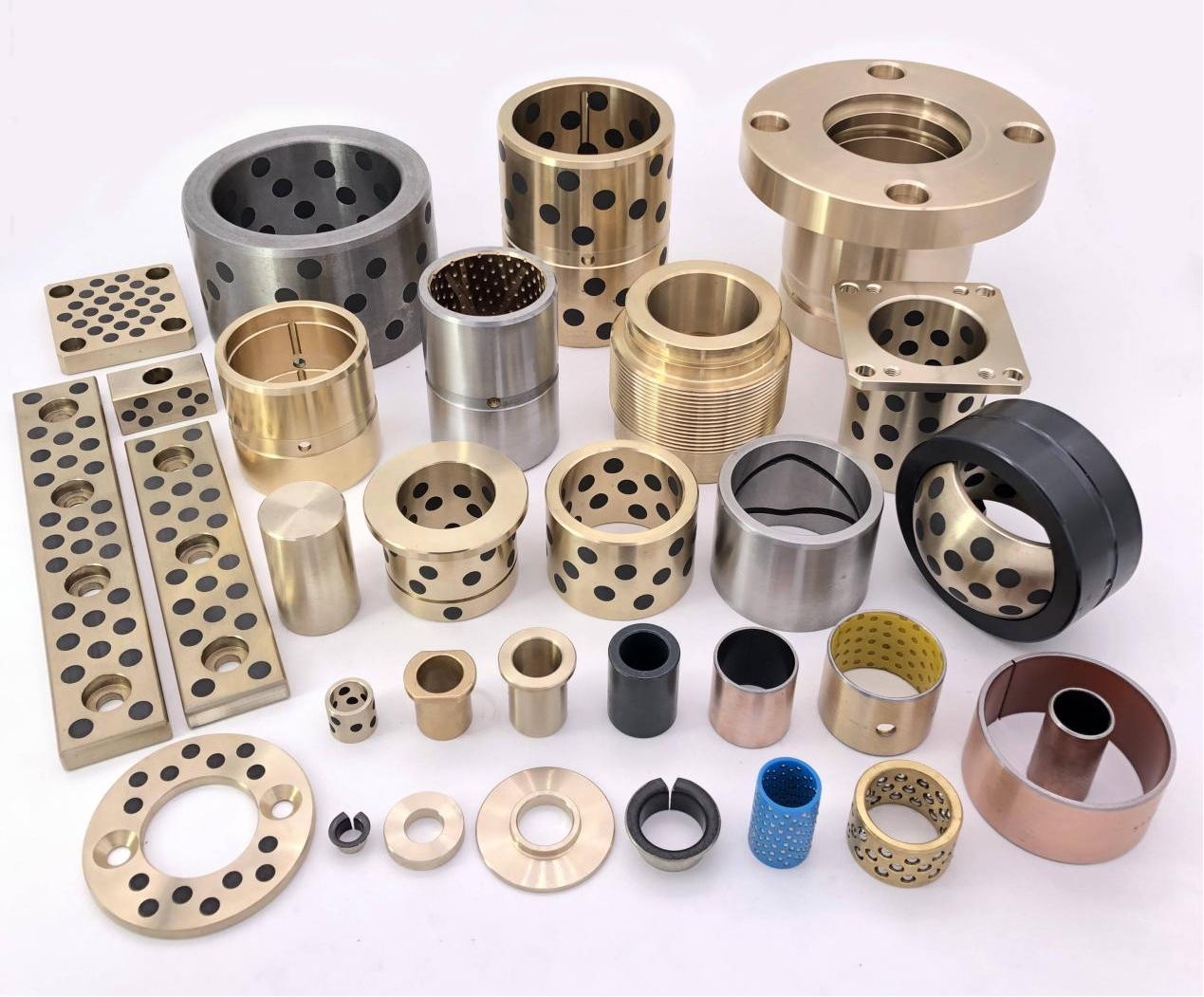
Bushings are critical components in machinery, designed to reduce friction, wear, and vibration between moving parts. Among the many types available, DX bushings and DU bushings are widely used in industrial and mechanical applications. Although they may look similar at first glance, these two bushings differ in structure, material composition, and performance characteristics. Understanding their differences helps engineers, maintenance teams, and procurement specialists choose the right type for each application.
