In many industrial and mechanical applications, the need for reliable, low-maintenance components is constant. Among these components, oil-free bearings, also known as self-lubricating bearings, stand out for their ability to function efficiently without the need for external lubrication. This article provides an in-depth exploration of what oil-free bearings are, how they work, the materials they are made from, their advantages and limitations, key application areas, and how they compare with traditional lubricated bearings.
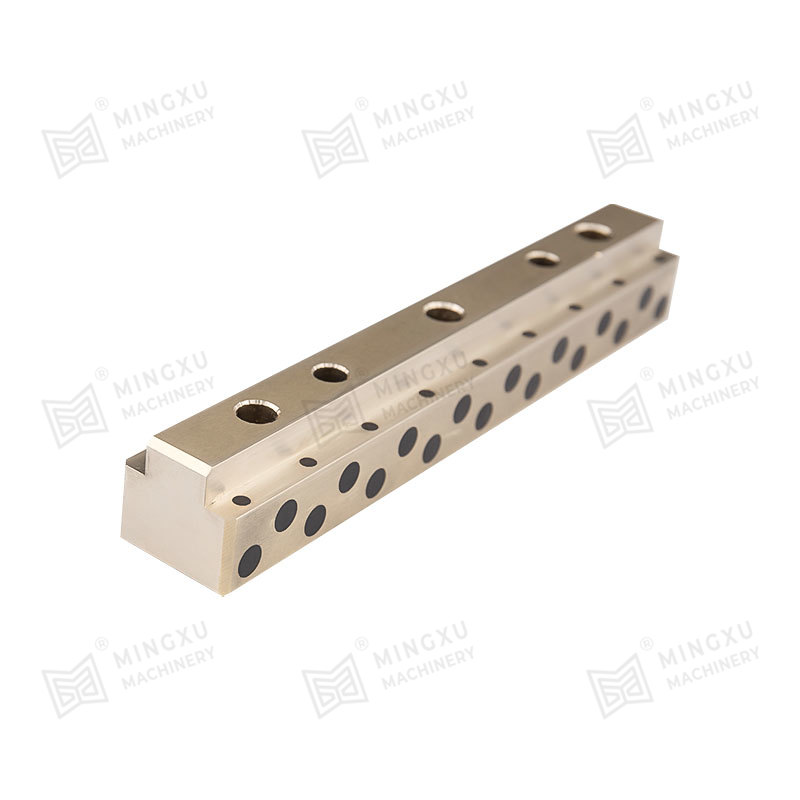
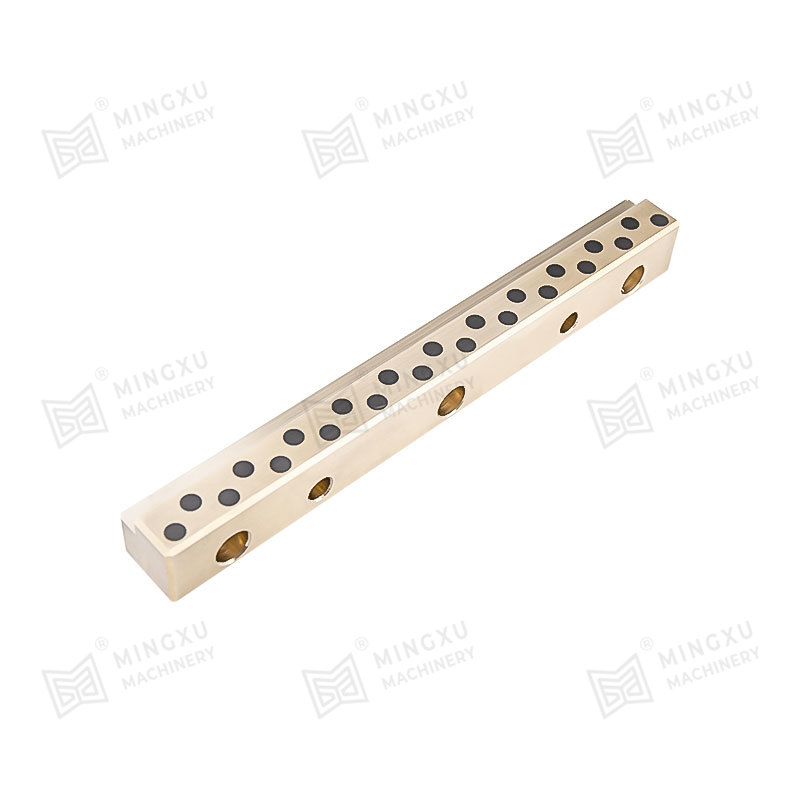
