Maintenance-free bearings epitomize the convergence of tribology, materials science, and precision engineering, delivering unprecedented operational longevity in extreme environments from aerospace propulsion to subsea energy systems. This article dissects the multi-physics design frameworks, self-lubricating nanocomposites, and failure prediction algorithms that define next-generation maintenance-free bearing systems, while addressing challenges in high-cycle fatigue, contamination immunity, and cross-industry certification compliance.
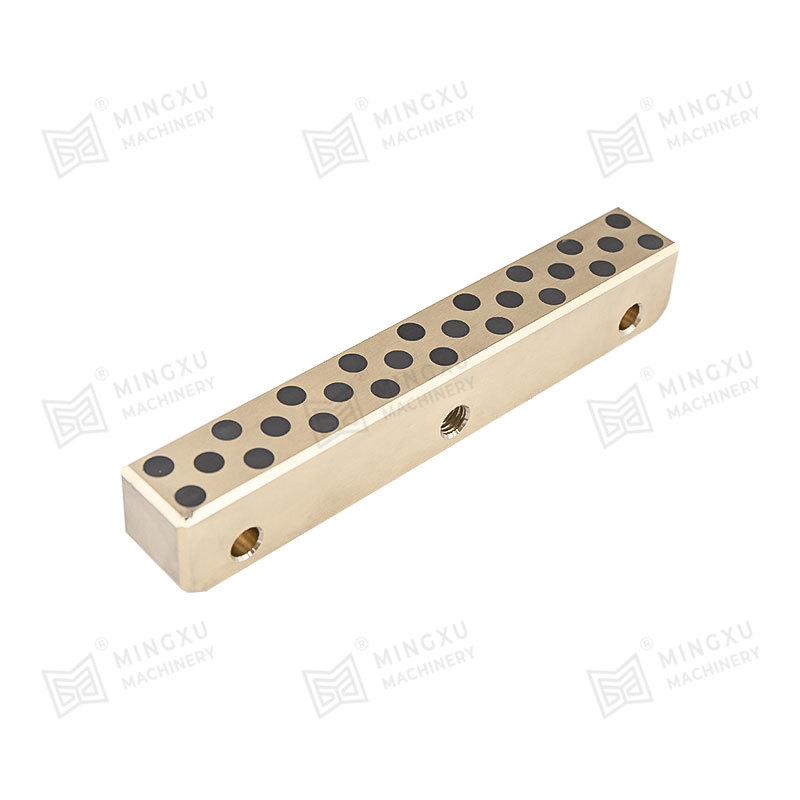