Overview of DX Bushings
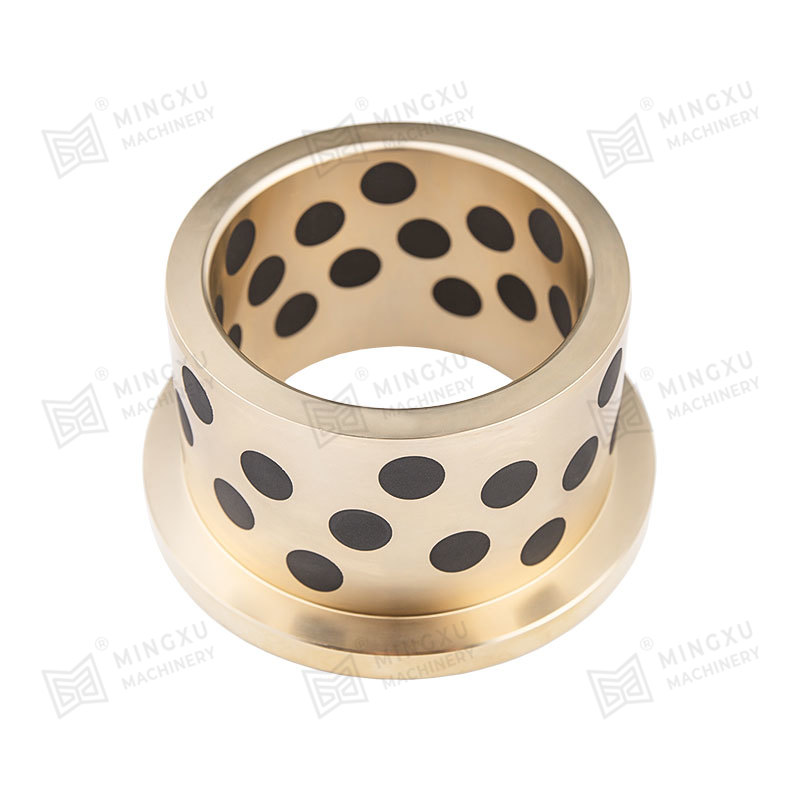
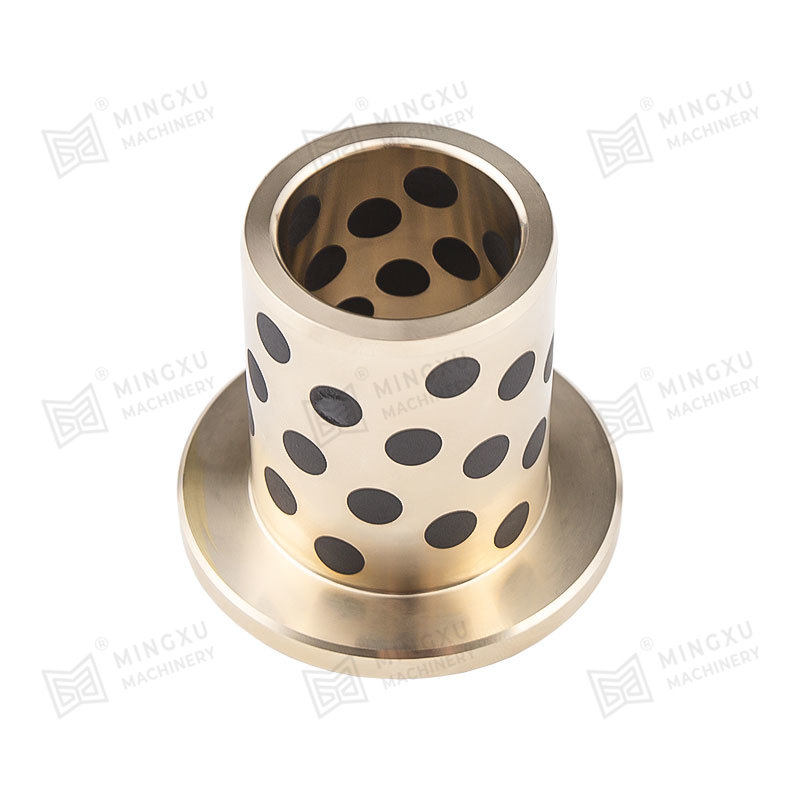
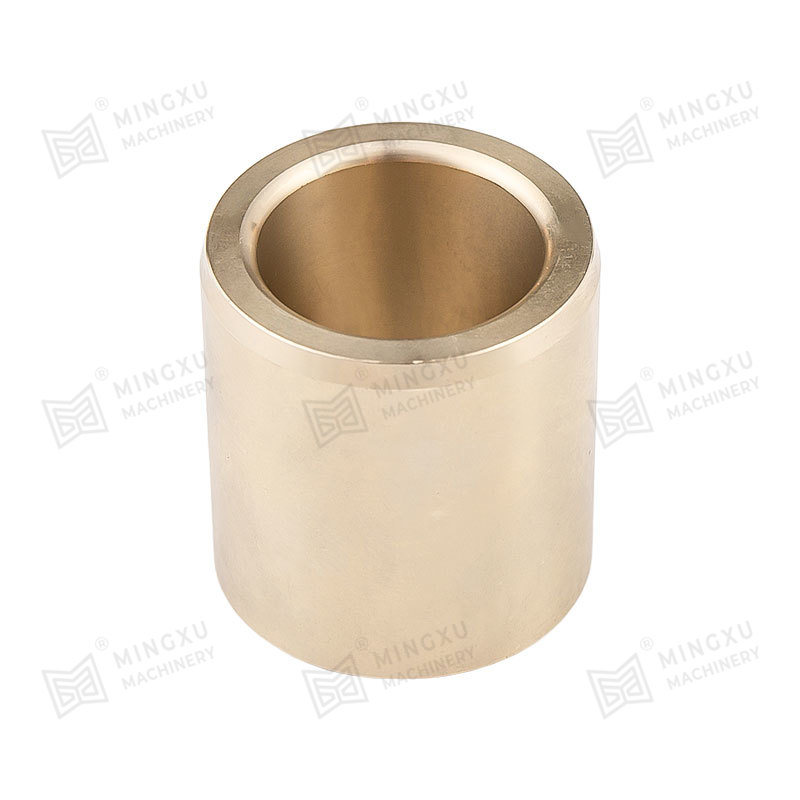
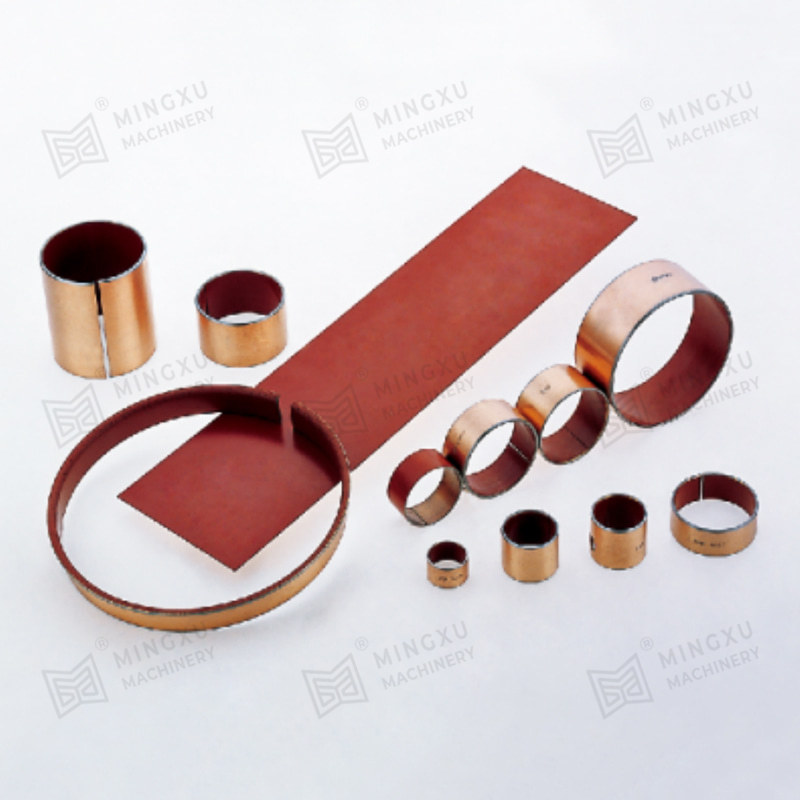
DX bushings are triple-layer composite bushings typically designed for applications requiring high load capacity and reliable lubrication. Their structure usually includes:
- A steel backing for strength and stability.