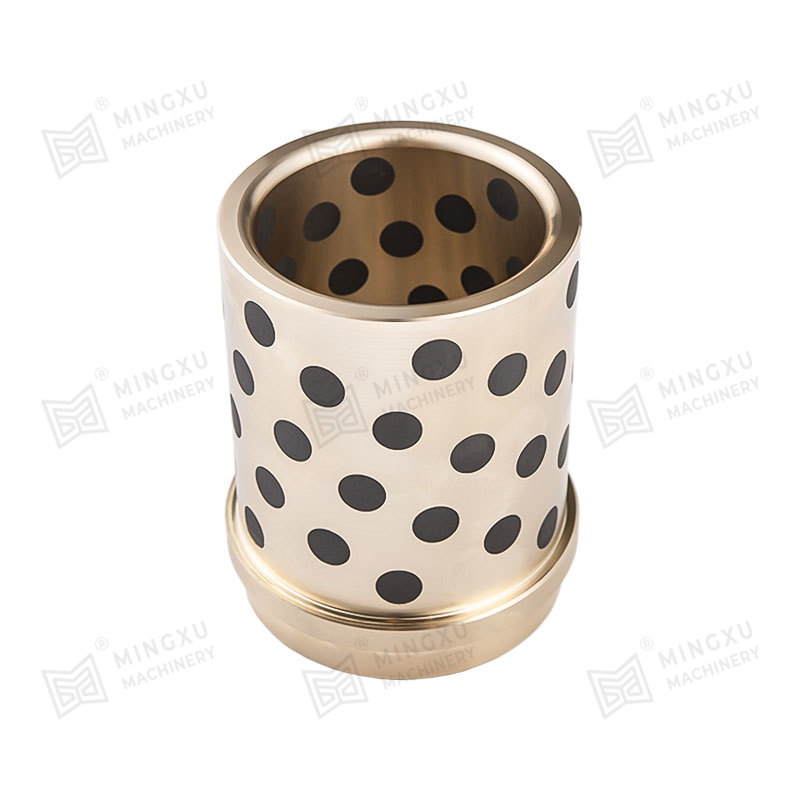
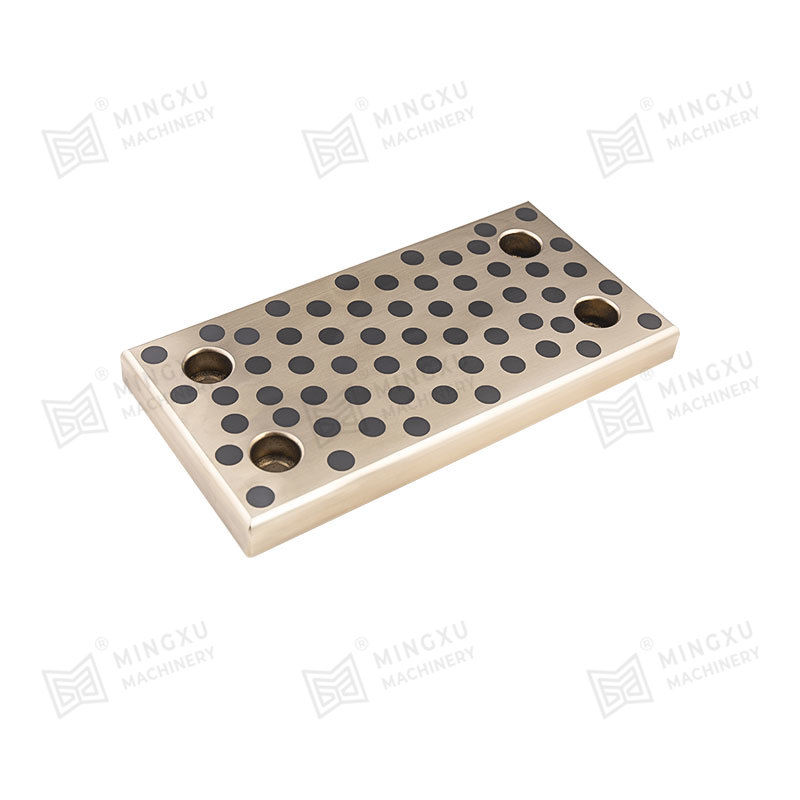
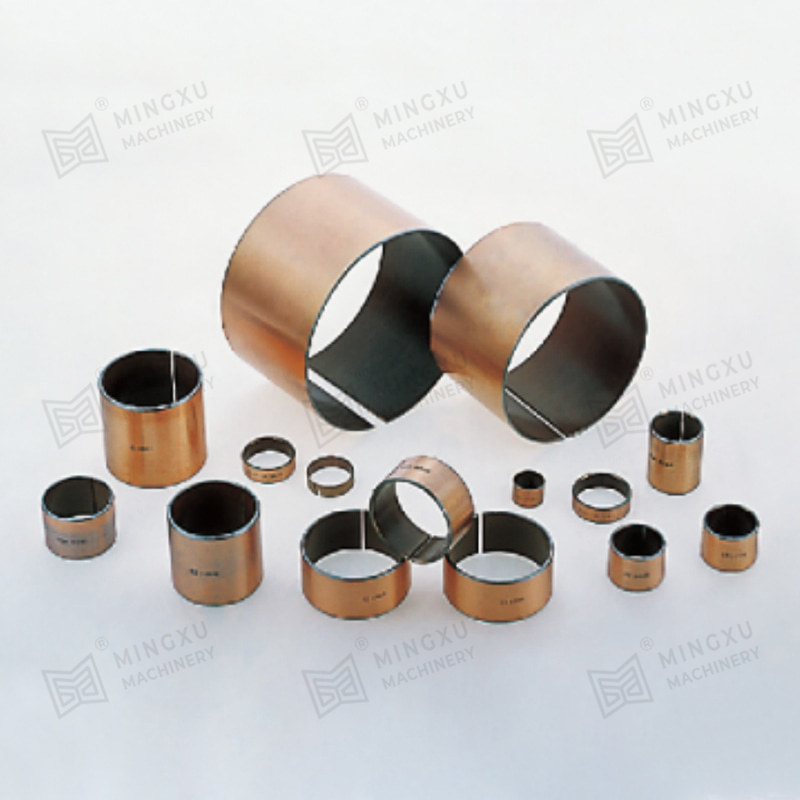
Oil-free bearings are mechanical components that support rotating or sliding shafts without requiring additional lubricants like oil or grease. Instead, they are designed with materials or structures that allow them to self-lubricate during operation. These bearings reduce friction and wear between moving parts, making them ideal for environments where regular lubrication is impractical or impossible.
Self-lubricating bearings can be classified as:
Each type uses different methods and materials to achieve self-lubrication.
How Do Self-Lubricating Bearings Work?
The working principle of oil-free bearings lies in the materials used in their design. These materials either contain solid lubricants like graphite, PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), or molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂), or they feature a porous structure that can retain lubricating agents internally.
-
Solid lubricant-based bearings release a small amount of lubricant onto the bearing surface as frictional heat increases.
