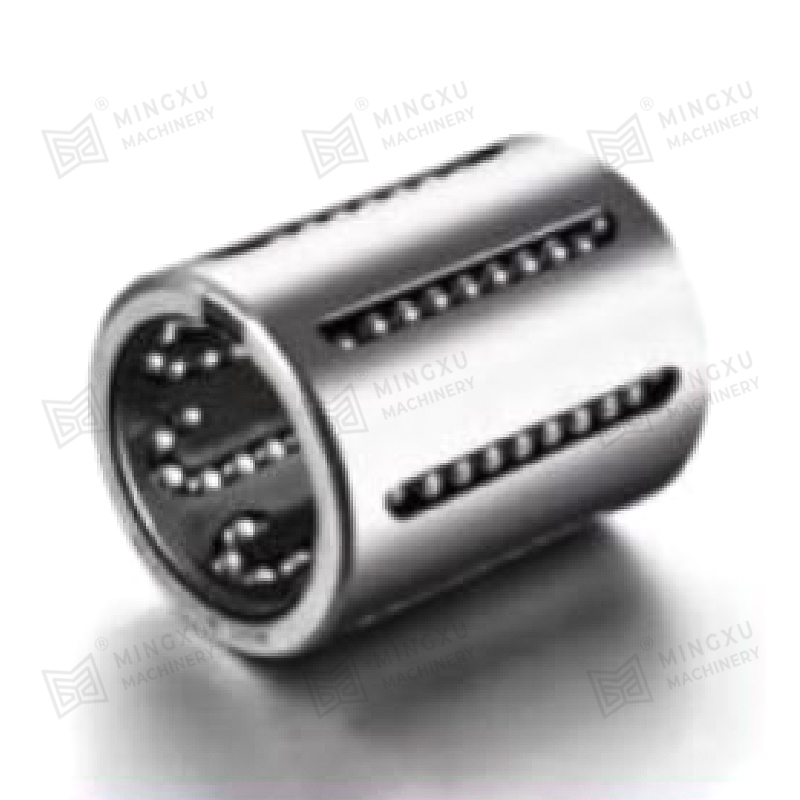
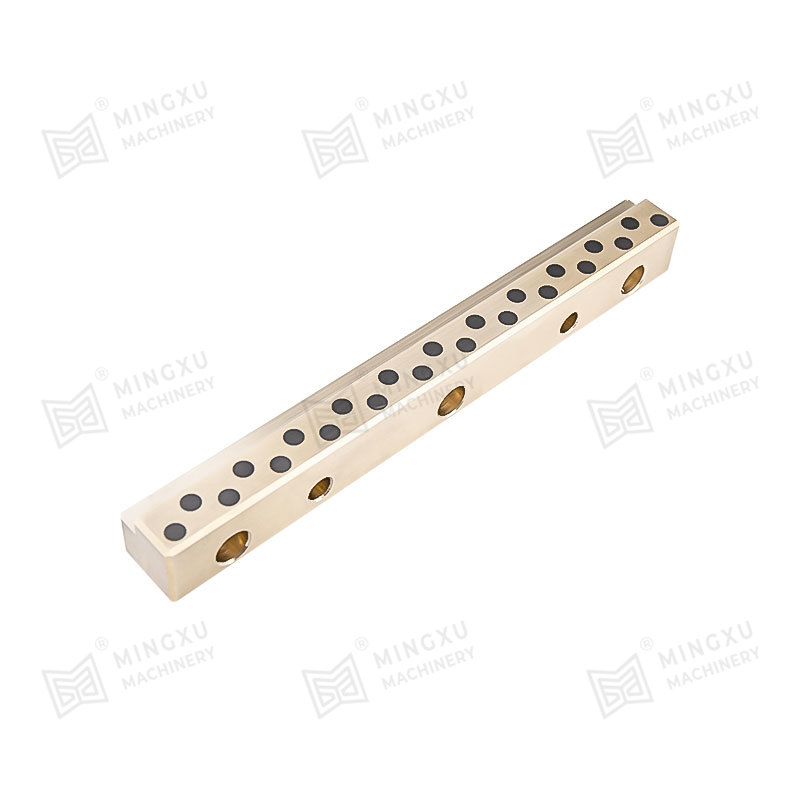
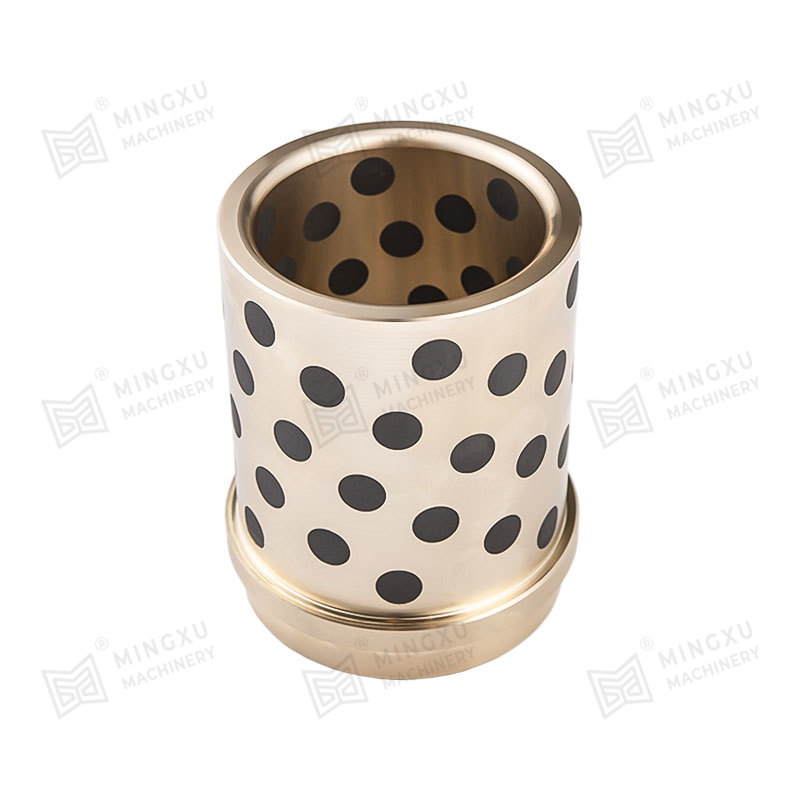
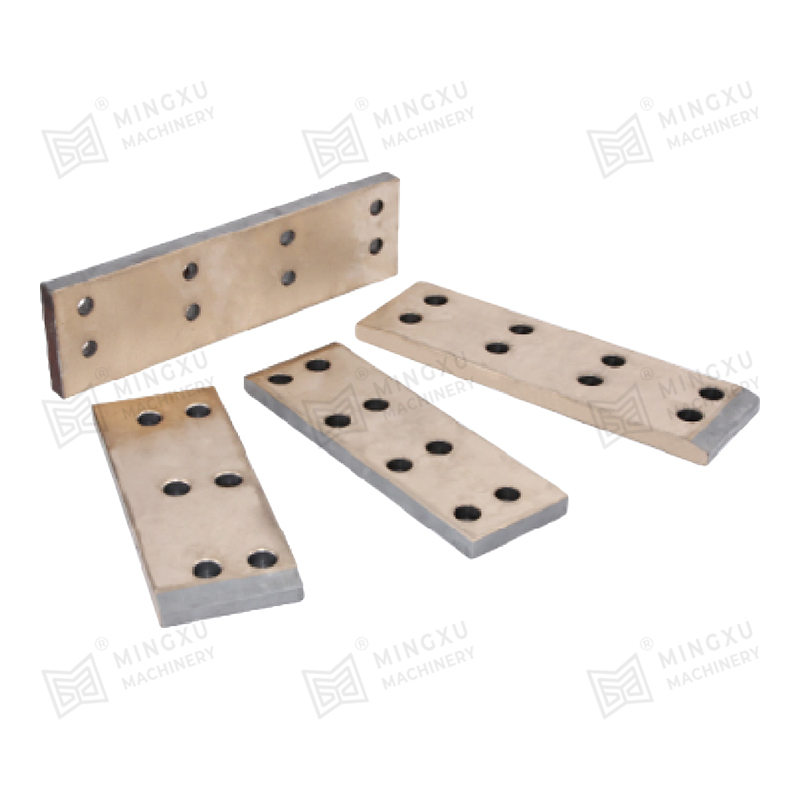
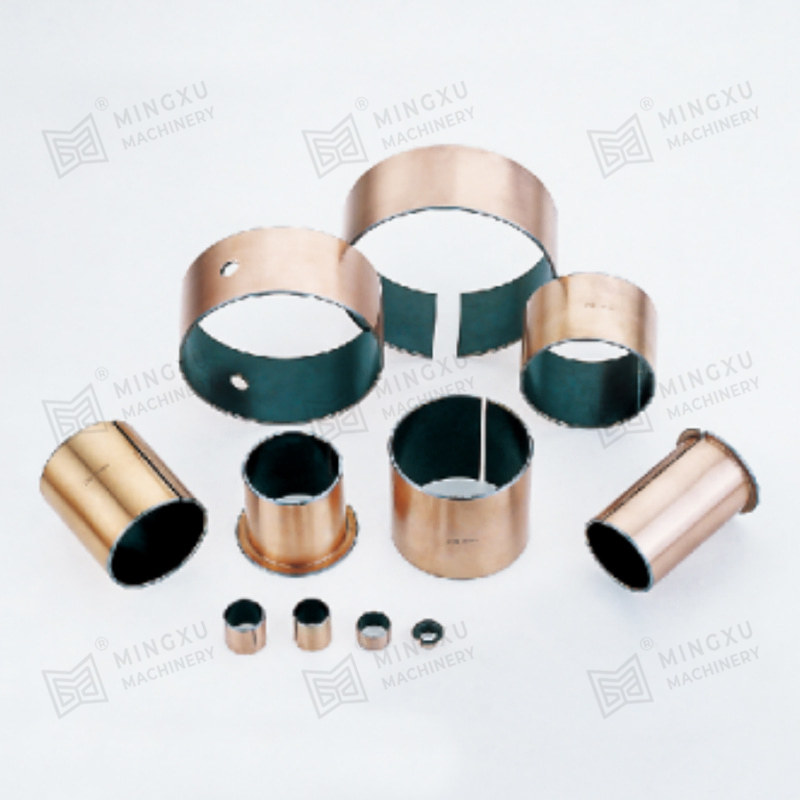
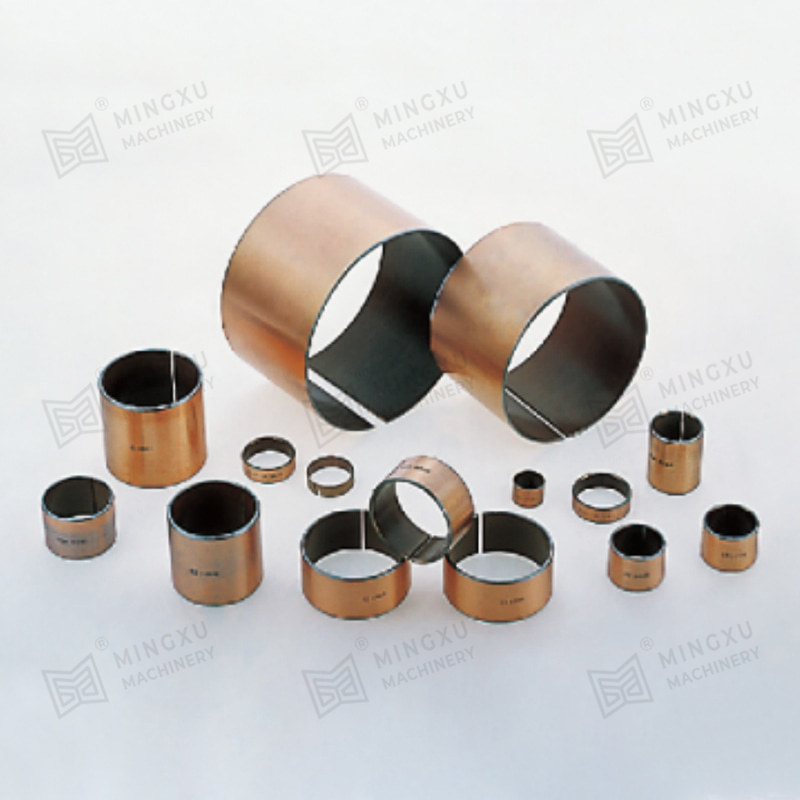
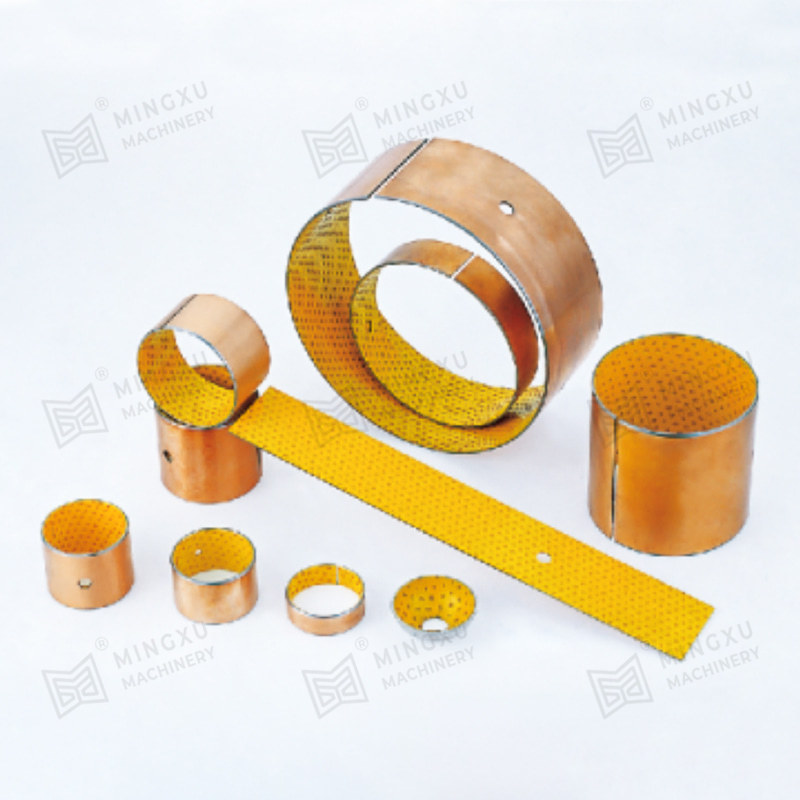
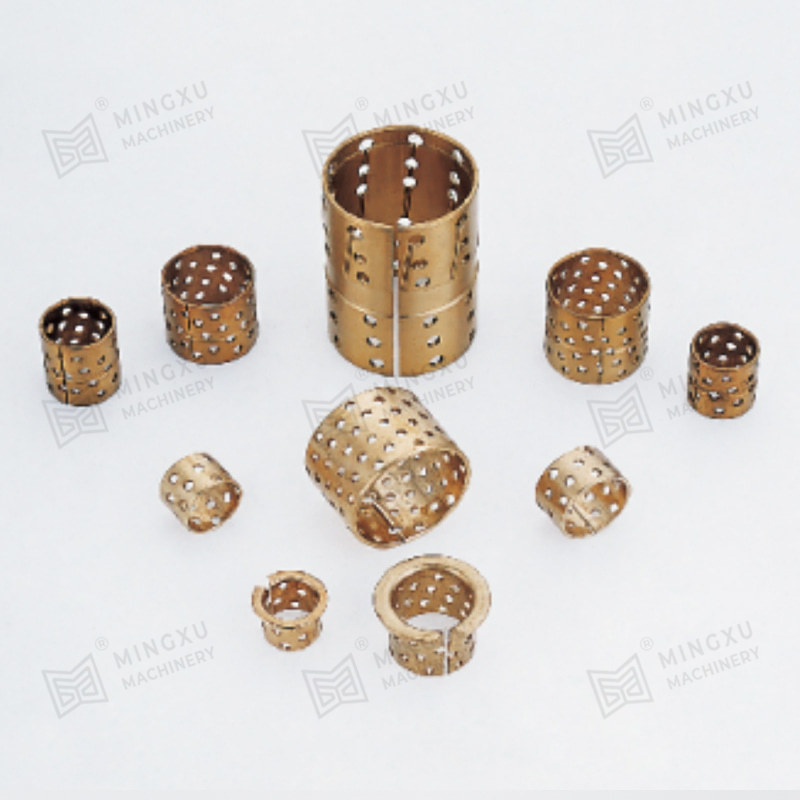
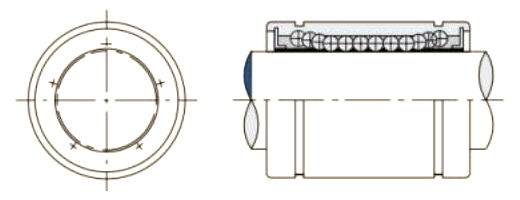
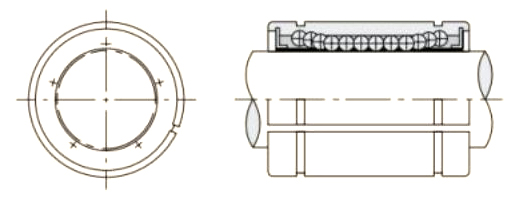
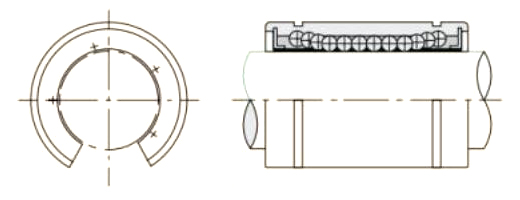
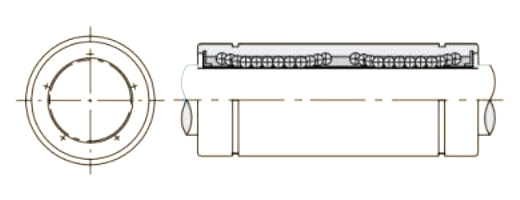