- A sintered bronze layer, which acts as a porous medium to hold lubricants.
- A PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) overlay, which provides a low-friction surface and reduces wear.
This design makes DX bushings well-suited for conditions where lubrication is available but needs to be retained effectively. They are widely applied in construction machinery, agricultural equipment, and heavy-duty industrial machines.
Key Features of DX Bushings:
- High load capacity.
- Good wear resistance under lubricated conditions.
- Reliable performance in heavy-duty applications.
- Requires regular lubrication for optimal operation.
Overview of DU Bushings
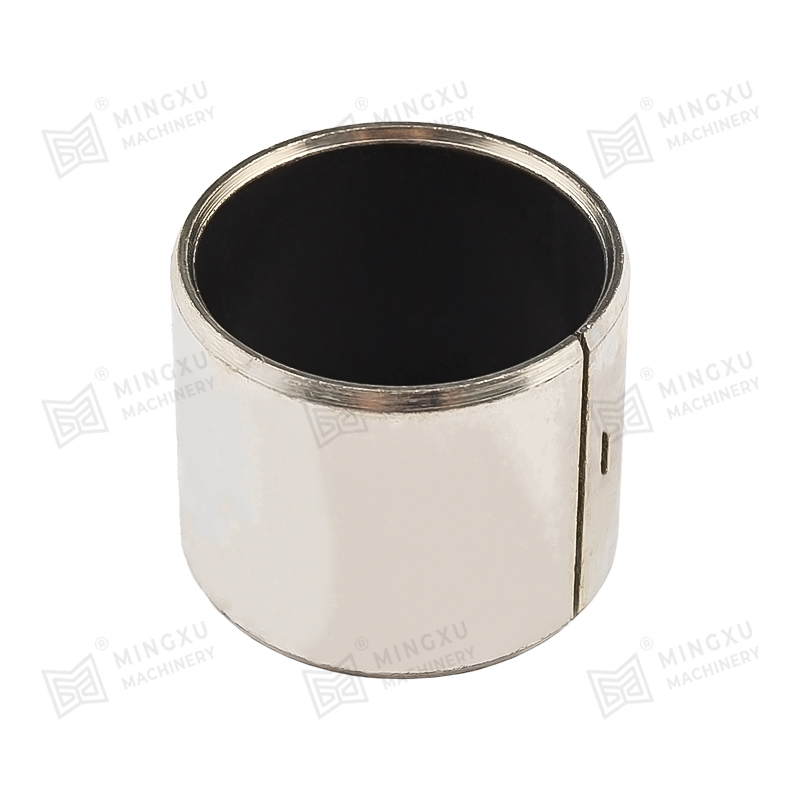
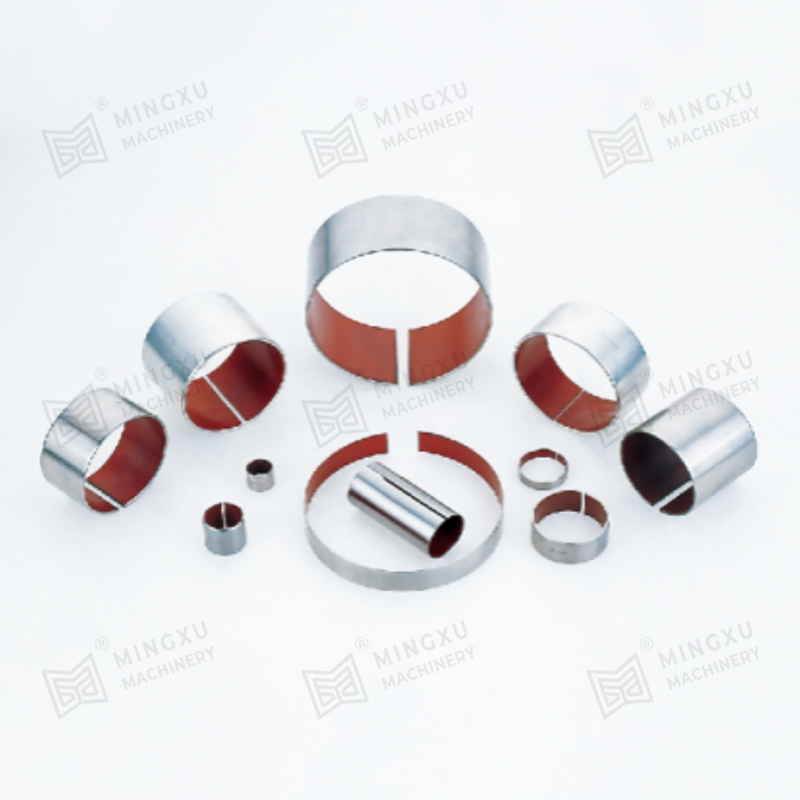
DU bushings are self-lubricating composite bushings, typically designed for maintenance-free performance in many applications. Their structure generally includes:
- A steel backing for mechanical strength.
- A porous bronze interlayer that holds and bonds the surface material.
- A PTFE-based sliding layer, which ensures self-lubrication and very low friction.
Unlike DX bushings, DU bushings are usually intended for applications where continuous external lubrication is difficult or undesirable. They are often used in automotive systems, office equipment, textile machinery, and general industrial machinery.

Key Features of DU Bushings:
- Maintenance-free, thanks to self-lubrication.
- Very low friction coefficient.
- Suitable for dry running or limited lubrication.
- Not as high in load capacity as DX bushings.