-
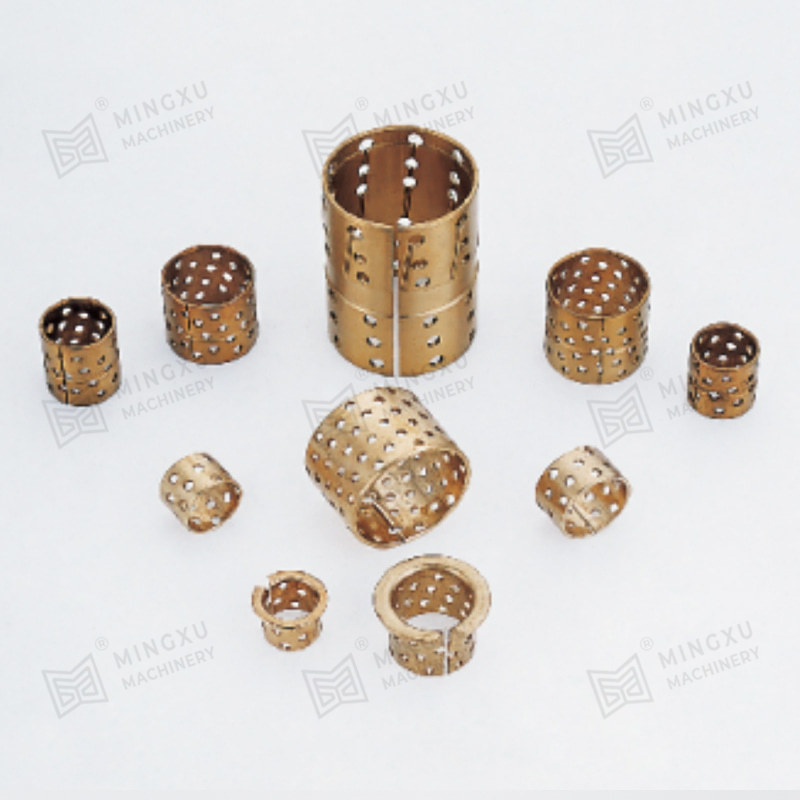
Porous sintered bearings hold lubricant in their microscopic pores and release it during operation due to capillary action and thermal expansion.
-
Polymer-based bearings incorporate low-friction materials that inherently reduce the need for added lubrication.
Materials Used in Oil-Free Bearings
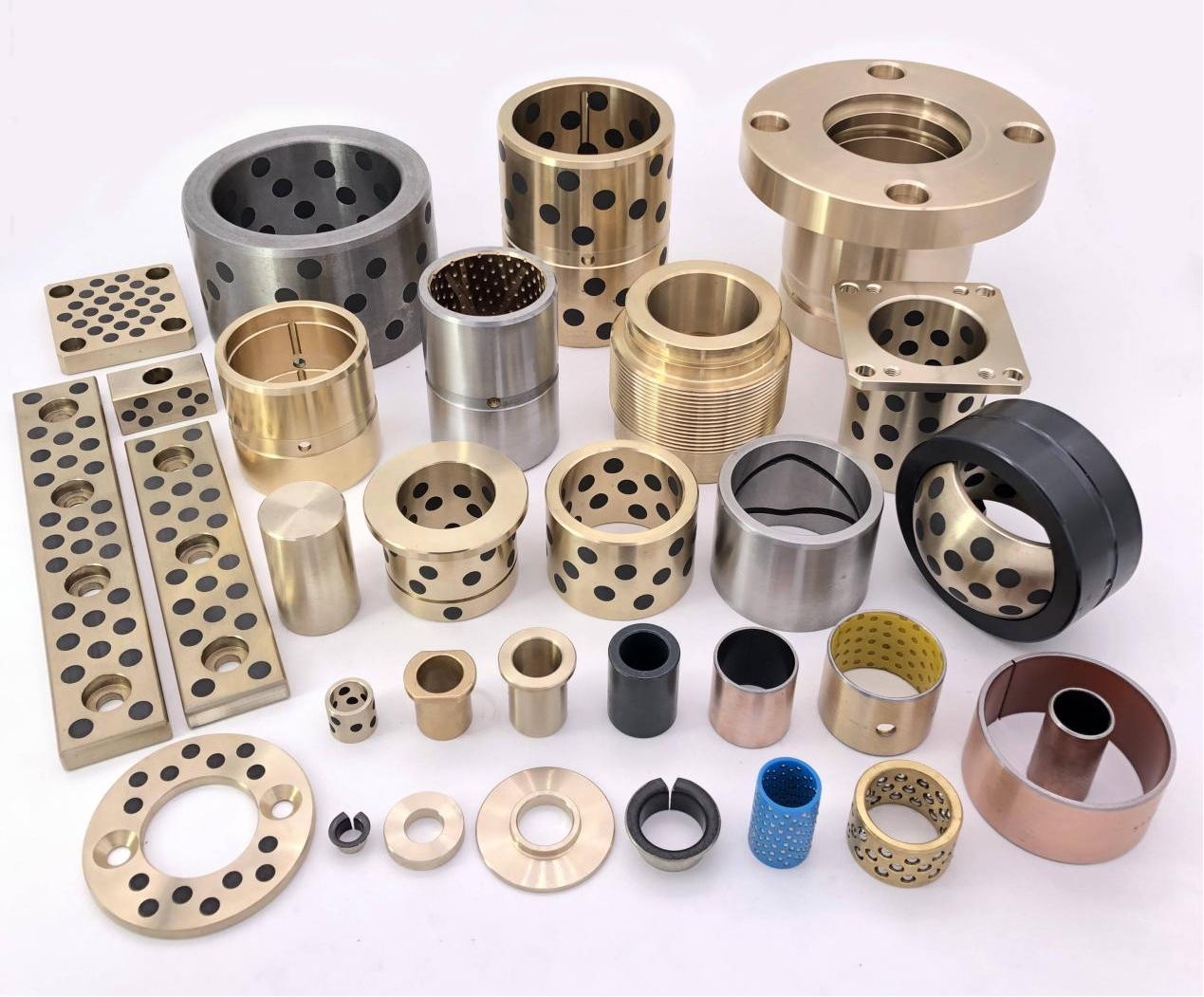
