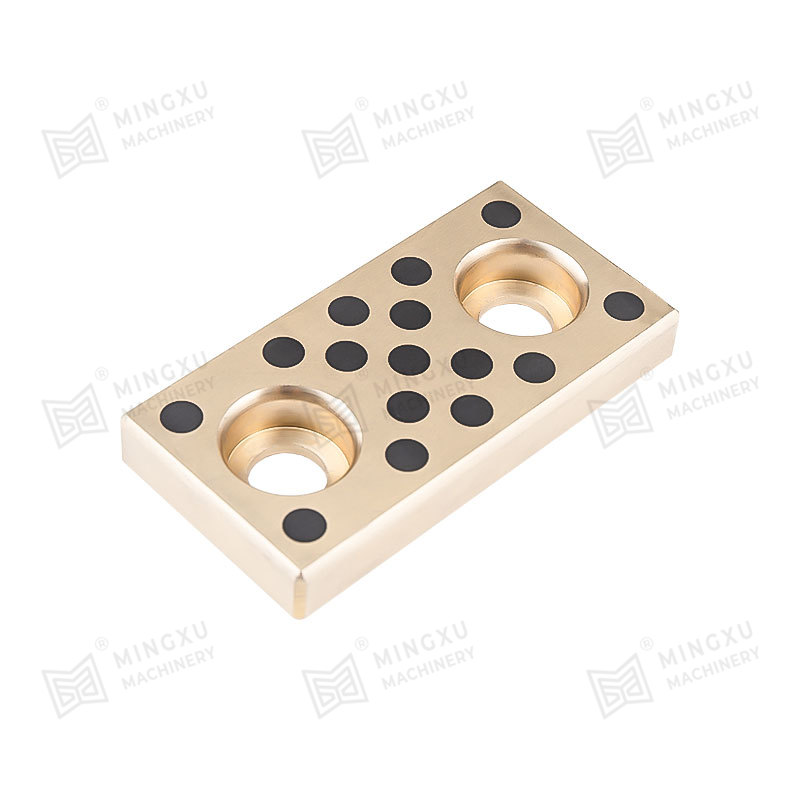
As critical mechanical components, self-lubricating bearings play a vital role in scenarios where conventional lubrication is impossible or difficult. Tin bronze and aluminum bronze, two common bronze materials, exhibit significant differences in self-lubricating bearing applications due to variations in their physical, chemical, and mechanical properties.
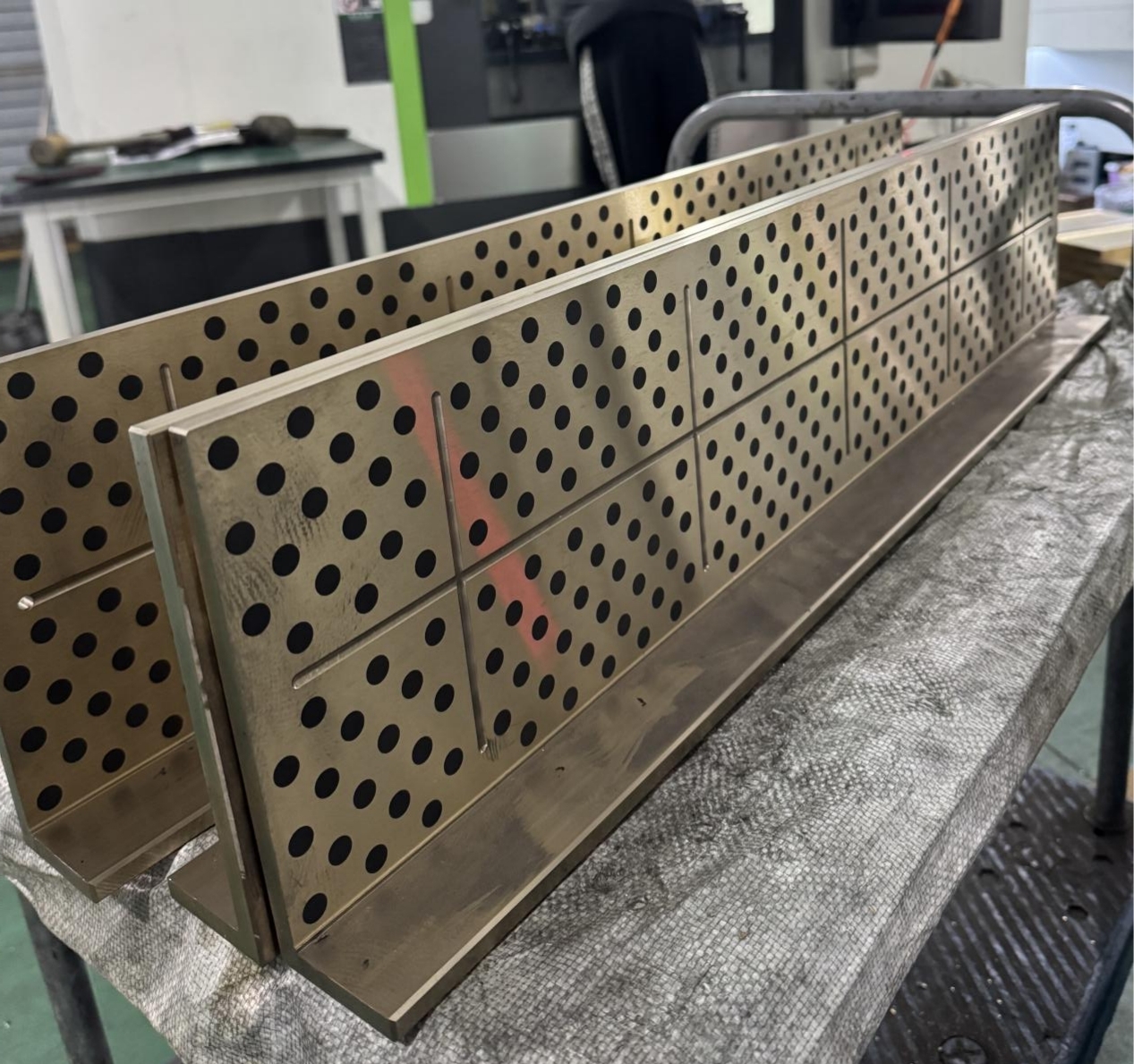