Main Differences Between DX and DU Bushings
| Aspect |
DX Bushing |
DU Bushing |
| Lubrication |
Requires lubrication; retains lubricant well |
Self-lubricating, maintenance-free in many cases |
| Load Capacity |
Higher, suitable for heavy-duty use |
Moderate, suitable for light to medium loads |
| Friction |
Low, but depends on lubrication |
Very low, even under dry running conditions |
| Applications |
Construction, agriculture, heavy machinery |
Automotive, office equipment, industrial machinery |
| Maintenance |
Requires periodic lubrication |
Typically maintenance-free |
Choosing Between DX and DU Bushings
-
Choose DX bushings if:
- Your application involves heavy loads and regular lubrication is possible.
- The environment is harsh, such as in construction or agricultural equipment.
-
Choose DU bushings if:
- You need a maintenance-free solution.
- The application has light to medium loads and lubrication is difficult to provide.
- Smooth, quiet, and efficient operation is a priority.
Conclusion
Both DX and DU bushings are valuable solutions, but their suitability depends on operating conditions. DX bushings excel in heavy-duty applications where lubrication is maintained, while DU bushings are ideal for lighter-duty uses where self-lubrication and maintenance-free operation are preferred. By evaluating load requirements, lubrication availability, and maintenance preferences, you can select the right bushing type to ensure long-lasting and reliable performance.


 English
English Español
Español

















Contact Us