Self-lubricating bearings are available in a wide range of materials, each suited for different applications and load capacities:
-
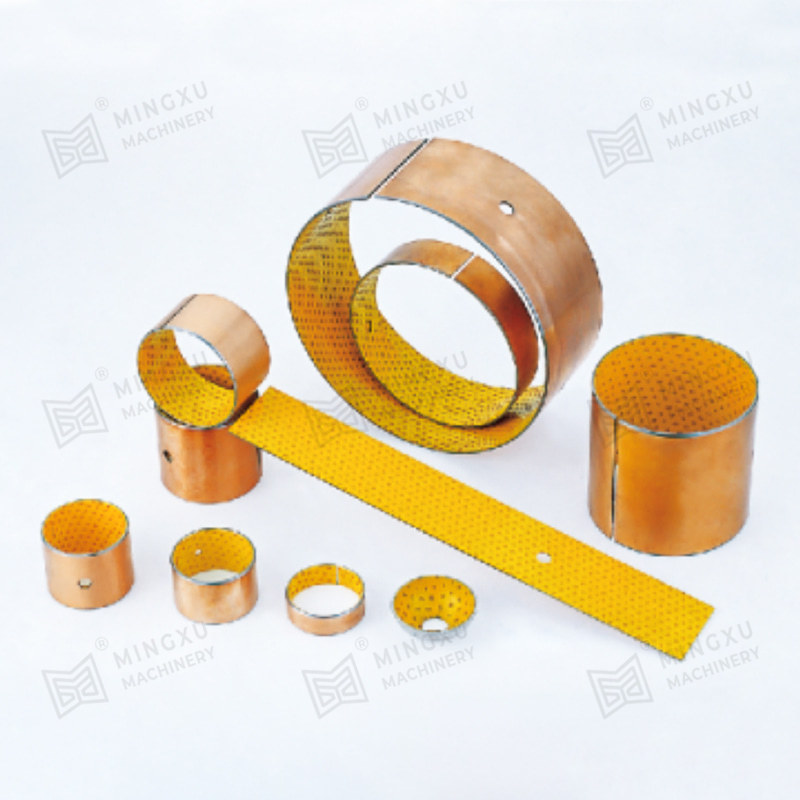
Bronze (Sintered or Embedded Lubricants)
Excellent thermal conductivity and wear resistance; used for medium to high load conditions.
-
PTFE (Teflon)
Very low coefficient of friction; ideal for light-load applications in clean environments.