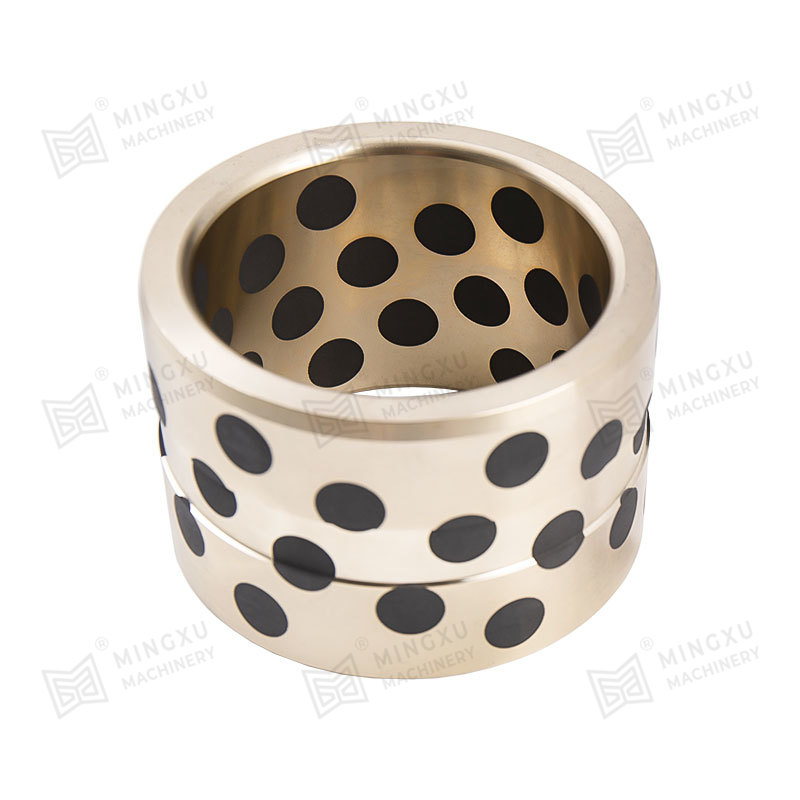
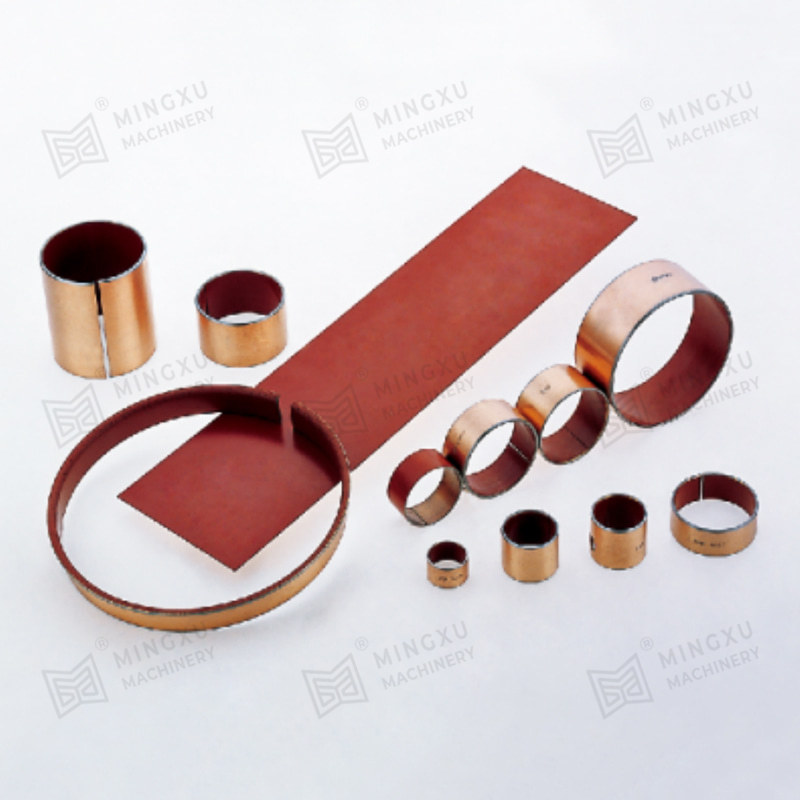
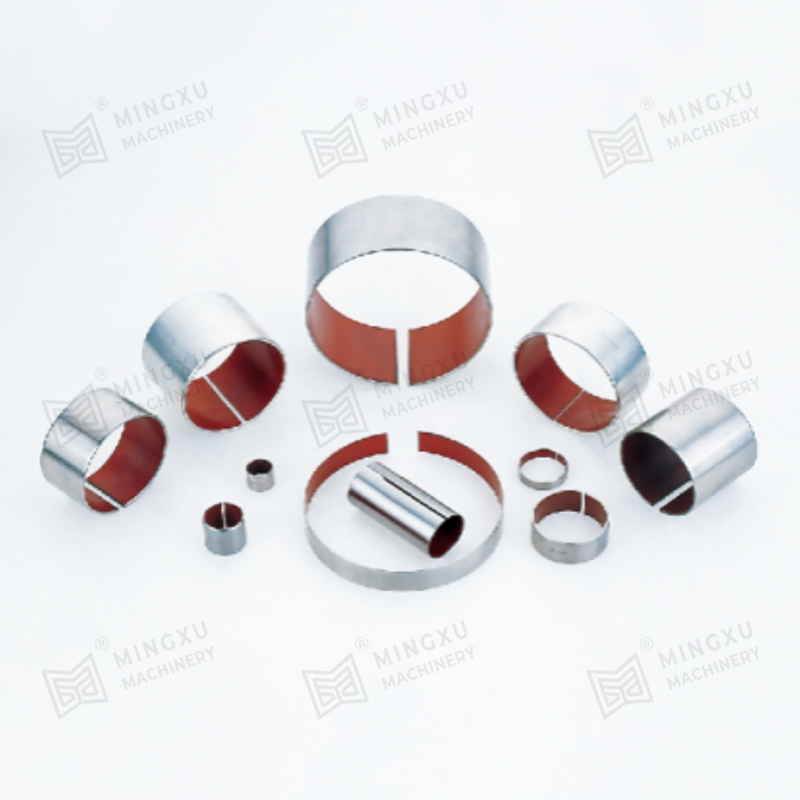
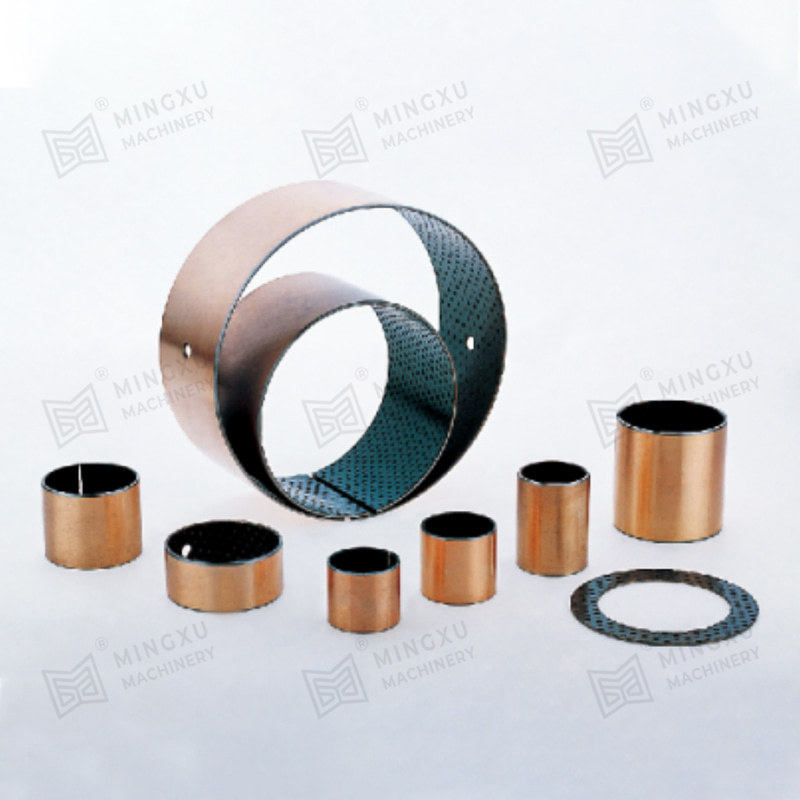
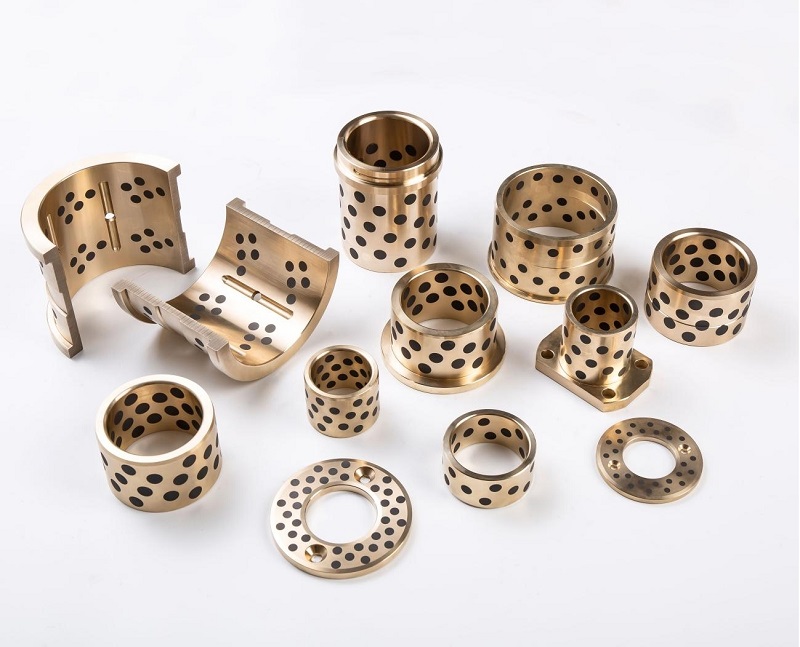
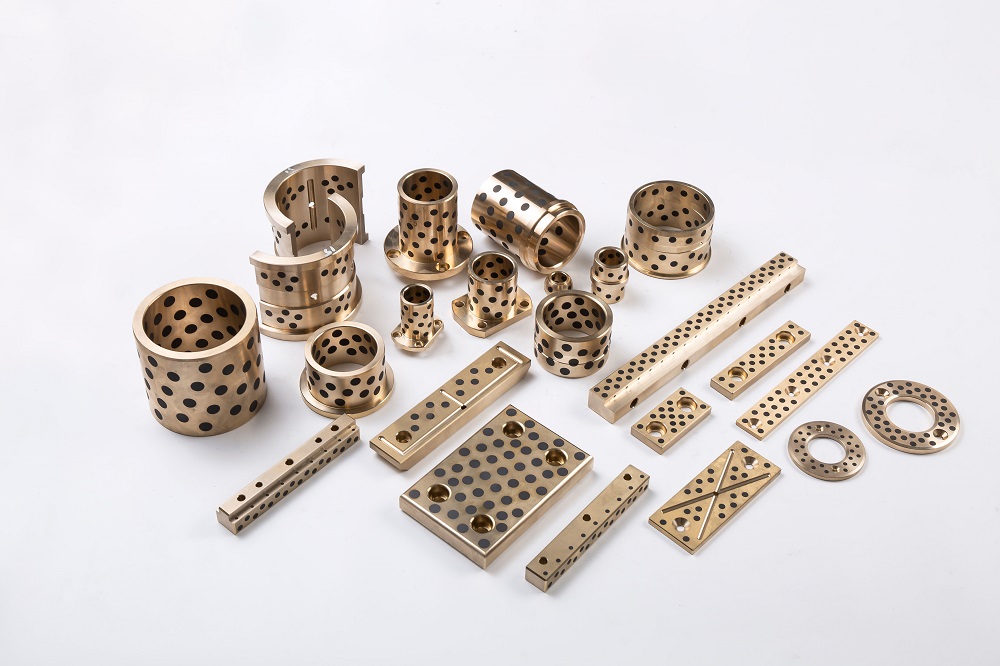
1. Core Material Engineering and Surface Topology Optimization
The operational permanence of maintenance-free bearings originates from atomic-scale material innovations:
2. Bearing Dynamics and Tribosystem Design
Advanced simulation frameworks optimize maintenance-free operation across operational envelopes:
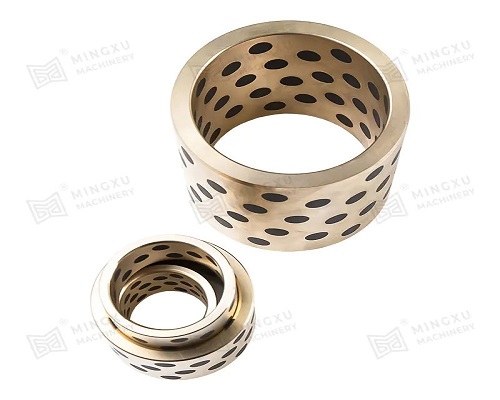

3. Self-Sustaining Lubrication Systems
Autonomous tribological systems eliminate external intervention:
4. Accelerated Life Testing and Predictive Analytics
Validation protocols simulate decades of service in compressed timelines:
-
Enhanced ASTM D4172 Testing:
-
3,000-hour Four-Ball tests under 4 GPa contact stress with in-situ μ-Raman wear mechanism analysis.
-
Combined fretting-corrosion testing per ASTM G204 with 5% NaCl mist exposure.
-
Digital Twin Prognostics:
-
Physics-informed neural networks (PINN) predicting L₅₀ life within ±5% accuracy using 12 operational parameters.
-
Blockchain-immutable lifetime records integrating 20+ sensor data streams (vibration, temperature, acoustic emissions).
-
Contamination Resilience Testing:
5. Cross-Industry Application Case Studies
A. Wind Energy Systems
B. Aerospace Actuation
C. Medical Robotics
6. Sustainability and Circular Lifecycle Strategies
Next-gen bearings align with ISO 14040 LCA standards through:
7. Frontier Technologies and Smart Integration
Market analysts (Frost & Sullivan, 2027) project 9.8% CAGR for maintenance-free bearings, driven by renewable energy and Industry 4.0 adoption.


 English
English Español
Español

















Contact Us