The manufacturing of carbon graphite bushings involves several processes that ensure the material meets the required performance characteristics for a given application, such as wear resistance, low friction, and high load-bearing capacity. The different methods used to produce carbon graphite bushings are as follows:
1. Compression Molding
-
Process: In compression molding, a pre-formed mixture of carbon particles and binder materials is placed into a mold cavity. The mold is then subjected to heat and pressure, causing the binder to melt and fuse the carbon particles together, forming the shape of the bushing.
-
Advantages:
-
Suitable for mass production.
-
Provides precise shapes with good dimensional accuracy.
-
Allows for the addition of different additives to modify material properties.
-
Applications: Often used for standardized bushing sizes in various industrial applications.
2. Extrusion
-
Process: Carbon graphite is mixed with a binder and other additives to form a paste-like consistency. This mixture is then forced through a die to create continuous shapes, which are cut into bushing sizes after cooling and solidification.
-
Advantages:
-
Applications: Used for custom-shaped bushings and parts requiring specific sizes or profiles.
3. Isostatic Pressing (Cold Isostatic Pressing, CIP)
-
Process: In this method, a powdered mixture of carbon graphite and binder is placed in a flexible rubber mold. The mold is then subjected to uniform pressure from all directions (usually in a liquid-filled press), resulting in a dense and uniform material structure.
-
Advantages:
-
Produces highly uniform density throughout the material.
-
Improves mechanical properties and strength of the finished product.
-
Ideal for producing complex shapes with intricate details.
-
Applications: Suitable for producing high-performance bushings that require enhanced mechanical strength.
4. Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
-
Process: This method combines high temperature and high pressure in a sealed environment to consolidate carbon graphite powder into a dense, high-quality material. The process eliminates voids and defects in the material, resulting in a superior bushing.
-
Advantages:
-
Applications: Used for producing high-performance carbon graphite bushings for industries such as aerospace, automotive, and heavy machinery.
5. Sintering
-
Process: Sintering involves heating the carbon graphite mixture (often with a binder) to a temperature just below its melting point, allowing the particles to fuse together. The material is then cooled and shaped into bushings.
-
Advantages:
-
Applications: Suitable for standard industrial bushings and those requiring moderate performance in terms of strength and wear resistance.

6. Machining
-
Process: After the initial molding or pressing of the carbon graphite material, it is often further shaped by machining, including turning, milling, and grinding. This step allows for precise finishing and the production of bushings with tight tolerances and specific surface finishes.
-
Advantages:
-
Applications: Typically used for high-precision bushings or components with tight tolerances that cannot be achieved during the initial manufacturing stages.
7. Casting
-
Process: This method involves melting the carbon graphite material and pouring it into a mold to solidify into the desired shape. The mold can be designed to create various sizes and geometries of bushings.
-
Advantages:
-
Applications: Common in producing specialized carbon graphite bushings with unique dimensions.
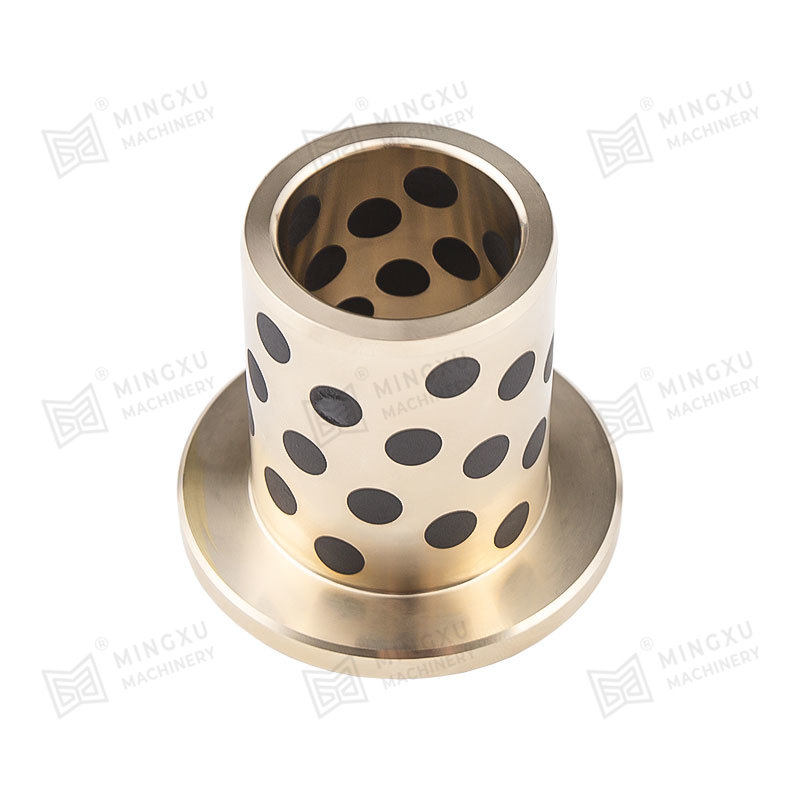
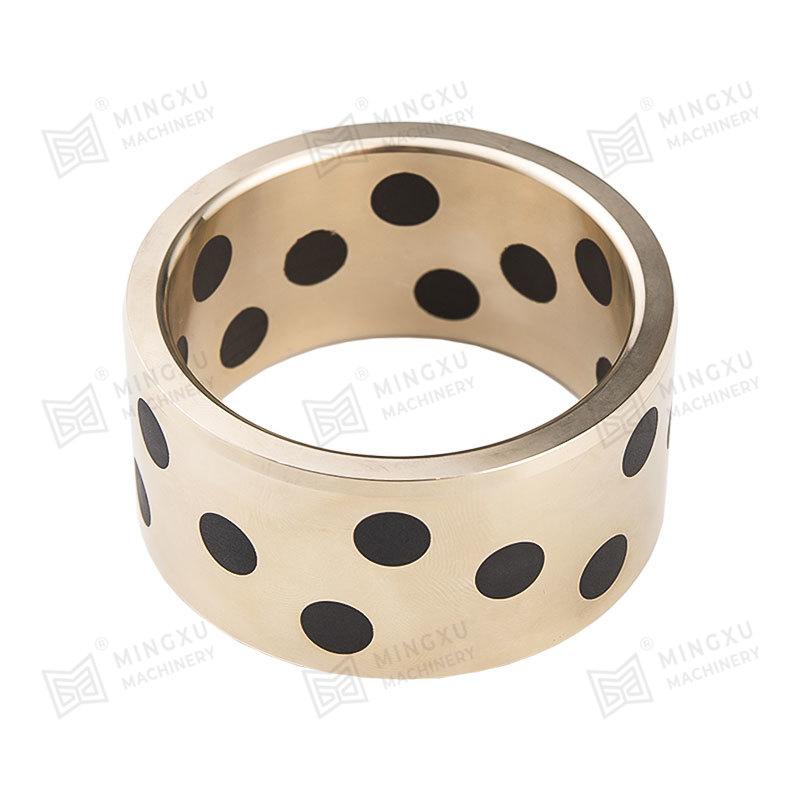
8. Impregnation and Graphitization
-
Process: Carbon graphite bushings are often impregnated with oils or resins to improve their wear resistance and lubricating properties. Additionally, some manufacturers apply a graphitization process to further enhance the material's structure by converting the binder to a more crystalline graphite form.
-
Advantages:
-
Enhances the material's lubricity, wear resistance, and thermal conductivity.
-
Graphitization improves the material's performance at higher temperatures.
-
Applications: Ideal for high-performance bushings used in high-temperature or high-friction environments, such as in the automotive or manufacturing industries.


 English
English Español
Español

















Contact Us