-
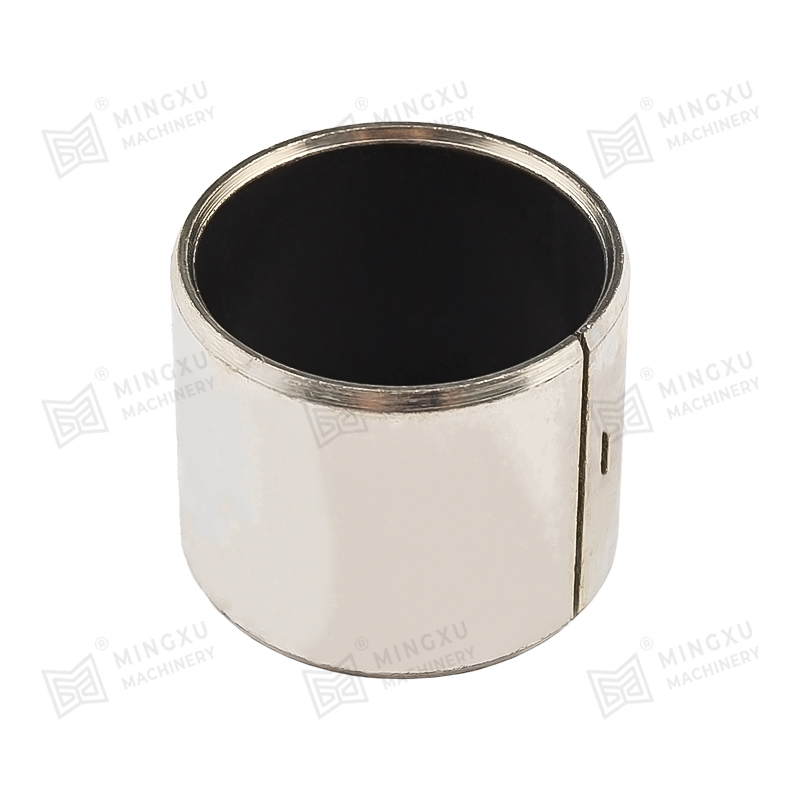
Graphite or MoS₂-based Composites
Good for high-temperature and dry environments; durable and reliable under heavy loads.
-
Plastic Polymers (e.g., POM, Nylon, UHMWPE)
Lightweight and corrosion-resistant; often used in food, medical, and water-related industries.
-
Metal-polymer Composites
A metal backing for strength and a polymer lining for self-lubrication, combining rigidity and smooth motion.
Advantages of Oil-Free Bearings
Oil-free or self-lubricating bearings provide several operational and maintenance benefits:
-
Maintenance-Free Operation
No need for regular lubrication, making them ideal for hard-to-reach or sealed environments.
-
Extended Service Life
Reduced wear due to consistent self-lubrication improves lifespan.
-
Clean Operation
No lubricant leakage reduces contamination in sensitive environments like food processing or electronics.
-
Cost Savings Over Time
Lower maintenance and longer replacement cycles reduce overall operational costs.
-
Environmental Benefits
Elimination of oils or greases helps reduce environmental impact and disposal issues.
-
Versatile Operating Conditions
Suitable for high or low temperatures, vacuum conditions, underwater applications, and dusty or dirty environments.
Limitations to Consider
Despite their many advantages, self-lubricating bearings also have some limitations:
-
Lower Load Capacity
In some cases, especially with plastic-based bearings, the load-bearing capability is lower than metal counterparts.
-
Thermal Limitations
Certain polymers or porous materials may degrade at high temperatures.
-
Speed Constraints
Excessive speed can lead to overheating and premature wear.
-
Cost of Specialized Materials
Advanced materials like graphite composites or metal-polymers may carry a higher initial cost.
Common Applications of Oil-Free Bearings
Thanks to their reliability and clean operation, oil-free bearings are widely used in diverse industries:
-
Automotive Industry
In suspension systems, pedals, and steering components where maintenance access is limited.
-
Home Appliances
Found in washing machines, fans, and kitchen equipment for silent and maintenance-free operation.
-
Food Processing Equipment
Non-contaminating bearings suitable for hygienic environments.
-
Medical Devices
Bearings used in pumps, surgical devices, and lab equipment due to cleanliness and quietness.