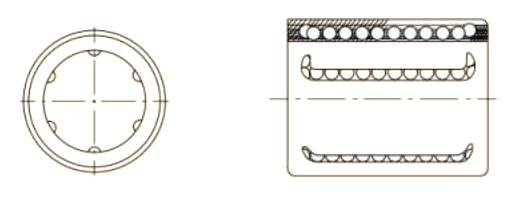
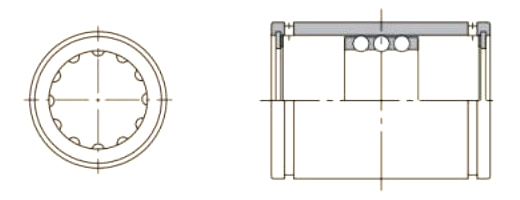
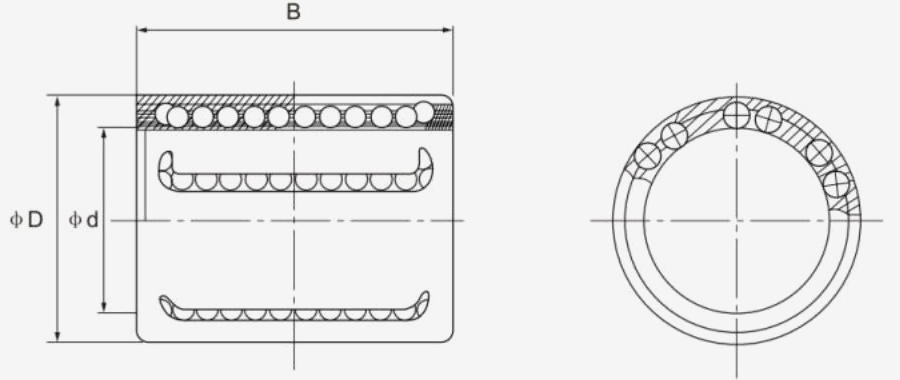
A Pressing Bush Bearing, also referred to as a Stamped Outer Ring Linear Bearing, is a linear motion component designed for use in mechanical systems requiring controlled straight-line movement. This type of bearing supports linear motion by reducing friction between moving parts and maintaining consistent alignment. It is commonly used in applications where space is limited, and where compact and efficient design is required.
The Pressing Bush Bearing typically includes four fundamental components: an outer ring formed through stamping, an inner ring, a series of rolling elements such as balls or cylindrical rollers, and a retainer that keeps the rolling elements evenly spaced. The retainer plays a key role in preventing direct contact between the rolling elements, helping to maintain smooth operation and reduce surface degradation during movement.
Compared to more traditional rolling bearings, the structure of a Pressing Bush Bearing is generally more straightforward. This can result in manufacturing and assembly processes that are less complex. In many cases, this simpler structure may also allow for quicker installation and more convenient maintenance, especially in systems where frequent disassembly is not feasible. For equipment designers, this can translate into fewer assembly steps and a more efficient integration into compact layouts.
Because of its reduced dimensions and efficient structure, the Pressing Bush Bearing is often chosen for applications where space efficiency is important. These include precision instruments, automation equipment, compact linear guides, and machinery where available installation volume is limited. While not designed for high-speed operation, this type of bearing performs reliably in lower-speed environments where space constraints and stable linear motion are the primary considerations.


 English
English Español
Español