I. Comparison of Material Properties
|
Property
|
Tin Bronze
|
Aluminum Bronze
|
|
Main Alloy Element
|
Tin (Sn, 3%~14% content)
|
Aluminum (Al, ≤11.5% content)
|
|
Strength
|
High, but lower than aluminum bronze
|
High strength, further enhanced by heat treatment
|
|
Wear Resistance
|
Excellent, suitable for medium to high-intensity wear scenarios
|
Exceptional, especially suitable for high-load, high-impact scenarios
|
|
Corrosion Resistance
|
Strong corrosion resistance in atmospheric, seawater, and freshwater environments
|
Good corrosion resistance in atmospheric, freshwater, and seawater environments, with superior high-temperature oxidation resistance
|
|
Thermal Conductivity
|
Good, suitable for applications requiring heat dissipation
|
Better, but slightly lower than tin bronze
|
|
Machinability
|
Excellent, easy to cast, weld, and machine
|
Good, but increased hardness after heat treatment may make machining more difficult
|
Actual Test Data:
• Strength Comparison: Aluminum bronze (QAL9-4) tensile strength can reach 750MPa, higher than tin bronze (QSn4-3) at 500MPa.
• Wear Resistance Test: Under the same working conditions, aluminum bronze bearings have a 30%-50% longer lifespan than tin bronze.
• Corrosion Experiment: The corrosion rate of aluminum bronze in a 3.5% NaCl solution is only half that of tin bronze.
II. Differences in Self-Lubricating Performance
Tin Bronze:
• Forms a stable self-lubricating film with a low friction coefficient (0.08~0.12), suitable for medium to low-speed, medium-load scenarios.
• Commonly used in ship propulsion shafts, architectural door hinges, and other applications requiring both lubrication and decorative properties.
Aluminum Bronze:
• Achieves oil-free lubrication by embedding solid lubricants such as graphite or PTFE, with a friction coefficient as low as 0.05.
• Suitable for extreme conditions such as high temperatures, high loads, and reciprocating motion, such as automotive transmissions and injection molding machine crossheads.
Engineering Cases:
• A mining excavator using aluminum bronze self-lubricating bearings experienced a 45% reduction in gearbox failure rates and a doubling of maintenance intervals.
• Ship rudders using tin bronze bearings showed no signs of corrosion after 5,000 hours of continuous operation in a seawater environment.
III. Application Focus
|
Application Scenario
|
Tin Bronze Advantages
|
Aluminum Bronze Advantages
|
|
Marine and Offshore Engineering
|
Strong corrosion resistance, suitable for seawater environments
|
High strength and impact resistance, suitable for high-load components such as propulsion systems and rudders
|
|
Construction Engineering
|
Combines decorative properties with wear resistance, suitable for doors, windows, and classical components
|
High-strength support structures, such as heavy machinery brackets
|
|
Automotive Components
|
Good electrical conductivity, suitable for sensors and connectors
|
Wear and heat resistance, suitable for transmission and differential gears
|
|
Extreme Condition Equipment
|
Stable performance at medium to low temperatures, such as in cold chain equipment
|
Strong high-temperature oxidation resistance, such as in metallurgical machinery continuous casters
|
IV. Processing and Cost Analysis
Machinability:
• Tin Bronze: Excellent casting performance, suitable for making complex-shaped components such as gears and worm wheels.
• Aluminum Bronze: Good hot workability, suitable for forging high-strength parts, but welding requires special processes.
Cost Comparison:
• Tin Bronze: Lower material cost and high processing efficiency, with a comprehensive cost 15%-20% lower than aluminum bronze.
• Aluminum Bronze: Higher material cost, but long lifespan reduces maintenance expenses, making it suitable for high-value-added equipment.
Tin bronze and aluminum bronze each have their advantages in self-lubricating bearings.
• Tin bronze excels in corrosion resistance, machinability, and economy, making it suitable for medium-load, corrosive environments.
• Aluminum bronze is renowned for its high strength, wear resistance, and temperature resistance, making it more suitable for high-load, extreme conditions.
In practical applications, material selection should be based on specific working conditions (such as load, temperature, and medium) to maximize material performance.

Zhejiang Mingxu Machinery Manufacturing Co., Ltd., as a professional manufacturer of self-lubricating components, can recommend the most suitable materials based on your working conditions and drawings, helping you reduce costs and increase efficiency. For procurement needs, please contact: [email protected].


 English
English Español
Español

















Contact Us