-
Aerospace and Defense
Bearings that must perform in extreme temperatures or vacuum conditions.
-
Textile Machinery
High-speed, low-noise bearings help improve equipment lifespan and reduce operational disruptions.
-
Printing Equipment
Precision, smooth motion, and low-maintenance needs are ideal for this sector.
Comparison: Oil-Free vs. Traditional Lubricated Bearings
| Feature |
Oil-Free Bearings |
Lubricated Bearings |
| Lubrication Need |
Built-in/self-lubricating |
Requires regular lubrication |
| Maintenance |
Low or zero |
High |
| Cleanliness |
Cleaner (no oil leakage) |
Risk of oil/gas contamination |
| Cost Over Time |
Lower total cost |
Higher due to maintenance |
| Operating Conditions |
Suitable for extreme environments |
May fail in extreme conditions |
| Load/Speed Capability |
Moderate to high (material dependent) |
Generally higher for heavy-duty use |
| Applications |
Diverse, including sensitive areas |
More suitable for high-load tasks |
Tips for Choosing the Right Self-Lubricating Bearing
When selecting an oil-free bearing for your project, consider:
Load and Speed Requirements
Operating Environment (Temperature, Humidity, Dust)
Precision Needs (Clearance, Tolerance)
Material Compatibility with Other Parts
Industry Standards and Certifications
Consulting with a bearing manufacturer or engineer can help ensure optimal performance and longevity for your specific use case.
Oil-free bearings or self-lubricating bearings offer a highly efficient, maintenance-free solution for a wide variety of industrial and commercial applications. From improving machine uptime to operating in extreme or sensitive environments, these bearings bring significant operational advantages. While they may not completely replace traditional lubricated bearings in every scenario, they continue to grow in popularity due to their durability, reliability, and low-maintenance performance. With continuous advancements in materials and design, the role of oil-free bearings in modern industry is only expected to expand.


 English
English Español
Español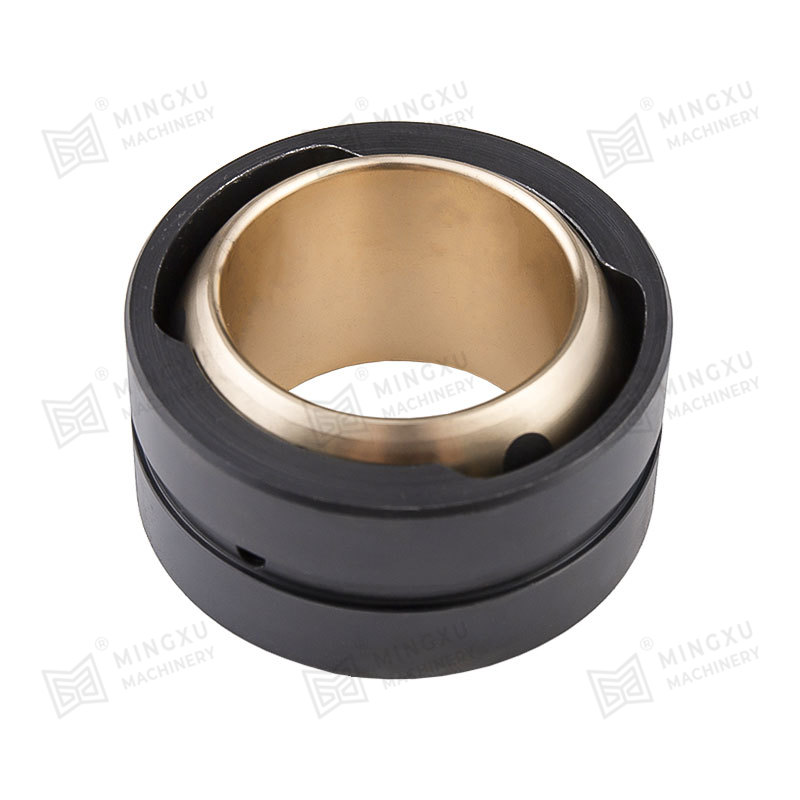
















Contact Us